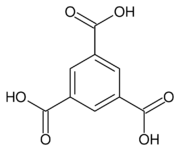
Trimesic acid
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | TMA |
| 2053080 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| 51147 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6O6 | |
| Molar mass | 210.14034 |
| Hazards[1] | |
| Safety data sheet | Oxford MSDS |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Trimesic acid, also known as benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid, is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(CO2H)3. It is one of three isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid.[2] A colorless solid, trimesic acid has some commercial value as a precursor to some plasticizers.[3]
Trimesic acid can be combined with para-hydroxypyridine to make a water-based gel, stable up to 95 °C.[4]
Trimesic acid crystallizes from water to form a hydrogen-bonded hydrated network with wide unidimensional empty channels.[5][6]
See also
- Trimellitic acid (1,2,4-benzenetricarboxylic acid)
- Hemimellitic acid (1,2,3-benzenetricarboxylic acid)
References
- ↑ "1,3,5-Benzenetricarboxylic acid" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/11138#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Marković, Zoran; Badjuk, Dalibor; Gutman, Ivan (2004). "Geometry and Conformations of Benzenecarboxylic Acids". J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 69 (11): 877–882. doi:10.2298/JSC0411877M.
- ↑ Röhrscheid, Freimund (2000). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_249.
- ↑ Tang, Li Ming; Wang, Yu Jiang (2009). "Highly Stable Supramolecular Hydrogels Formed from 1,3,5-Benzenetricarboxylic Acid and Hydroxyl Pyridines". Chinese Chemical Letters 20 (10): 1259–1262. doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2009.04.030.
- ↑ Li, Penghao; Ryder, Matthew R.; Stoddart, J. Fraser (2020). "Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Frameworks: A Rising Class of Porous Molecular Materials". Accounts of Materials Research 1 (1): 77–87. doi:10.1021/accountsmr.0c00019.
- ↑ Herbstein, Frank H. (1987). "Structural Parsimony and Structural Variety Among Inclusion Complexes (with Particular Reference to the Inclusion Compounds of Trimesic acid, N-(p-tolyl)-tetrachlorophthalimide, and the Heilbron "Complexes")". Top. Curr. Chem.. Topics in Current Chemistry. 140. pp. 107–139. doi:10.1007/bfb0003838. ISBN 3-540-17307-2.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Trimesic_acid31 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 23:29:45↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF