Outline of water
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 7 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 7 min
Short description: Overview of and topical guide to water
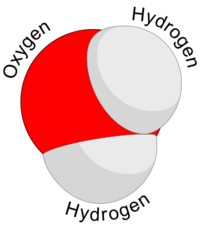
Structure of the water molecule (H2O)
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to water:
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state (water vapor or steam). Under nomenclature used to name chemical compounds, Dihydrogen monoxide is the scientific name for water, though it is almost never used.[1]
History
Chemical properties and use
- Chemistry:Properties of water – Physical and chemical properties of pure water
- Physics:Electrolysis of water – Electricity-induced chemical reaction
- Physics:Water of crystallization – Water molecules present inside crystals
- Chemistry:Dealkalization of water – Removal of alkalinity ions from water
- Chemistry:Drinking water quality standards – Quality parameters set for drinking water
- Chemistry:Portable water purification – Self-contained, easily transported units used to purify water from untreated sources
- Physics:Self-ionization of water – Autoprotolysis or exchange of a proton between two water molecules
- Chemistry:Water-in-water emulsion
- Earth:Water purification – Process of removing impurities from water
- Earth:Water treatment – Process that improves the quality of water
- Chemistry:Water (data page) – Chemical data page for water
- Physics:Hard water – Water that has a high mineral content
- Chemistry:Soft water
- Chemistry:Water softening – Removing positive ions from hard water
- Chemistry:Heavy water – Form of water
- Chemistry:Distilled water – Water that has had many of its impurities removed through distillation
- Earth:Salinity – Proportion of salt dissolved in water
- Chemistry:Saline water
- Earth:Seawater – Water from a sea or an ocean
- Chemistry:Hydrate – Substance containing water or its constituent elements
- Physics:Boiling – Rapid phase transition from liquid to gas or vapour
Physical properties
- Chemistry:Properties of water – Physical and chemical properties of pure water
- Color of water – Water color in different conditions
- Physics:Water vapor – Gaseous phase of water
- Physics:Vapour pressure of water – Pressure exerted by molecules of water vapour in gaseous form
- Physics:Steam – Water in the gas phase
- Earth:Ice – Frozen water: the solid state of water
- Astronomy:Lunar water – Presence of water on the moon
- Physics:Optical properties of water and ice
- Earth:Water quality – Assessment against standards for use
- Chemistry:Water (data page) – Chemical data page for water
- Chemistry:Mineral water – Drinking water from a mineral spring
Geography
Formation of a waterfall
- Earth:Origin of water on Earth – Hypotheses for the possible sources of the water on Earth
- Astronomy:Extraterrestrial liquid water – Liquid water naturally occurring outside Earth
- Astronomy:List of extrasolar candidates for liquid water – Possible existence of liquid water beyond Earth
- Earth:Hydrosphere – Total amount of water on a planet
- Earth:Hydrology – Science of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets
- Earth:Water distribution on Earth – Overview of the distribution of water on planet Earth
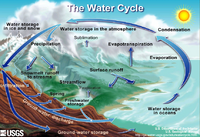
- Physics:Water cycle – Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth
- Earth:Groundwater – Water located beneath the ground surface
- Earth:Hydrology – Science of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets
- Earth:Body of water – Any significant accumulation of water, generally on a planet's surface
- Salt water
- Earth:Seawater – Water from a sea or an ocean
- Earth:Ocean – Body of salt water covering the majority of Earth
- Earth:Sea – Large body of salt water
- Earth:Tide – Rise and fall of the sea level under astronomical gravitational influences
- Earth:Brine – Concentrated solution of salt in water
- Earth:Brackish water – Water with salinity between freshwater and seawater
- Earth:Fresh water – Naturally occurring water with low amounts of dissolved salts
- Earth:Aquifer – Underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock
- Earth:River – Natural flowing watercourse
- Earth:Drainage divide – Elevated terrain that separates neighbouring drainage basins
- Earth:Drainage basin – Area of land where precipitation collects and drains off into a common outlet
- Earth:Lake – Large body of relatively still water
- Salt water
- Earth:Glacier
- Earth:Geyser – Hydrothermal explosion of hot water
- Earth:Waterfall – A point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop
- Earth:List of waterfalls – List of notable waterfalls of the world
Weather

Snow-covered trees.
- Earth:Freezing rain – Rain maintained at temperatures below freezing
- Physics:Snow – Precipitation in the form of ice crystal flakes
- Earth:Hail – Form of solid precipitation
- Earth:Ice crystals – Solid frozen water molecules
- Earth:Frost – Coating or deposit of ice
- Earth:Cloud – Visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals suspended in the atmospheres
- Earth:Mist – Phenomenon caused by small droplets of water suspended in air
- Earth:Spindrift – Spray blown from cresting waves in gales
- Earth:Flood – Water overflow submerging usually-dry land
- Wave – Repeated oscillation around equilibrium
- Physics:Wind wave – Surface waves generated by wind on open water
- Tsunami – Series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water
- Earth:Drought – Extended period of deficiency in a region's water supply
In nature and life
- Earth:Origin of water on Earth – Hypotheses for the possible sources of the water on Earth
- Medicine:Water intoxication – Potentially fatal overhydration
- Medicine:Drowning – Respiratory impairment resulting from being in or underneath a liquid
- Medicine:Dehydration – Deficit of total body water
Marine and aquatic life
- Earth:Underwater – The aquatic or submarine environment
- Biology:Marine biology – Scientific study of organisms that live in the ocean
- Biology:Marine life – Organisms that live in salt water
- Biology:Hydrobiology – Science of life and life processes in water
- Earth:Aquatic ecosystem – Ecosystem in a body of water
Politics and issues
- Chemistry:Human right to water and sanitation – Human right recognized by the United Nations General Assembly in 2010
- Earth:Water resources – Sources of water that are potentially useful
- Earth:Water efficiency
- Earth:Water footprint – Extent of water use in relation to consumption by people
- Earth:Water industry – Drinking and wastewater services
- Chemistry:Water export – Outbound trade involving freshwater
- Earth:Water pollution – Contamination of water bodies
Supply and sanitation

An example of a Reservoir, Ladybower Reservoir.
- Engineering:Water supply network – System of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components providing water
- Earth:Reservoir – Storage space for water
- Engineering:Pump – Device that imparts energy to the fluids by mechanical action
- Earth:Water well
- Engineering:Plumbing – Systems for conveying fluids
- Engineering:Tap (valve) – Valve controlling the release of a liquid or gas
- Engineering:Water supply network – System of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components providing water
- Engineering:Sanitation – Public health conditions related to clean water and proper excreta and sewage disposal
- Chemistry:Water fluoridation – Addition of fluoride to a water supply to reduce tooth decay
In culture and sport

Poseidon, Greek god of water. The Roman water god, Neptune, was almost identical to Poseidon
- Chemistry:Water (classical element) – One of four primary substances in antiquity
- Religion:Holy water – Water blessed by a religious figure
- Chemistry:Adam's ale – Colloquial allusion to water
- Chemistry:Fountain – Architecture which pours water into a basin or jets it into the air
Uses
- Engineering:Water wheel – Machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power
- Physics:Hydropower – Power generation via movement of water
- Earth:Marine current power – Extraction of power from ocean currents
- Earth:Marine energy – Energy stored in the waters of oceans
- Physics:Osmotic power – Energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water
- Engineering:Tidal power – Technology to convert the energy from tides into useful forms of power
- Physics:Wave power – Transport of energy by wind waves, and the capture of that energy to do useful work
- Physics:Steam engine – Heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid
- Biology:Drinking – Ingestion of water or other liquids
- Earth:Tap water – Publicly available water supplied to homes
- Physics:Water clock – Time piece in which time is measured by the flow of liquid into or out of a vessel
- Earth:Irrigation
- Engineering:Sink – Bowl-shaped plumbing fixture
- Engineering:Bathtub – Large container for holding water in which a person may bathe
- Engineering:Shower – Place in which a person bathes under a spray of water
- Engineering:Pressure washing – Use of high-pressure water jet for cleaning hard surfaces
Fishing
See also
References
- ↑ Bramer, Scott. "Chemical Nomenclature". Widener University, Department of Chemistry. http://science.widener.edu/svb/pset/nomen_b.html.
External links
- OECD Water statistics
- The World's Water Data Page
- FAO Comprehensive Water Database, AQUASTAT
- The Water Conflict Chronology: Water Conflict Database
- US Geological Survey Water for Schools information
- Portal to The World Bank's strategy, work and associated publications on water resources
- America Water Resources Association
- America Water Resources Association
- Water structure and science
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Outline_of_water62 views | Status: cached on December 23 2023 07:37:57↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF