Polyunsaturated fat
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
| Types of fat]]s in food |
|---|
| See also |
In biochemistry and nutrition, a polyunsaturated fat is a fat that contains a polyunsaturated fatty acid (abbreviated PUFA), which is a subclass of fatty acid characterized by a backbone with two or more carbon–carbon double bonds.[1][2] Some polyunsaturated fatty acids are essentials. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are precursors to and are derived from polyunsaturated fats, which include drying oils.[3]



Nomenclature
The position of the carbon-carbon double bonds in carboxylic acid chains in fats is designated by Greek letters.[1] The carbon atom closest to the carboxyl group is the alpha carbon, the next carbon is the beta carbon and so on. In fatty acids the carbon atom of the methyl group at the end of the hydrocarbon chain is called the omega carbon because omega is the last letter of the Greek alphabet. Omega-3 fatty acids have a double bond three carbons away from the methyl carbon, whereas omega-6 fatty acids have a double bond six carbons away from the methyl carbon. The illustration below shows the omega-6 fatty acid, linoleic acid.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids can be classified in various groups by their chemical structure:
- methylene-interrupted polyenes
- conjugated fatty acids
- other PUFAs
Based on the length of their carbon backbone, they are sometimes classified in two groups:[4] All feature pentadiene groups.
- short chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (SC-PUFA), with 18 carbon atoms. These are more common. Key members include linoleic acid, α-linolenic acid, and arachidonic acid.[5]
- long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFA) with 20 or more carbon atoms
Production
PUFAs with 18 carbon atoms, which are the most common variety, are not produced by mammals. Since they have important dietary functions, their biosynthesis has received much attention. Plants produce PUFAs from oleic acid. Key enzymes are called fatty acid desaturases, which introduce additional double bonds. Desaturases convert oleic acid into linoleic acid the precursor to alpha-linolenic acid, gamma-linolenic acid and dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid.[6]
Industrial PUFAs are generally obtained by hydrolysis of fats that contain PUFAs. The process is complicated by the sensitive nature of PUFAs, leading to side reactions and colorization. Thus, steam hydrolysis often fails for this reason. Alkaline hydrolysis of fats followed by acidification is expensive. Lipases, a family of enzymes, show potential as mild and green catalysts for the production of PUFAs from triglycerides.[3]
In general, outside of dietary contexts, PUFAs are undesirable components of vegetable oils, so there is great interest in their removal from, say, olive oil. One technology for lowering the PUFA contact is by selective formation of derivatives with ureas.[3]
Reactions
From the perspective of chemical analysis, PUFA's have high iodine numbers. These high values are simply a reflection of the fact that PUFAs are polyunsaturated. Hydrogenation of PUFAs gives less unsaturated derivatives. For unsaturated products from partial hydrogenation often contain some trans isomers. The trans monounsaturated C20 species elaidic acid can be prepared in this way.[3]
Peroxidation
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are susceptible to lipid peroxidation, far more so than monounsaturated or saturated analogues. The basis for this reactivity is the weakness of doubly allylic C-H bonds. They are drying oils, i.e. film-forming liquids suitable as painting. One practical consequence is that polyunsaturated fatty acids have poor shelf life, owing to their tendency toward autoxidation, leading, in the case of edibles, to rancidification. Metals accelerate the degradation. A range of reactions with oxygen occur. Products include fatty acid hydroperoxides, epoxy-hydroxy polyunsaturated fatty acids, jasmonates, divinylether fatty acids, and leaf aldehydes. Some of these derivatives are signalling molecules, some are used in plant defense (antifeedants), some are precursors to other metabolites that are used by the plant.[5]
Types
Methylene-interrupted polyenes
These fatty acids have 2 or more cis double bonds that are separated from each other by a single methylene bridge (–CH
2–). This form is also sometimes called a divinylmethane pattern.[7]
| −C−C=C−C−C=C− |
The essential fatty acids are all omega-3 and -6 methylene-interrupted fatty acids. See more at Essential fatty acids—Nomenclature[8]
Omega-3
| Common name | Lipid name | Chemical name |
|---|---|---|
| Hexadecatrienoic acid (HTA) | 16:3 (n-3) | all-cis-7,10,13-hexadecatrienoic acid |
| α-Linolenic acid (ALA) | 18:3 (n-3) | all-cis-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid |
| Stearidonic acid (SDA) | 18:4 (n-3) | all-cis-6,9,12,15,-octadecatetraenoic acid |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (ETE) | 20:3 (n-3) | all-cis-11,14,17-eicosatrienoic acid |
| Eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA) | 20:4 (n-3) | all-cis-8,11,14,17-eicosatetraenoic acid |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, Timnodonic acid) | 20:5 (n-3) | all-cis-5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid |
| Heneicosapentaenoic acid (HPA) | 21:5 (n-3) | all-cis-6,9,12,15,18-heneicosapentaenoic acid |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA, Clupanodonic acid) | 22:5 (n-3) | all-cis-7,10,13,16,19-docosapentaenoic acid |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, Cervonic acid) | 22:6 (n-3) | all-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid |
| Tetracosapentaenoic acid | 24:5 (n-3) | all-cis-9,12,15,18,21-tetracosapentaenoic acid |
| Tetracosahexaenoic acid (Nisinic acid) | 24:6 (n-3) | all-cis-6,9,12,15,18,21-tetracosahexaenoic acid |
Omega-6
| Common name | Lipid name | Chemical name |
|---|---|---|
| Linoleic acid (LA) | 18:2 (n-6) | all-cis-9,12-octadecadienoic acid |
| gamma-Linolenic acid (GLA) | 18:3 (n-6) | all-cis-6,9,12-octadecatrienoic acid |
| Eicosadienoic acid | 20:2 (n-6) | all-cis-11,14-eicosadienoic acid |
| Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA) | 20:3 (n-6) | all-cis-8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid |
| Arachidonic acid (AA) | 20:4 (n-6) | all-cis-5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid |
| Docosadienoic acid | 22:2 (n-6) | all-cis-13,16-docosadienoic acid |
| Adrenic acid (AdA) | 22:4 (n-6) | all-cis-7,10,13,16-docosatetraenoic acid |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) | 22:5 (n-6) | all-cis-4,7,10,13,16-docosapentaenoic acid |
| Tetracosatetraenoic acid | 24:4 (n-6) | all-cis-9,12,15,18-tetracosatetraenoic acid |
| Tetracosapentaenoic acid | 24:5 (n-6) | all-cis-6,9,12,15,18-tetracosapentaenoic acid |
Conjugated fatty acids
| -C=C-C=C- |
| Common name | Lipid name | Chemical name |
|---|---|---|
| Conjugated linoleic acids (two conjugated double bonds) | ||
| Rumenic acid | 18:2 (n-7) | 9Z,11E-octadeca-9,11-dienoic acid |
| 18:2 (n-6) | 10E,12Z-octadeca-10,12-dienoic acid | |
| Conjugated Linolenic Acids (three conjugated double bonds) | ||
| α-Calendic acid | 18:3 (n-6) | 8E,10E,12Z-octadecatrienoic acid |
| β-Calendic acid | 18:3 (n-6) | 8E,10E,12E-octadecatrienoic acid |
| Jacaric acid | 18:3 (n-6) | 8Z,10E,12Z-octadecatrienoic acid |
| α-Eleostearic acid | 18:3 (n-5) | 9Z,11E,13E-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid |
| β-Eleostearic acid | 18:3 (n-5) | 9E,11E,13E-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid |
| Catalpic acid | 18:3 (n-5) | 9Z,11Z,13E-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid |
| Punicic acid | 18:3 (n-5) | 9Z,11E,13Z-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid |
| Other | ||
| Rumelenic acid | 18:3 (n-3) | 9E,11Z,15E-octadeca-9,11,15-trienoic acid |
| α-Parinaric acid | 18:4 (n-3) | 9E,11Z,13Z,15E-octadeca-9,11,13,15-tetraenoic acid |
| β-Parinaric acid | 18:4 (n-3) | all trans-octadeca-9,11,13,15-tetraenoic acid |
| Bosseopentaenoic acid | 20:5 (n-6) | 5Z,8Z,10E,12E,14Z-eicosapentaenoic acid |
Other polyunsaturated fatty acids
| Common name | Lipid name | Chemical name |
|---|---|---|
| Pinolenic acid | 18:3 (n-6) | (5Z,9Z,12Z)-octadeca-5,9,12-trienoic acid |
| Sciadonic acid | 20:3 (n-6) | (5Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosa-5,11,14-trienoic acid |
Function and effects
The biological effects of the ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids are largely mediated by their mutual interactions, see Essential fatty acid interactions for detail.
Health
Potential benefits
Because of their effects in the diet, unsaturated fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) are often referred to as good fats; while saturated fats are sometimes referred to as bad fats. Some fat is needed in the diet, but it is usually considered that fats should not be consumed excessively, unsaturated fats should be preferred, and saturated fats in particular should be limited.[9][10][11][12]
In preliminary research, omega-3 fatty acids in algal oil, fish oil, fish and seafood have been shown to lower the risk of heart attacks.[13] Other preliminary research indicates that omega-6 fatty acids in sunflower oil and safflower oil may also reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.[14]
Among omega-3 fatty acids, neither long-chain nor short-chain forms were consistently associated with breast cancer risk. High levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), however, the most abundant omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid in erythrocyte (red blood cell) membranes, were associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer.[15] DHA is vital for the grey matter structure of the human brain, as well as retinal stimulation and neurotransmission.[1]
Contrary to conventional advice, an evaluation of evidence from 1966–1973 pertaining to the health impacts of replacing dietary saturated fat with linoleic acid found that participants in the group doing so had increased rates of death from all causes, coronary heart disease, and cardiovascular disease.[16] Although this evaluation was disputed by many scientists,[17] it fueled debate over worldwide dietary advice to substitute polyunsaturated fats for saturated fats.[18]
Taking isotope-reinforced polyunsaturated fatty acids, for example deuterated linoleic acid where two atoms of hydrogen substituted with its heavy isotope deuterium, with food (heavy isotope diet) can suppress lipid peroxidation and prevent or treat the associated diseases.[19][20]
Pregnancy
Polyunsaturated fat supplementation does not decrease the incidence of pregnancy-related disorders, such as hypertension or preeclampsia, but may increase the length of gestation slightly and decreased the incidence of early premature births.[1]
Expert panels in the United States and Europe recommend that pregnant and lactating women consume higher amounts of polyunsaturated fats than the general population to enhance the DHA status of the fetus and newborn.[1]
Cancer
Results from observational clinical trials on polyunsaturated fat intake and cancer have been inconsistent and vary by numerous factors of cancer incidence, including gender and genetic risk.[13] Some studies have shown associations between higher intakes and/or blood levels of polyunsaturated fat omega-3s and a decreased risk of certain cancers, including breast and colorectal cancer, while other studies found no associations with cancer risk.[13][21]
Dietary sources
Template:Vegetable oils, composition Polyunsaturated fat can be found mostly in nuts, seeds, fish, seed oils, and oysters.[1] "Unsaturated" refers to the fact that the molecules contain less than the maximum amount of hydrogen (if there were no double bonds). These materials exist as cis or trans isomers depending on the geometry of the double bond.
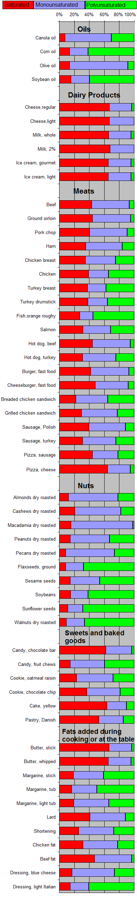
| Food | Saturated | Mono- unsaturated |
Poly- unsaturated |
|---|---|---|---|
| As weight percent (%) of total fat | |||
| Cooking oils | |||
| Algal oil[22] | 04 | 92 | 04 |
| Canola[23] | 08 | 64 | 28 |
| Coconut oil | 87 | 13 | 00 |
| Corn oil | 13 | 24 | 59 |
| Cottonseed oil[23] | 27 | 19 | 54 |
| Olive oil[24] | 14 | 73 | 11 |
| Palm kernel oil[23] | 86 | 12 | 02 |
| Palm oil[23] | 51 | 39 | 10 |
| Peanut oil[25] | 17 | 46 | 32 |
| Rice bran oil | 25 | 38 | 37 |
| Safflower oil, high oleic[26] | 06 | 75 | 14 |
| Safflower oil, linoleic[23][27] | 06 | 14 | 75 |
| Soybean oil | 15 | 24 | 58 |
| Sunflower oil[28] | 11 | 20 | 69 |
| Mustard oil | 11 | 59 | 21 |
| Dairy products | |||
| Butterfat[23] | 66 | 30 | 04 |
| Cheese, regular | 64 | 29 | 03 |
| Cheese, light | 60 | 30 | 00 |
| Ice cream, gourmet | 62 | 29 | 04 |
| Ice cream, light | 62 | 29 | 04 |
| Milk, whole | 62 | 28 | 04 |
| Milk, 2% | 62 | 30 | 00 |
| *Whipping cream[29] | 66 | 26 | 05 |
| Meats | |||
| Beef | 33 | 38 | 05 |
| Ground sirloin | 38 | 44 | 04 |
| Pork chop | 35 | 44 | 08 |
| Ham | 35 | 49 | 16 |
| Chicken breast | 99 | 34 | 21 |
| Chicken | 34 | 23 | 30 |
| Turkey breast | 30 | 20 | 30 |
| Turkey drumstick | 32 | 22 | 30 |
| Fish, orange roughy | 23 | 15 | 46 |
| Salmon | 28 | 33 | 28 |
| Hot dog, beef | 42 | 48 | 05 |
| Hot dog, turkey | 28 | 40 | 22 |
| Burger, fast food | 36 | 44 | 06 |
| Cheeseburger, fast food | 43 | 40 | 07 |
| Breaded chicken sandwich | 20 | 39 | 32 |
| Grilled chicken sandwich | 26 | 42 | 20 |
| Sausage, Polish | 37 | 46 | 11 |
| Sausage, turkey | 28 | 40 | 22 |
| Pizza, sausage | 41 | 32 | 20 |
| Pizza, cheese | 60 | 28 | 05 |
| Nuts | |||
| Almonds dry roasted | 09 | 65 | 21 |
| Cashews dry roasted | 20 | 59 | 17 |
| Macadamia dry roasted | 15 | 79 | 02 |
| Peanut dry roasted | 14 | 50 | 31 |
| Pecans dry roasted | 08 | 62 | 25 |
| Flaxseeds, ground | 08 | 23 | 65 |
| Sesame seeds | 14 | 38 | 44 |
| Soybeans | 14 | 22 | 57 |
| Sunflower seeds | 11 | 19 | 66 |
| Walnuts dry roasted | 09 | 23 | 63 |
| Sweets and baked goods | |||
| Candy, chocolate bar | 59 | 33 | 03 |
| Candy, fruit chews | 14 | 44 | 38 |
| Cookie, oatmeal raisin | 22 | 47 | 27 |
| Cookie, chocolate chip | 35 | 42 | 18 |
| Cake, yellow | 60 | 25 | 10 |
| Pastry, Danish | 50 | 31 | 14 |
| Fats added during cooking or at the table | |||
| Butter, stick | 63 | 29 | 03 |
| Butter, whipped | 62 | 29 | 04 |
| Margarine, stick | 18 | 39 | 39 |
| Margarine, tub | 16 | 33 | 49 |
| Margarine, light tub | 19 | 46 | 33 |
| Lard | 39 | 45 | 11 |
| Shortening | 25 | 45 | 26 |
| Chicken fat | 30 | 45 | 21 |
| Beef fat | 41 | 43 | 03 |
| Goose fat[30] | 33 | 55 | 11 |
| Dressing, blue cheese | 16 | 54 | 25 |
| Dressing, light Italian | 14 | 24 | 58 |
| Other | |||
| Egg yolk fat[31] | 36 | 44 | 16 |
| Avocado[32] | 16 | 71 | 13 |
| Unless else specified in boxes, then reference is:[33] | |||
| * 3% is trans fats | |||
Non-dietary applications
PUFA's are significant components of alkyd resins, which are used in coatings.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "Essential Fatty Acids". Micronutrient Information Center, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR. May 2014. http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/other-nutrients/essential-fatty-acids.
- ↑ "Omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil, alpha-linolenic acid". Mayo Clinic. 2017. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/fish-oil/NS_patient-fishoil/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Anneken, David J.; Both, Sabine; Christoph, Ralf; Fieg, Georg; Steinberner, Udo; Westfechtel, Alfred (2006). "Fatty Acids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_245.pub2. ISBN 3-527-30673-0.
- ↑ "Selection in Europeans on Fatty Acid Desaturases Associated with Dietary Changes". Mol Biol Evol 34 (6): 1307–1318. 2017. doi:10.1093/molbev/msx103. PMID 28333262.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Feussner, Ivo; Wasternack, Claus (2002). "The Lipoxygenase Pathway". Annual Review of Plant Biology 53: 275–297. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135248. PMID 12221977.
- ↑ Jiao, Jingjing; Zhang, Yu (2013). "Transgenic Biosynthesis of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Sustainable Biochemical Engineering Approach for Making Essential Fatty Acids in Plants and Animals". Chemical Reviews 113 (5): 3799–3814. doi:10.1021/cr300007p. PMID 23421688.
- ↑ Baggott, James (1997). The divinylmethane pattern in fatty acids. Salt Lake City, UT: Knowledge Weavers.
- ↑ "National nutrient database for standard reference, release 23". United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. 2011. https://www.nal.usda.gov/human-nutrition-and-food-safety/dri-calculator.
- ↑ "Fats explained". https://www.heartuk.org.uk/downloads/factsheets/fats-explained.pdf.
- ↑ "Key Recommendations: Components of Healthy Eating Patterns". https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines/chapter-1/key-recommendations/.
- ↑ "Live Well, Eat well, Fat: the facts". https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/different-fats-nutrition/.
- ↑ "Dietary Guidelines for Indians - A Manual". http://ninindia.org/DietaryGuidelinesforNINwebsite.pdf.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 "Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Health: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals". US National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. 2 November 2016. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/.
- ↑ "The role of dietary n-6 fatty acids in the prevention of cardiovascular disease". Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine 8 (Suppl 1): S42-5. September 2007. doi:10.2459/01.JCM.0000289275.72556.13. PMID 17876199.
- ↑ "Erythrocyte membrane fatty acids and subsequent breast cancer: a prospective Italian study". Journal of the National Cancer Institute 93 (14): 1088–95. July 2001. doi:10.1093/jnci/93.14.1088. PMID 11459870.
- ↑ "Use of dietary linoleic acid for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease and death: evaluation of recovered data from the Sydney Diet Heart Study and updated meta-analysis". BMJ 346. February 2013. doi:10.1136/bmj.e8707. PMID 23386268.
- ↑ Interview: Walter Willett (2017). "Research Review: Old data on dietary fats in context with current recommendations: Comments on Ramsden et al. in the British Medical Journal". TH Chan School of Public Health, Harvard University, Boston. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2016/04/13/diet-heart-ramsden-mce-bmj-comments/.
- ↑ "Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: The Way Forward in Times of Mixed Evidence". BioMed Research International 2015. 2015. doi:10.1155/2015/143109. PMID 26301240.
- ↑ Hill, S. (2012). "Small amounts of isotope-reinforced PUFAs suppress lipid autoxidation". Free Radical Biology & Medicine 53 (4): 893–906. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.06.004. PMID 22705367.
- ↑ Shchepinov, M. S. (2020). "Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Deuteration against Neurodegeneration". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 41 (4): 236–248. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2020.01.010. PMID 32113652.
- ↑ "Marine fatty acid intake is associated with breast cancer prognosis". The Journal of Nutrition 141 (2): 201–6. February 2011. doi:10.3945/jn.110.128777. PMID 21178081.
- ↑ "Thrive Culinary Algae Oil". https://www.thrivealgae.com/our-product/.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 23.4 23.5 "Fatty acid composition of fats and oils". Colorado Springs: University of Colorado, Department of Chemistry. http://www.uccs.edu/Documents/danderso/fats_oils.pdf. Retrieved April 8, 2017.
- ↑ "NDL/FNIC Food Composition Database Home Page". United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/search/. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- ↑ "Basic Report: 04042, Oil, peanut, salad or cooking". USDA. http://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/foods/show/634?fg=Fats+and+Oils&man=&lfacet=&format=&count=&max=25&offset=&sort=&qlookup=.
- ↑ "Oil, vegetable safflower, oleic". nutritiondata.com. Condé Nast. http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/fats-and-oils/574/2.
- ↑ "Oil, vegetable safflower, linoleic". nutritiondata.com. Condé Nast. http://nutritiondata.self.com/facts/fats-and-oils/573/2.
- ↑ "Oil, vegetable, sunflower". nutritiondata.com. Condé Nast. http://nutritiondata.com/facts/fats-and-oils/572/2.
- ↑ USDA Basic Report Cream, fluid, heavy whipping
- ↑ "Nutrition And Health". The Goose Fat Information Service. http://www.goosefat.co.uk/page/nutrition-and-health.
- ↑ "Egg, yolk, raw, fresh". nutritiondata.com. Condé Nast. http://www.nutritiondata.com/facts/dairy-and-egg-products/113/2.
- ↑ "09038, Avocados, raw, California". National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 26. United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. http://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/foods/show/2235. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- ↑ "Feinberg School > Nutrition > Nutrition Fact Sheet: Lipids". Northwestern University. Archived from the original on 2011-07-20. https://web.archive.org/web/20110720014201/nuinfo-proto4.northwestern.edu/nutrition/factsheets/lipids.html.
Sources
- Cyberlipid. "Polyenoic Fatty Acids". http://www.cyberlipid.org/fa/acid0003.htm.
- Gunstone, Frank D. "Lipid Glossary 2". http://www.plantbiology.msu.edu/ohlrogge/labweb/lipid_glossary.pdf.
- "Common (non-systematic) Names for Fatty Acids". 2003-09-17. http://aocs.org/member/division/analytic/fanames.asp.
- Heinz; Roughan, PG (1983). "Similarities and Differences in Lipid Metabolism of Chloroplasts Isolated from 18:3 and 16:3 Plants". Plant Physiol 72 (2): 273–279. doi:10.1104/pp.72.2.273. PMID 16662992.
 |
 KSF
KSF