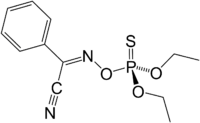
Phoxim
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(E,Z)-N-[(Diethoxyphosphorothioyl)oxy]benzenecarboximidoyl cyanide
| |
| Other names
Baythion
Valexone Phoxime Sebacil Valexon Volaton | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Phoxim |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H15N2O3PS | |
| Molar mass | 298.30 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Brownish red liquid |
| Density | 1.17 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 6.1 °C (43.0 °F; 279.2 K) |
| Boiling point | 102 |
| 7 ppm | |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATCvet code} | QP53AE03 (WHO) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H317, H361f, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+312, P302+352, P308+313, P321, P330, P333+313, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Phoxim is an organophosphate insecticide that is produced by the Bayer corporation. It is an analogous dimethyl ester and an organothiophosphate acaricide. It is allowed for use in limited applications in the European Union.[2] It is banned for use on crops in the European Union since 22 December 2007.[3]
It is used in veterinary medicine to treat ectoparasitic acarids.
This pesticide should be used with caution since some insects like Helicoverpa assulta become even more resistant when exposed.[4]
References
- ↑ "Phoxim PubChem entry". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=9570290&loc=ec_rcs.
- ↑ Commission for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Phoxim Summary Report
- ↑ COMMISSION DECISION of 21 June 2007 concerning the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I to Council Directive 91/414/EEC and the withdrawal of authorisations for plant protection products containing these substances
- ↑ Wang, Kai-Yun; Zhang, Yong; Wang, Hong-Yan; Xia, Xiao-Ming; Liu, Tong-Xian (2010-01-01). "Influence of three diets on susceptibility of selected insecticides and activities of detoxification esterases of Helicoverpa assulta (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)". Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology 96 (1): 51–55. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2009.09.003.
External links
- Phoxim in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Phoxim8 views | Status: cached on August 13 2024 07:43:12↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF