Skraup reaction
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
| Skraup reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Zdenko Hans Skraup |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000062 |
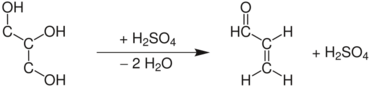
The Skraup synthesis is a chemical reaction used to synthesize quinolines. It is named after the Czech chemist Zdenko Hans Skraup (1850-1910). In the archetypal Skraup reaction, aniline is heated with sulfuric acid, glycerol, and an oxidizing agent such as nitrobenzene to yield quinoline.[1][2][3][4]
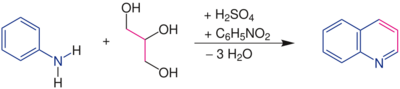
In this example, nitrobenzene serves as both the solvent and the oxidizing agent. The reaction, which otherwise has a reputation for being violent, is typically conducted in the presence of ferrous sulfate.[5] Arsenic acid may be used instead of nitrobenzene and the former is better since the reaction is less violent.[6]
Mechanism
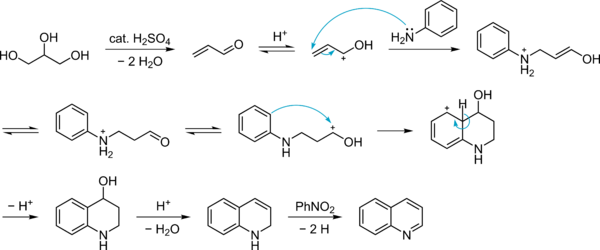
See also
- Bischler-Napieralski reaction
- Doebner-Miller reaction
References
- ↑ Skraup, Z. H. (1880). "Eine Synthese des Chinolins". Berichte 13: 2086.
- ↑ Manske, R. H. F. (1942). "The Chemistry of Quinolines.". Chem. Rev. 30: 113–144. doi:10.1021/cr60095a006.
- ↑ Manske, Richard H. F.; Kulka, Marshall (1953). "The Skraup Synthesis of Quinolines". Org. React. 7: 80–99. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or007.02. ISBN 0471264180.
- ↑ Wahren, M. (1964). "Stabilisotop markierte verbindungen—II , Untersuchung der skraupschen chinolin-synthese mit hilfe von 15N". Tetrahedron 20 (12): 2773. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)98495-9.
- ↑ Clarke, H. T.; Davis, A. W. (1941). "Quinoline". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv1p0478.; Collective Volume, 1, pp. 478
- ↑ Finar, Ivor Lionel (1973). Organic Chemistry, Volume 1 (6th ed.). p. 857. ISBN 978-0582442214.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Skraup_reaction15 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 03:10:23↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF