Mesoionic
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
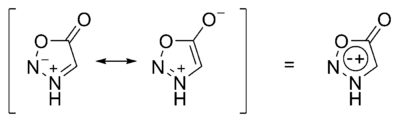
In chemistry, a mesoionic compound is one in which a heterocyclic structure is dipolar and where both the negative and the positive charges are delocalized.[1][2] A completely uncharged structure cannot be written and mesoionic compounds cannot be represented satisfactorily by any one mesomeric structure.[2] Mesoionic compounds are a subclass of betaines.[2] Examples are sydnones and sydnone imines (e.g. the stimulant mesocarb), münchnones,[1][2][3] and mesoionic carbenes.
The formal positive charge is associated with the ring atoms and the formal negative charge is associated either with ring atoms or an exocyclic nitrogen or other atom.[4] These compounds are stable zwitterionic compounds[5] and belong to nonbenzenoid aromatics.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bhosale, Sachin K.; Deshpande, Shreenivas R.; Wagh, Rajendra D. (2012). "Mesoionic sydnone derivatives: An overview". Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research 4 (2): 1185–99. http://jocpr.com/vol4-iss2-2012/JCPR-2012-4-2-1185-1199.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "mesoionic compounds". doi:10.1351/goldbook.M03842
- ↑ Ollis, W.David; Stanforth, Stepher P.; Ramsden, Christopher A. (1985). "Heterocyclic mesomeric betaines". Tetrahedron 41 (12): 2239–2329. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)96625-6.
- ↑ "SYDNONES". http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/3033/7/07_chapter%201.pdf.[page needed]
- ↑ "Seeking Mesoionic Compounds". https://www.innocentive.com/ar/challenge/9932814.
- ↑ Badami, Bharati V (2006). "Mesoionic compounds". Resonance 11 (10): 40–48. doi:10.1007/BF02835674.
Further reading
- Senff-Ribeiro, A; Echevarria, A; Silva, EF; Franco, CR; Veiga, SS; Oliveira, MB (2004). "Cytotoxic effect of a new 1,3,4-thiadiazolium mesoionic compound (MI-D) on cell lines of human melanoma". British Journal of Cancer 91 (2): 297–304. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601946. PMID 15199390.
- Mickleburgh, I; Geng, F; Tiley, L (2009). "Mesoionic heterocyclic compounds as candidate messenger RNA cap analogue inhibitors of the influenza virus RNA polymerase cap-binding activity". Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy 19 (5): 213–8. doi:10.1177/095632020901900504. PMID 19483269.
- Cadena, Silvia M.S.C.; Carnieri, Eva G.S.; Echevarria, Aurea; De Oliveira, Maria Benigna Martinelli (2002). "Interference of MI-D, a new mesoionic compound, on artificial and native membranes". Cell Biochemistry and Function 20 (1): 31–7. doi:10.1002/cbf.932. PMID 11835268.
- Papageorgiou, M.; Kokkou, S. C.; Rentzeperis, P. J.; Tsoleridis, C. (1983). "Structure of the mesoionic compound N-[1-methyl-3-(p-tolyl)-4-(1,2,3-triazolio)]acetamidate (MMTAT), C12H14N4O". Acta Crystallographica Section C 39 (11): 1581–1583. doi:10.1107/S0108270183009348.
- Potts, K. T.; Husain, Syeda (1971). "Mesoionic compounds. XIV. Mesoionic compounds of the imidazole series". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 36 (22): 3368–3372. doi:10.1021/jo00821a022.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Mesoionic23 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 04:12:57↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF