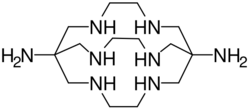
Sarcophagine
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
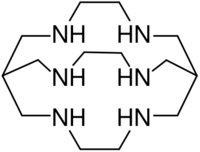
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,6,10,13,16,19-Hexazabicyclo[6.6.6]icosane | |
| Other names
Sar chelate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H32N6 | |
| Molar mass | 284.452 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Sarcophagine (Sar) is a bicyclic cage-like metal chelator molecule[1] derived from cyclam. Chemical formula of sarcophagine is 3,6,10,13,16,19-hexaazabicyclo(6,6,6)icosane[2] and additional functional groups are often linked to this structure, such as in DiAmSar (1,8-diamino-Sar). This and many related hexadentate clathrochelates are prepared by template reactions.[3]
Sarcophagine derivatives are used, for example, as ligands in radiopharmaceuticals that require incorporating a radioactive metal cation into an organic and/or biological structure, such as an antibody.[4]
References
- ↑ Liu, Shuanglong; Li, Dan; Huang, Chiun-Wei; Yap, Li-Peng; Park, Ryan; Shan, Hong; Li, Zibo; Conti, Peter S. (2012). "The Efficient Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Bi-Functionalized Sarcophagine for 64Cu Radiopharmaceuticals" (in en). Theranostics 2 (6): 589–596. doi:10.7150/thno.4295. PMID 22737194. PMC 3381345. http://www.thno.org/v02p0589.htm. Retrieved 2017-10-06.
- ↑ Pubchem. "Diamsar chelate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/146286.
- ↑ Gahan, L. R.; Harrowfield, J. M. (2015). "Sepulchrate: Four decades on". Polyhedron 94: 1–51. doi:10.1016/j.poly.2015.03.036.
- ↑ Liu, Shuanglong; Li, Zibo; Conti, Peter S. (2014-04-03). "Development of Multi-Functional Chelators Based on Sarcophagine Cages" (in en). Molecules 19 (4): 4246–4255. doi:10.3390/molecules19044246. PMID 24705567.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Sarcophagine14 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 07:47:25↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF