Potassium-sparing diuretic
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
Potassium-sparing diuretics or antikaliuretics[1] refer to drugs that cause diuresis without causing potassium loss in the urine.[2] They are typically used as an adjunct in management of hypertension, cirrhosis, and congestive heart failure.[3] The steroidal aldosterone antagonists can also be used for treatment of primary hyperaldosteronism. Spironolactone, a steroidal aldosterone antagonist, is also used in management of female hirsutism and acne from PCOS or other causes.[4][5]
Types of potassium-sparing diuretics
- Epithelial sodium channel blockers:[6]
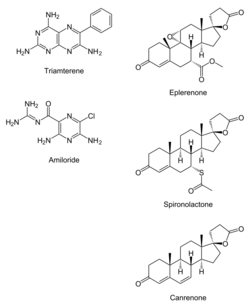
- Amiloride – better tolerated than triamterene
- Triamterene – increased renal side-effects
- Aldosterone antagonists, also known as mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists:[7]
- Spironolactone – most widespread use, inexpensive
- Eplerenone – more selective so reduced side-effects but more expensive and less potent
- Finerenone – non-steroidal, more selective and potent than spironolactone and eplerenone
- Canrenone – very limited use
Mechanism of action
Normally, sodium is reabsorbed in the collecting tubules of a renal nephron. This occurs via epithelial sodium channels or ENaCs, located on the luminal surface of principal cells that line the collecting tubules. Positively-charged Na+ entering the cells during reabsorption leads to an electronegative luminal environment causing the secretion of potassium (K+) into the lumen/ urine in exchange.[2] Sodium reabsorption also causes water retention.[8][9]
When the kidneys detect low blood pressure, the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) is activated and eventually, aldosterone is secreted. Aldosterone binds to aldosterone receptors (mineralocorticoid receptors) increasing sodium reabsorption in an effort to increase blood pressure and improve fluid status in the body. When excessive sodium reabsorption occurs, there is an increasing loss of K+ in the urine and can lead to clinically significant decreases, termed hypokalemia. Increased sodium reabsorption also increases water retention.[8][9]
Potassium-sparing diuretics act to prevent sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubule by either binding ENaCs (amiloride, triamterene) or by inhibiting aldosterone receptors (spironolactone, eplerenone). This prevents excessive excretion of K+ in urine and decreased retention of water, preventing hypokalemia.[10]
Because these diuretics are weakly natriuretic, they do not cause clinically significant blood pressure changes and thus, are not used as primary therapy for hypertension.[11] They can be used in combination with other anti-hypertensives or drugs that cause hypokalemia to help maintain a normal range for potassium. For example, they are often used as an adjunct to loop diuretics (usually furosemide) to treat fluid retention in congestive heart failure and ascites in cirrhosis.[11]
Adverse effects
On their own this group of drugs may raise potassium levels beyond the normal range, termed hyperkalemia, which risks potentially fatal arrhythmias. Triamterene, specifically, is a potential nephrotoxin and up to half of the patients on it can have crystalluria or urinary casts.[12][13] Due to its activity as an androgen receptor antagonist and progesterone receptor agonist, spironolactone causes adverse effects, including gynecomastia or decreased libido in males and menstrual abnormalities in females.[14] Spironolactone also causes hyperkalemia[15] and renal insufficiency.[16]
Drug Interactions
Spironolactone interacts with the following medications:[17]
- ACE inhibitors/ARBs: increases hyperkalemia risk
- Alcohol: risk of orthostatic hypotension
- Barbiturates: risk of orthostatic hypotension
- Narcotics: risk of orthostatic hypotension
- NSAIDs: increases hyperkalemia risk and decreases diuretic effect of potassium-sparing diuretics
- Digoxin: increases digoxin plasma concentrations, leading to increased toxicity
See also
- C03D Potassium-sparing agents
- Kaliuresis
References
- ↑ Knepper, Mark A.; Kleyman, Thomas; Gamba, Gerardo (2005), "Diuretics: Mechanisms of Action", Hypertension (Elsevier): pp. 638–652, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7216-0258-5.50152-6, ISBN 978-0-7216-0258-5, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-7216-0258-5.50152-6, retrieved 2024-03-24
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Diuretics". Kidney Int. 39 (2): 336–52. February 1991. doi:10.1038/ki.1991.43. PMID 2002648.
- ↑ "Aldosterone and antialdosterone therapy in congestive heart failure". The American Journal of Cardiology 71 (3): A3–A11. January 1993. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(93)90238-8. PMID 8422002.
- ↑ "Evaluation and Treatment of Hirsutism in Premenopausal Women: An Endocrine Society* Clinical Practice Guideline". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 103 (4): 1233–1257. 1 April 2018. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00241. PMID 29522147.
- ↑ "Spironolactone for the Treatment of Acne: A 4-Year Retrospective Study". Dermatology 233 (2–3): 141–144. 2017. doi:10.1159/000471799. PMID 28472793.
- ↑ "Triamterene and the Kidney". Nephron 51 (4): 454–461. 1989. doi:10.1159/000185375. PMID 2662034.
- ↑ "Safety profile of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: Spironolactone and eplerenone". International Journal of Cardiology 200: 25–29. December 2015. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.05.127. PMID 26404748.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Struthers, Allan; Krum, Henry; Williams, Gordon H. (April 2008). "A Comparison of the Aldosterone-blocking Agents Eplerenone and Spironolactone" (in en). Clinical Cardiology 31 (4): 153–158. doi:10.1002/clc.20324. ISSN 0160-9289. PMID 18404673.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Batterink, Josh; Stabler, Sarah N; Tejani, Aaron M; Fowkes, Curt T (2010-08-04). Cochrane Hypertension Group. ed. "Spironolactone for hypertension" (in en). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008169.pub2. https://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/14651858.CD008169.pub2.
- ↑ "Potassium-Sparing Diuretics". Kidney and Blood Pressure Research 10 (3–4): 198–220. 1987. doi:10.1159/000173130. PMID 2455308.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Tubular action of diuretics: Distal effects on electrolyte transport and acidification". Kidney International 28 (3): 477–489. September 1985. doi:10.1038/ki.1985.154. PMID 4068482.
- ↑ "Clinical course of 91 consecutive near-drowning victims". Chest 70 (2): 231–8. August 1976. doi:10.1378/chest.70.2.231. PMID 780069.
- ↑ "Triamterene-induced crystalluria and cylinduria: clinical and experimental studies.". Clinical Nephrology 26 (4): 169–73. October 1986. PMID 3780069.
- ↑ Batterink, Josh; Stabler, Sarah N; Tejani, Aaron M; Fowkes, Curt T (2010-08-04). Cochrane Hypertension Group. ed. "Spironolactone for hypertension" (in en). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008169.pub2. https://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/14651858.CD008169.pub2.
- ↑ Struthers, Allan; Krum, Henry; Williams, Gordon H. (April 2008). "A Comparison of the Aldosterone-blocking Agents Eplerenone and Spironolactone" (in en). Clinical Cardiology 31 (4): 153–158. doi:10.1002/clc.20324. ISSN 0160-9289. PMID 18404673.
- ↑ Marrs, Joel C (November 2010). "Spironolactone Management of Resistant Hypertension" (in en). Annals of Pharmacotherapy 44 (11): 1762–1769. doi:10.1345/aph.1P338. ISSN 1060-0280. PMID 20978214. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1345/aph.1P338.
- ↑ Marrs, Joel C (November 2010). "Spironolactone Management of Resistant Hypertension" (in en). Annals of Pharmacotherapy 44 (11): 1762–1769. doi:10.1345/aph.1P338. ISSN 1060-0280. PMID 20978214. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1345/aph.1P338.
External links
- Potassium+Sparing+Diuretics at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |
 KSF
KSF