Potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
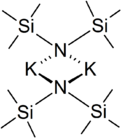
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Potassium 1,1,1-trimethyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)silanaminide | |
| Other names
Potassium hexamethyldisilazide
Potassium hexamethylsilazane[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | KHMDS |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UN number | 3263 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| KSi2C6NH18 | |
| Molar mass | 199.4831 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White, opaque crystals |
| Reacts | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | DANGER |
| H314[2] | |
| P280, P305+351+338, P310[2] | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (commonly abbreviated as KHMDS, Potassium(K) HexaMethylDiSilazide) or potassium hexamethyldisilazane[1] is the chemical compound with the formula ((CH3)3Si)2NK. It is a strong, non-nucleophilic base with an approximate pKa of 26 (compare to lithium diisopropylamide, at 36).[citation needed]
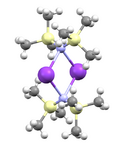
Structure
In the solid state, the unsolvated compound is dimeric, with two potassium and two nitrogen atoms forming a square. This compound is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents and conducts electricity poorly in solution and in the melt. This is attributed to very strong ion pairing.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Potassium Hexamethyldisilazane". https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/ES/es/search/potassium-hexamethyldisilazane?focus=products&page=1&perpage=30&sort=relevance&term=potassium%20hexamethyldisilazane&type=product.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide, Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Tesh, Kris F.; Hanusa, Timothy P.; Huffman, John C. (1990). "Ion pairing in [bis(trimethylsilyl)amido]potassium: The x-ray crystal structure of unsolvated [KN(SiMe3)2]2". Inorg. Chem. 29 (8): 1584–1586. doi:10.1021/ic00333a029.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Potassium_bis(trimethylsilyl)amide1 | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF