Phenols
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group.[1] The simplest is phenol, C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.


Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms.[2]
Properties
Acidity
Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides, according to the IUPAC Gold Book).[citation needed]
Condensation with aldehydes and ketones
Phenols are susceptible to electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with formaldehyde gives resinous materials, famously Bakelite.[citation needed]
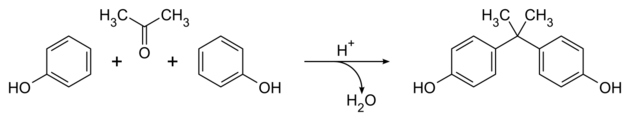
Another industrial-scale electrophilic aromatic substitution is the production of bisphenol A, which is produced by the condensation with acetone.[3]
C-Alkylation with alkenes
- CH2=CR2 + C6H5OH → R2CHCH2-2-C6H4OH
More than 100,000 tons of tert-butyl phenols are produced annually (year: 2000) in this way, using isobutylene (CH2=CMe2) as the alkylating agent. Especially important is 2,6-ditert-butylphenol, a versatile antioxidant.[3]
Other reactions
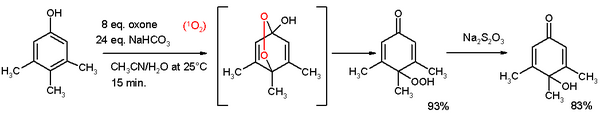
Phenols undergo esterification. Phenol esters are active esters, being prone to hydrolysis. Phenols are reactive species toward oxidation. Oxidative cleavage, for instance cleavage of 1,2-dihydroxybenzene to the monomethylester of 2,4-hexadienedioic acid with oxygen, copper chloride in pyridine.[4] Oxidative de-aromatization to quinones also known as the Teuber reaction. Oxidizing reagents are Fremy's salt[5] and oxone.[6] In reaction depicted below 3,4,5-trimethylphenol reacts with singlet oxygen generated from oxone/sodium carbonate in an acetonitrile/water mixture to a para-peroxyquinole. This hydroperoxide is reduced to the quinole with sodium thiosulfate.
Phenols are oxidized to hydroquinones in the Elbs persulfate oxidation.
Reaction of naphtols and hydrazines and sodium bisulfite in the Bucherer carbazole synthesis.
Synthesis
Many phenols of commercial interest are prepared by elaboration of phenol or cresols. They are typically produced by the alkylation of benzene/toluene with propylene to form cumene then O2 is added with H2SO4 to form phenol (Hock process). In addition to the reactions above, many other more specialized reactions produce phenols:
- rearrangement of esters in the Fries rearrangement[7][8]
- rearrangement of N-phenylhydroxylamines in the Bamberger rearrangement[9][10]
- dealkylation of phenolic ethers
- reduction of quinones
- replacement of an aromatic amine by an hydroxyl group with water and sodium bisulfide in the Bucherer reaction[11]
- thermal decomposition of aryl diazonium salts, the salts are converted to phenol[12]
- by the oxidation of aryl silanes—an aromatic variation of the Fleming-Tamao oxidation[13]
- catalytic synthesis from aryl bromides and iodides using nitrous oxide[14]
Classification
There are various classification schemes.[15]: 2 A commonly used scheme is based on the number of carbons and was devised by Jeffrey Harborne and Simmonds in 1964 and published in 1980:[15]: 2 [16]
| Phenol | the parent compound, used as a disinfectant and for chemical synthesis |
| Bisphenol A | and other bisphenols produced from ketones and phenol / cresol |
| BHT | (butylated hydroxytoluene) - a fat-soluble antioxidant and food additive |
| 4-Nonylphenol | a breakdown product of detergents and nonoxynol-9 |
| Orthophenyl phenol | a fungicide used for waxing citrus fruits |
| Picric acid | (trinitrophenol) - an explosive material |
| Phenolphthalein | pH indicator |
| Xylenol | used in antiseptics & disinfectants |
Drugs and bioactive natural products
More than 371 drugs approved by the FDA between the years of 1951 and 2020 contain either a phenol or a phenolic ether (a phenol with an alkyl), with nearly every class of small molecule drugs being represented, and natural products making up a large portion of this list.[17]
| tyrosine | one of the 20 standard amino acids |
| L-DOPA | dopamine prodrug used to treat Parkinson's disease |
| propofol | short-acting intravenous anesthetic agent |
| vitamin K hydroquinone | blood-clotting agent that converts |
| levothyroxine (L-thyroxine) | Top-selling drug to treat thyroid hormone deficiency. |
| amoxicillin | Top-selling antibiotic |
| estradiol | the major female sex hormone |
Analysis
In chemical analysis, phenols can be detected using 2,6‑dibromoquinonechlorimide.[18] It reacts with phenols to form indophenols, resulting in a color change.[19]
References
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "phenols". doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04539
- ↑ Hättenschwiler, Stephan; Vitousek, Peter M. (2000). "The role of polyphenols in terrestrial ecosystem nutrient cycling". Trends in Ecology & Evolution 15 (6): 238–243. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(00)01861-9. PMID 10802549.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Fiege H; Voges H-W; Hamamoto T; Umemura S; Iwata T; Miki H; Fujita Y; Buysch H-J et al. (2000). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313.
- ↑ 2,4-Hexadienedioic acid, monomethyl ester, (Z,Z)- Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 8, p. 490 (1993); Vol. 66, p. 180 (1988) Article.
- ↑ "2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione, 2,3,5-trimethyl". Organic Syntheses 52: 83. 1972.
- ↑ Carreño, M. Carmen; González-López, Marcos; Urbano, Antonio (2006). "Oxidative De-aromatization of para-Alkyl Phenols into para-Peroxyquinols and para-Quinols Mediated by Oxone as a Source of Singlet Oxygen". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 45 (17): 2737–2741. doi:10.1002/anie.200504605. PMID 16548026.
- ↑ Fries, K.; Finck, G. (1908). "Über Homologe des Cumaranons und ihre Abkömmlinge". Chemische Berichte 41 (3): 4271–4284. doi:10.1002/cber.190804103146. https://zenodo.org/record/1426311.
- ↑ Fries, K.; Pfaffendorf, W. (1910). "Über ein Kondensationsprodukt des Cumaranons und seine Umwandlung in Oxindirubin". Chemische Berichte 43 (1): 212–219. doi:10.1002/cber.19100430131. https://zenodo.org/record/1426389.
- ↑ Bamberger, E. (1894). "Ueber die Reduction der Nitroverbindungen". Chemische Berichte 27 (2): 1347–1350. doi:10.1002/cber.18940270229. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k907342/f163.
- ↑ Bamberger, E. (1894). "Über das Phenylhydroxylamin". Chemische Berichte 27 (2): 1548–1557. doi:10.1002/cber.18940270276. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k907342/f376.table.
- ↑ H. Bucherer (1904). "Über die Einwirkung schwefligsaurer Salze auf aromatische Amido- und Hydroxylverbindungen" (in German). J. Prakt. Chem. 69 (1): 49–91. doi:10.1002/prac.19040690105. https://zenodo.org/record/1428014.
- ↑ H. E. Ungnade, E. F. Orwoll (1943). "3-Bromo-4-hydroxytoluene". Organic Syntheses 23: 11. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.023.0011.
- ↑ Bracegirdle, Sonia; Anderson, Edward A. (2010). "Arylsilane oxidation—new routes to hydroxylated aromatics". Chem. Comm. 46 (20): 3454–6. doi:10.1039/b924135c. PMID 20582346.
- ↑ Le Valliant, Franck; Mateos Calbet, Ana; González-Pelayo, Silvia; Reijerse, Edward J.; Ni, Shengyang; Busch, Julia; Cornella, Josep (2022). "Catalytic synthesis of phenols with nitrous oxide". Nature 604 (7907): 677–683. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04516-4. PMID 35478236. Bibcode: 2022Natur.604..677L.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Wilfred Vermerris and Ralph Nicholson. Phenolic Compound Biochemistry Springer, 2008.
- ↑ Harborne, J. B. (1980). "Plant phenolics". in Bell, E. A.; Charlwood, B. V.. Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, volume 8 Secondary Plant Products. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 329–395.
- ↑ Scott, Kevin A.; Cox, Philip B.; Njardarson, Jon T. (2022-05-26). "Phenols in Pharmaceuticals: Analysis of a Recurring Motif" (in en). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 65 (10): 7044–7072. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00223. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 35533692. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00223.
- ↑ Ettinger, M. B.; Ruchhoft, C. C. (1948-12-01). "Determination of Phenol and Structurally Related Compounds by Gibbs Method". Analytical Chemistry 20 (12): 1191–1196. doi:10.1021/ac60024a018. ISSN 0003-2700. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60024a018.
- ↑ Gibbs, H.D. (1 April 1927). "PHENOL TESTS" (in en). Journal of Biological Chemistry 72 (2): 649–664. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)84338-1. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0021925818843381.
 |
 KSF
KSF