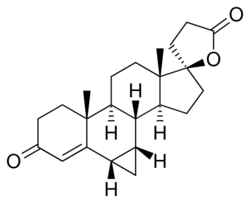
Prorenone
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | SC-23133; 3-(17β-Hydroxy-6β,7β-methylene-3-oxo-4-androsten-17α-yl)propionic acid γ-lactone |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 354.490 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Prorenone (developmental code name SC-23133) is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group related to spironolactone that was never marketed.[1] It is the lactonic form of prorenoic acid (prorenoate), and prorenoate potassium (SC-23992), the potassium salt of prorenoic acid, also exists.[1] Prorenoate potassium is about 8 times more potent than spironolactone as an antimineralocorticoid in animals, and it may act as a prodrug to prorenone.[1] In addition to the mineralocorticoid receptor, prorenone also binds to the glucocorticoid, androgen, and progesterone receptors.[2][3] The antiandrogenic potency of prorenone in vivo in animals is close to that of spironolactone.[3] Similarly to spironolactone, prorenone is also a potent inhibitor of aldosterone biosynthesis.[4]
Chemistry
Synthesis
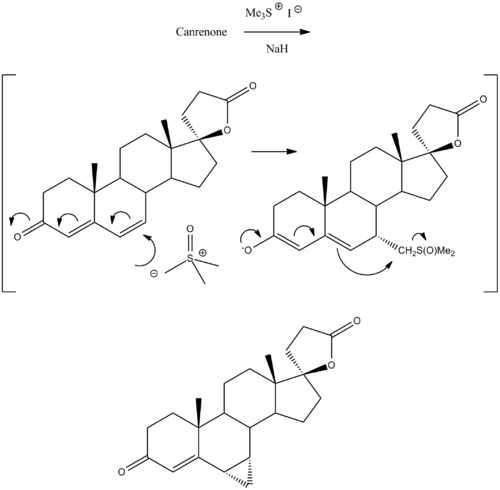
Prorenone can be synthesized via a Johnson–Corey–Chaykovsky reaction by reaction of canrenone with trimethylsulfoxonium iodide and sodium hydride.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Mechanism of action of a new antialdosterone compound, prorenone". Endocrinology 104 (4): 1194–1200. April 1979. doi:10.1210/endo-104-4-1194. PMID 436757.
- ↑ Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Antihypertensive Agents. CRC Press. 19 December 1990. pp. 87–. ISBN 978-0-8493-4724-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=LMl4Sd38q4kC&pg=PA87.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Aldosterone antagonists. 2. Synthesis and biological activities of 11,12-dehydropregnane derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 30 (9): 1647–1658. September 1987. doi:10.1021/jm00392a022. PMID 3040999.
- ↑ "Relative inhibitory potency of five mineralocorticoid antagonists on aldosterone biosynthesis in vitro". Biochemical Pharmacology 34 (2): 189–194. January 1985. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(85)90123-6. PMID 2981534.
- ↑ Chinn L, "7-Halomethyl-17-hydroxy-3-oxo-17alpha-pregn-4-ene-21-carboxylic acid gamma-lactones", US patent 3845041, issued 19 October 1974, assigned to GD Searle LLC.
 |
 KSF
KSF