Piceol
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
Short description: Phenolic compound found in Norway spruces
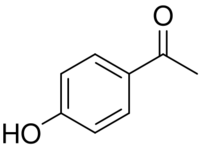 Chemical structure of piceol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethan-1-one | |
| Other names
1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanone
4-Hydroxyacetophenone 4'-Hydroxyacetophenone p-Hydroxyacetophenone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Piceol is a phenolic compound found in the needles and in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces (Picea abies).[1][2] Picein is the glucoside of piceol.[3]
Uses
Piceol is used in the synthesis of several pharmaceutical drugs including octopamine, sotalol, bamethan, and dyclonine.[citation needed]
Piceol can be used to make acetaminophen by oxime formation with hydroxylamine and subsequent Beckmann rearrangement in acid.[4]
Anticonvulsants are also possible by Mannich reaction:[5]
Metabolism
Diprenylated derivatives of piceol can be isolated from Ophryosporus macrodon.[6]
4-Hydroxyacetophenone monooxygenase is an enzyme that transforms piceol into O-acetylhydroquinone. This enzyme is found in Pseudomonas fluorescens.
See also
- Paroxypropione, where the acetyl group is replaced by a propionyl group.
- Apocynin
References
- ↑ Løkke, H. (1990). "Picein and piceol concentrations in Norway spruce". Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 19 (3): 301–9. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(90)90032-z. PMID 2364913.
- ↑ Münzenberger, Babette; Heilemann, Jürgen; Strack, Dieter; Kottke, Ingrid; Oberwinkler, Franz (1990). "Phenolics of mycorrhizas and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruce". Planta 182 (1): 142–8. doi:10.1007/BF00239996. PMID 24197010.
- ↑ Løkke, Hans (1990). "Picein and piceol concentrations in Norway spruce". Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 19 (3): 301–309. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(90)90032-Z. PMID 2364913.
- ↑ U.S. Patent 4,524,217
- ↑ Keshari, Amit K.; Tewari, Aseem; Verma, Shweta S.; Saraf, Shailendra K. (2017). "Novel Mannich-bases as Potential Anticonvulsants: Syntheses, Characterization and Biological Evaluation". Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 17 (3). doi:10.2174/1871524917666170717113524. ISSN 1871-5249.
- ↑ Sigstad, Elizabeth; Catalán, César A.N.; Diaz, Jesús G.; Herz, Werner (1993). "Diprenylated derivatives of p-hydroxyacetophenone from Ophryosporus macrodon". Phytochemistry 33: 165–169. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(93)85415-N.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Piceol71 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 09:18:55↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF