Pfitzner–Moffatt oxidation
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
The Pfitzner–Moffatt oxidation, sometimes referred to as simply the Moffatt oxidation, is a chemical reaction for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones, respectively. The oxidant is a combination of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC). The reaction was first reported by J. Moffatt and his student K. Pfitzner in 1963.[1][2]
Stoichiometry and mechanism
The reaction requires one equivalent each of the diimide, which is the dehydrating agent, and the sulfoxide, the oxidant:
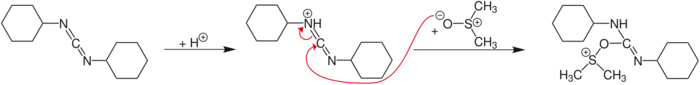
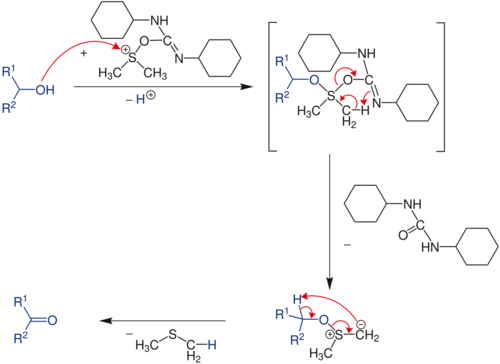
- (CH3)2SO + (CyN)2C + R2CHOH → (CH3)2S + (CyNH)2CO + R2C=O
Typically the sulfoxide and diimide are used in excess.[3] The reaction cogenerates dimethyl sulfide and a urea. Dicyclohexylurea ((CyNH)2CO) can be difficult to remove from the product.
In terms of mechanism, the reaction is proposed to involve the intermediary of an sulfonium group, formed by a reaction between DMSO and the carbodiimide.
This species is highly reactive and is attacked by the alcohol. Rearrangement give an alkoxysulfonium ylide which decomposes to give dimethyl sulfide and the carbonyl compound.
This reaction has been largely displaced by the Swern oxidation, which also uses DMSO as an oxidant in the presence of an electrophilic activator. Swern oxidations tend to give higher yields and simpler workup; however, they typically employ cryogenic conditions.[4][5]
See also
- Parikh–Doering oxidation - mechanistically similar alcohol oxidation, replaces carbodiimide with sulfur trioxide
- Corey–Kim oxidation
- Swern oxidation
- Alcohol oxidation
- Sulfonium-based oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes
References
- ↑ Pfitzner, K. E.; Moffatt, J. G. (1963). "A New and Selective Oxidation of Alcohols". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85 (19): 3027–3028. doi:10.1021/ja00902a036.
- ↑ J. G. Moffatt, “Sulfoxide-Carbodiimide and Related Oxidations” in Oxidation vol. 2, R. L. Augustine, D. J. Trecker, Eds. (Dekker, New York, 1971) pp 1–64.
- ↑ John G. Moffatt (1967). "Cholane-24-al". Org. Synth. 47: 25. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.047.0025.
- ↑ Tidwell, T. T. (1990). "Oxidation of Alcohols by Activated Dimethyl Sulfoxide and Related Reactions: An Update". Synthesis 1990 (10): 857–870. doi:10.1055/s-1990-27036.
- ↑ Lee, T. V. Compr. Org. Synth. 1991, 7, 291–303. (Review)
 |
 KSF
KSF