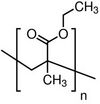
Poly(ethyl methacrylate)
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| Abbreviations | PEMA |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| Properties | |
| (C6H10O2)n | |
| Appearance | powder [5] |
| insoluble in water [6] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Poly(ethyl methacrylate) (PEMA) is a hydrophobic synthetic acrylate polymer. It has properties similar to the more common PMMA, however it produces less heat during polymerization, has a lower modulus of elasticity and has an overall softer texture.[7] It may be vulcanized using lead oxide as a catalyst[8] and it can be softened using ethanol.
It is used as an impression material of ear canals for the fabrication of hearing aids.[9][10] It is also used in dentistry as a chair-side denture reline material for partial and complete dentures as well as a tissue conditioner with implant-supported dentures. It is used as a component of fossil coating and preservation [11] and for fabricating artificial nails [12]
References
- ↑ Chambers, Michael. "ChemIDplus - 9003-42-3 - Poly(ethylmethacrylate) - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information." (in en). https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/9003-42-3.
- ↑ "Poly(ethyl methacrylate) - Alfa Chemistry" (in en). https://www.alfa-chemistry.com/poly-ethyl-methacrylate-cas-9003-42-3-item-164300.htm.
- ↑ "Common Chemistry - Substance Details - 9003-42-3 : 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, ethyl ester, homopolymer". http://www.commonchemistry.org/ChemicalDetail.aspx?ref=9003-42-3.
- ↑ "poly(ethyl methacrylate) macromolecule (CHEBI:53221)". https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:53221.
- ↑ "POLY(ETHYL METHACRYLATE)". https://www.chemicalbook.com/Error/Message.html.
- ↑ "CAS DataBase List POLY(ETHYL METHACRYLATE)". https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductList_En.aspx?kwd=POLY(ETHYL%20METHACRYLATE).
- ↑ Anusavice, Kenneth J. (2003). Phillips' Science of Dental Materials 11th edition e-book. Elsevier/Saunders. ISBN 9781437724189. OCLC 934359978.
- ↑ "Document Display (PURL) | NSCEP | US EPA". pp. 6–80. https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=000035VX.txt.
- ↑ Krumenacker, Suzanne (2019-03-13). Hearing aid dispensing training manual (Second ed.). San Diego, CA. p. 138. ISBN 9781635501322. OCLC 1089445836.
- ↑ Audiology. Treatment. Valente, Michael., Hosford-Dunn, Holly., Roeser, Ross J.. New York: Thieme. 2000. p. 79. ISBN 0865778590. OCLC 42726605.
- ↑ Leiggi, Patrick May, Peter (2005). Vertebrate paleontological techniques. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521459001. OCLC 474958103.
- ↑ Baran, Robert; Maibach, Howard, eds (2010-10-15). Textbook of Cosmetic Dermatology. doi:10.3109/9781841847641. ISBN 9780429110962.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Poly(ethyl_methacrylate)33 views | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF