Morin (flavonol)
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
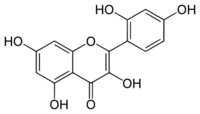
2′,3,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Aurantica
Al-Morin Morin hydrate Calico Yellow Toxylon pomiferum Bois d'arc Osage orange extract | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H10O7 | |
| Molar mass | 302.238 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.799 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Morin is a yellow chemical compound that can be isolated from Maclura pomifera (Osage orange), Maclura tinctoria (old fustic), and from leaves of Psidium guajava (common guava).[1] In a preclinical in vitro study, morin was found to be a weak inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with an IC50 of 2.33 μM.[2] Morin was also found to inhibit amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide (or amylin) and disaggregate amyloid fibers.[3]
Morin exhibit inhibitory action against IgE-mediated allergic response. Morin treatment significantly down-regulated expressions of BLT2, NF-κB, and Th2-cytokine (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-13) in lungs of murine model of allergic asthma.[4]
Morin can be used to test for the presence of aluminium or tin in a solution, since it forms characteristically fluorescent coordination complexes with them under UV light.
Glycosides
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Rattanachaikunsopon, Pongsak; Phumkhachorn, Parichat (2007). "Bacteriostatic effect of flavonoids isolated from leaves of Psidium guajava on fish pathogens". Fitoterapia 78 (6): 434–436. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2007.03.015. PMID 17553634.
- ↑ Tian, Wei-Xi (2006). "Inhibition of Fatty Acid Synthase by Polyphenols". Current Medicinal Chemistry 13 (8): 967–977. doi:10.2174/092986706776361012. PMID 16611078.
- ↑ Noor, Harris; Cao, Ping; Raleigh, Daniel P. (2012). "Morin hydrate inhibits amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide and disaggregates amyloid fibers". Protein Science 21 (3): 373–382. doi:10.1002/pro.2023. PMID 22238175.
- ↑ Kandhare, Amit D.; Liu, Zihao; Mukherjee, Anwesha A.; Bodhankar, Subhash L. (2019). "Therapeutic Potential of Morin in Ovalbumin-induced Allergic Asthma Via Modulation of SUMF2/IL-13 and BLT2/NF-kB Signaling Pathway". Current Molecular Pharmacology 12 (2): 122–138. doi:10.2174/1874467212666190102105052. PMID 30605067.
 |
 KSF
KSF