Tarocin
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
Short description: Class of chemical compounds
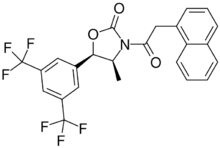
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4S,5R)-5-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-methyl-3-(2-naphthalen-1-ylacetyl)-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H17F6NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 481.394 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
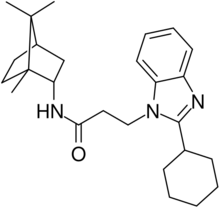
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-(2-cyclohexylbenzimidazol-1-yl)-N-[(1R,2R,4R)-1,7,7-trimethyl-2-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl]propanamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H37N3O | |
| Molar mass | 407.602 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tarocin A and tarocin B are two structurally unrelated compounds that inhibit the TarO enzyme involved in teichoic acid biosynthesis in bacteria.[1]
Using either of them with β-lactam antibiotics seems to be effective in mice against some β-lactam-resistant bacteria.[1]
Because the tarocins lack activity when used alone it may simplify the clinical trials for approval for medical use.[1]
References
Further reading
- S. H. Lee (2016). "TarO-specific inhibitors of wall teichoic acid biosynthesis restore β-lactam efficacy against methicillin-resistant staphylococci". Science Translational Medicine 8 (329): 329ra32. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aad7364. PMID 26962156.
- Swoboda, J. G; Campbell, J; Meredith, T. C; Walker, S (2010). "Wall Teichoic Acid Function, Biosynthesis, and Inhibition". ChemBioChem 11 (1): 35–45. doi:10.1002/cbic.200900557. PMID 19899094.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Tarocin6 views | Status: cached on November 27 2024 04:40:14↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF