Thiete
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2H-Thiete | |
| Other names
1-Thiacyclobut-2-ene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4S | |
| Molar mass | 72.12886 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
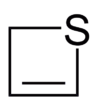
Thiete is a heterocyclic compound containing an unsaturated four-membered ring with three carbon atoms and one sulfur atom.[1][2][3] It is more commonly encountered not on its own, but in anellated derivatives, several of which have been synthesized. Thietes are generally not very stable.[4]
Structure
Thiete is a valence isomer of the compound thioacrolein (CH2=CHCH=S) and undergoes ring opening to it at temperatures below 400 °C.[5] Thiete has been shown to be planar, with a C-S-C angle of 76.8 degrees.[6]
Derivatives
Benzothietes are thietes annulated to benzo group. Such species are prepared by flash vacuum pyrolysis of 2-mercaptobenzyl alcohols. They are precursors to other S-heterocycles.[7]
Thiete 1,1-dioxides are sulfones, the parent being C3H4SO2. They are more stable than the parent thietes.[8] Substituted thiete-1,1-dioxides can also be prepared by [2+2] cycloaddition of sulfenes and ynamines.
See also
- Dithiete - analogue with two sulfur atoms
References
- ↑ Leśniak, S; Lewkowski, J; Kudelska, W; Zając, A (2008). "Thietanes and Thietes: Monocyclic". Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III 2 (7): 389–428. doi:10.1016/B978-008044992-0.00207-8.
- ↑ Block, E (2007). "Thietes and Derivatives". Sci. Synth. 33: 187–202.
- ↑ Block, E; DeWang, M (1996). "Thietanes and Thietes: Monocyclic". Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II 1 (24): 773–802. doi:10.1016/B978-008096518-5.00024-1.
- ↑ Dittmer, DC; Davis, FA (1965). "Evidence for a Thiete (Thiacyclobutene)". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 87 (9): 2064–2065. doi:10.1021/ja01087a048.
- ↑ Block, Eric; Wang, Ming De (1996). "Thietanes and Thietes: Monocyclic". in Katritzky, Alan R.. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II. 1B (2nd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 780. ISBN 978-0-08-096518-5.
- ↑ Rodler, M; Bauder, A (1985). "Microwave spectrum, dipole moment and molecular structure of 1,2-dithiete". Chemical Physics Letters 114 (5–6): 575–578. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(85)85145-9.
- ↑ Herbert Meier , Axel Mayer, Dieter Gröschl "Benzothietes—versatile Synthons For The Preparation Of Heterocycles" Sulfur Reports, 1994, volume 16, 23-56, doi:10.1080/01961779408048965
- ↑ Thomas C. Sedergran and Donald C. Dittmer "Thiete 1,1-dioxide and Chlorothiete 1,1-dioxide" Org. Synth. 1984, vol. 62, 210.doi:10.15227/orgsyn.062.0210
 |
 KSF
KSF