Polychloro phenoxy phenol
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
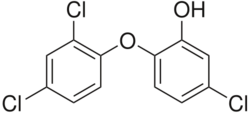
Polychloro phenoxy phenols (polychlorinated phenoxy phenols, PCPPs) are a group of organic polyhalogenated compounds. Among them include triclosan and predioxin which can degrade to produce certains types of dioxins and furans.[1] Notably, however, the particular dioxin formed by degradation of triclosan, 2,8-DCDD,[2] was found to be non-toxic in fish embryos.[3]
References
- ↑ "Formation of chloroform and chlorinated organics by free-chlorine-mediated oxidation of triclosan". Environ. Sci. Technol. 39 (9): 3176–85. 2005. doi:10.1021/es048943+. PMID 15926568. Bibcode: 2005EnST...39.3176R.
- ↑ Latch, Douglas E.; Packer, Jennifer L.; Arnold, William A.; McNeill, Kristopher (2003). "Photochemical conversion of triclosan to 2,8-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in aqueous solution". Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 158: 63–66. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00103-5.
- ↑ Wisk, Joseph D.; Cooper, Keith R. (1990). "Comparison of the toxicity of several polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in embryos of the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes)". Chemosphere 20 (3–4): 361. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(90)90067-4. Bibcode: 1990Chmsp..20..361W.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Polychloro_phenoxy_phenol17 views | Status: cached on January 26 2026 23:14:37↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF