Tris(4-bromophenyl)ammoniumyl hexachloroantimonate
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| [(p-BrC 6H 4) 3N•]+ [SbCl 6]− | |
| Molar mass | 816.47 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | blue solid |
| Melting point | 141 to 142 °C (286 to 288 °F; 414 to 415 K) |
| acetonitrile | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
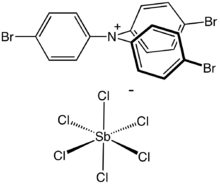
Tris(4-bromophenyl)ammoniumyl hexachloroantimonate is the organic compound with the formula [(4-BrC6H4)3N]SbCl6.[1] Commonly known as magic blue, it is the hexachloroantimonate salt of an amine radical cation. It is a blue solid that reacts with many solvents but is soluble in acetonitrile. The compound is a popular oxidizing agent in organic and organometallic chemistry, with a reduction potential of 0.67 V versus ferrocene/ferrocenium (acetonitrile solution) or 0.70 V versus ferrocene/ferrocenium (dichloromethane solution).[2]
The structure of the cation consists of a three-bladed propeller structure with a planar amine. It is nearly identical to the parent triphenylamine. The weakly coordinating anion is SbCl−6, which is octahedral.[3]
Related compounds
- Magic green, tris(2,4-dibromophenyl)ammoniumyl hexachloroantimonate,[4]
References
- ↑ Earle, Martyn J.; Vibert, Aude; Jahn, Ullrich (2011). "Tris(4-bromophenyl)aminium Hexachloroantimonate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt397.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ↑ Connelly, N. G.; Geiger, W. E. (1996). "Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic Chemistry". Chem. Rev. 96 (2): 877–910. doi:10.1021/cr940053x. PMID 11848774.
- ↑ Quiroz-Guzman, Mauricio; Brown, Seth N. (2010). "Tris(4-bromophenyl)aminium hexachloridoantimonate ('Magic Blue'): A strong oxidant with low inner-sphere reorganization". Acta Crystallographica Section C 66 (7): m171–m173. doi:10.1107/S0108270110019748. PMID 20603548.
- ↑ Schmidt, Werner; Steckhan, Eberhard (1980). "Über organische Elektronenüberträgersysteme, I. Elektrochemische und spektroskopische Untersuchung bromsubstituierter Triarylamin‐Redoxsysteme". Chemische Berichte 113 (2): 577–585. doi:10.1002/cber.19801130215.
 |
 KSF
KSF