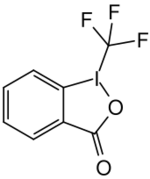
Togni reagent II
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(Trifluoromethyl)-1λ3,2-benziodoxol-3(1H)-one | |
| Other names
Togni's reagent II; Togni reagent 2
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H4F3IO2 | |
| Molar mass | 316.018 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 122.4–123.4 °C (252.3–254.1 °F; 395.5–396.5 K) |
| soluble in methylene chloride, chloroform, acetonitrile, methanol, ethanol, acetone | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Togni reagent II (1-trifluoromethyl-1,2-benziodoxol-3(1H)-one) is a chemical compound used in organic synthesis for direct electrophilic trifluoromethylation.[1][2]
History
Synthesis, properties, and reactivity of the compound were first described in 2006 by Antonio Togni and his coworkers at ETH Zurich.[3] The article also contains information on Togni reagent I (1,3-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl-1-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-benziodoxole).
Preparation
The synthesis consists of three steps. In the first step, 2-iodobenzoic acid is oxidized by sodium periodate and cyclized to 1-hydroxy-1,2-benziodoxol-3(1H)-one. The target compound can then be obtained by acylation with acetic anhydride and subsequent substitution reaction with trifluoromethyltrimethylsilane.[4]
Alternatively, trichloroisocyanuric acid can be used as oxidant in the place of sodium periodate for a newer one-pot synthesis method.[5]
Properties
Physical properties
The compound crystallized in a monoclinic crystal structure. The space group is P21/n with four molecules in the unit cell.[3] From the crystallographic data, a density of 2.365 g·cm−3 was deduced.[3]
Chemical properties
Pure Togni reagent II is metastable at room temperature. Heating it above the melting point will lead to strong exothermic decomposition, in which trifluoroiodomethane (CF3I) is released.[4] The heat of composition at a temperature of 149 °C and higher has been determined to be 502 J·g−1.[6] From recrystallization in acetonitrile, small amounts of trifluoromethyl-2-iodobenzoate and 2-iodobenzyl fluoride were observed as decomposition products.[4] Togni reagent II reacts violently with strong bases and acids, as well as reductants.[4] In tetrahydrofuran, the compound polymerizes.[4]
Uses
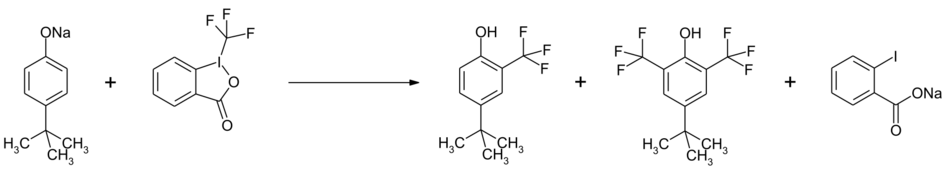
Togni reagent II is used for trifluoromethylation of organic compounds. For phenolates, the substitution takes place preferably in the ortho position. It is possible to obtain a second substitution by using an excess of Togni reagent II.[7]
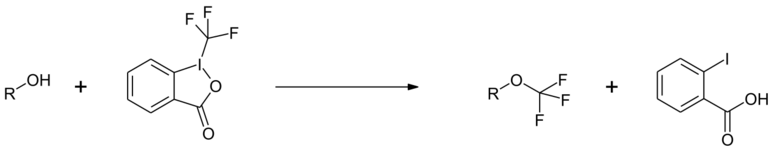
Reactions with alcohols yield the corresponding trifluoromethyl ethers.[8]
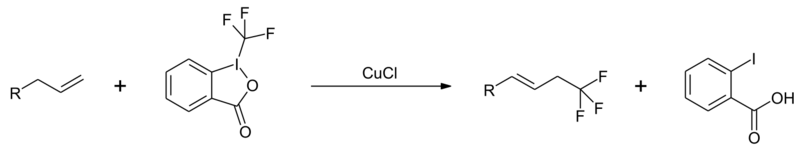
Trifluoromethylation of alkenes is possible under copper catalysis.[9]
References
- ↑ PubChem. "1-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2-benziodoxol-3(1H)-one". National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/24850981.
- ↑ Kieltsch, Iris; Eisenberger, Patrick; Stanek, Kyrill; Togni, Antonio (2008-04-30). "Recent Advances in Electrophilic CF3-Transfer Using Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagents" (in en). Chimia International Journal for Chemistry 62 (4): 260–263. doi:10.2533/chimia.2008.260. http://openurl.ingenta.com/content/xref?genre=article&issn=0009-4293&volume=62&issue=4&spage=260.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Eisenberger, Patrick; Gischig, Sebastian; Togni, Antonio (2006-03-08). "Novel 10-I-3 Hypervalent Iodine-Based Compounds for Electrophilic Trifluoromethylation" (in en). Chemistry - A European Journal 12 (9): 2579–2586. doi:10.1002/chem.200501052. ISSN 0947-6539. PMID 16402401.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Stanek, Kyrill; Koller, Raffael; Kieltsch, Iris; Eisenberger, Patrick; Togni, Antonio (2009-09-15), John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, ed. (in en), 1-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2-benziodoxol-3(1 H )-one, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. rn01121, doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn01121, ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7
- ↑ Matoušek, Václav; Pietrasiak, Ewa; Schwenk, Rino; Togni, Antonio (2013-07-05). "One-Pot Synthesis of Hypervalent Iodine Reagents for Electrophilic Trifluoromethylation" (in en). The Journal of Organic Chemistry 78 (13): 6763–6768. doi:10.1021/jo400774u. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 23734560.
- ↑ Fiederling, Nikolaus; Haller, Jan; Schramm, Heiko (2013-03-15). "Notification about the Explosive Properties of Togni's Reagent II and One of Its Precursors" (in en). Organic Process Research & Development 17 (3): 318–319. doi:10.1021/op400035b. ISSN 1083-6160.
- ↑ Stanek, Kyrill; Koller, Raffael; Togni, Antonio (2008-10-03). "Reactivity of a 10-I-3 Hypervalent Iodine Trifluoromethylation Reagent With Phenols" (in en). The Journal of Organic Chemistry 73 (19): 7678–7685. doi:10.1021/jo8014825. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 18771328.
- ↑ Koller, Raffael; Stanek, Kyrill; Stolz, Daniel; Aardoom, Raphael; Niedermann, Katrin; Togni, Antonio (2009-06-02). "Zinc-Mediated Formation of Trifluoromethyl Ethers from Alcohols and Hypervalent Iodine Trifluoromethylation Reagents" (in en). Angewandte Chemie 121 (24): 4396–4400. doi:10.1002/ange.200900974.
- ↑ Parsons, Andrew T.; Buchwald, Stephen L. (2011-09-19). "Copper-Catalyzed Trifluoromethylation of Unactivated Olefins" (in en). Angewandte Chemie 123 (39): 9286–9289. doi:10.1002/ange.201104053. PMID 21919144.
 |
 KSF
KSF