Tropane
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane
| |||
| Other names
2,3-Dihydro-8-methylnortropidine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H15N | |||
| Molar mass | 125.211 g/mol | ||
| Density | 0.9259 at 15 °C | ||
| Boiling point | 163 to 169 °C (325 to 336 °F; 436 to 442 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
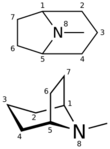
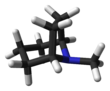
Tropane is a nitrogenous bicyclic organic compound. It is mainly known for the other alkaloids derived from it, which include atropine and cocaine, among others. Tropane alkaloids occur in plants of the families Erythroxylaceae (including coca) and Solanaceae (including mandrake, henbane, deadly nightshade, datura, potato, tomato).[2][3]
Structurally, tropane is cycloheptane with a nitrogen bridge between carbons 1 and 5 and an additional methyl group attached to the nitrogen. While carbons 1 and 5 are asymmetric carbons, tropane itself is optically inactive due to mirror symmetry.
8-Azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane (tropane without the N-methyl group) is known as nortropane or nor-tropane.
See also
- Phenyltropane
- Tropane alkaloid
- Tropine
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9689.
- ↑ "Atropine content of plants". USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program. Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases. [Online Database] National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. http://sun.ars-grin.gov:8080/npgspub/xsql/duke/chemdisp.xsql?chemical=ATROPINE.
- ↑ "Cocaine content of plants". USDA, ARS, National Genetic Resources Program. Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases. [Online Database] National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. http://sun.ars-grin.gov:8080/npgspub/xsql/duke/chemdisp.xsql?chemical=COCAINE.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Tropane44 views | Status: cached on February 12 2026 11:58:00↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF