Gartner
Topic: Company
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
 Headquarters in Stamford | |
| Type | Public |
|---|---|
| Industry | Business services |
| Founded | 1979 in Stamford, Connecticut, U.S |
| Founder | Gideon Gartner |
| Headquarters | Stamford, Connecticut, U.S. |
Key people | |
| Products |
|
| Revenue | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
Number of employees | 21,044 (2024) |
| Website | {{{1}}} |
| Footnotes / references [2] | |
Gartner, Inc. is an American research and advisory firm focusing on business and technology topics. Gartner provides its products and services through research reports, conferences, and consulting. Its clients include large corporations, government agencies, technology companies, and investment firms.
Operations
Gartner is a research and advisory firm[3][4][5] with three business segments: research, conferences, and consulting. As of December 2024, Gartner has over 21,000 employees globally and operates in 90 countries and territories. It is headquartered in Stamford, Connecticut.[6] Gene A. Hall is the chief executive officer.[7]
Gartner is a publicly traded company listed on the S&P 500.[8]
History
1980s
Gideon Gartner and David Stein founded Gartner, Inc. in 1979[9] to provide IT industry research and analysis to businesses buying and selling computer hardware.[10] Gideon Gartner had previously worked at IBM, and his new firm specialized in information about IBM and its products.[11]
Gartner's reports were often delivered as a one-pager containing only high-level insights.[12][13] Gartner analysts developed the Magic Quadrant visual framework of placing companies within defined market quadrants during the early 1980s[14] and began to integrate the methodology into their presentations and later reports.[15] By 1983, the firm employed 80 research analysts and generated $8 million in revenue.[16]
In 1985, Gartner's brokerage and investment division separated from the firm to become a wholly owned subsidiary called Gartner Securities.[17] Two years later, the name was changed to SoundView Financial Group,[18] which eventually operated as SoundView Technology Group.[19]
In July 1986, Gartner rebranded as Gartner Group and became a publicly traded company.[20][21] In January 1987, Gartner Group acquired another technology research firm, the Cupertino-based Infocorp.[22] That same year Gartner reported $25 million in sales and $1.9 million in earnings.[23]
The U.K.-based Saatchi & Saatchi acquired Gartner Group in 1988.[23][24]
1990s
In 1990, Gartner Group was taken private by Gideon Gartner and other executives[25] in an acquisition deal backed by funding from Bain Capital and Dun & Bradstreet, then a Bain client.[26][27] Under Bain ownership, Gartner refocused on IT industry pricing data and expanded its profit margins from 10 percent to 30 percent.[28] Dun & Bradstreet acquired a majority share in Gartner in 1993.[29]
Gartner went public again in October 1993, with Dun & Bradstreet maintaining a 50 percent stake.[30]
Over the next eight years, Gartner acquired or made substantial investments in 30 companies,[31] including the market research firm Dataquest[32] and the online news outlet TechRepublic.[33] The deals were part of a diversification strategy that coincided with the dot-com bubble, and Gartner acknowledged that it struggled to integrate these new companies into its operations.[34] Gartner sold TechRepublic to CNET only a year after acquiring the company.[35]
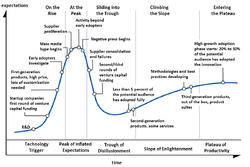
In 1995, Gartner introduced its hype cycle framework, which purported to show how emerging technology is applied and adopted over a typical life cycle.[36]
2000s–present
In August 2004, Gene A. Hall became Gartner's new CEO,[37] replacing Michael D. Fleisher.[38] Hall previously worked with the consulting firm McKinsey & Company before managing a division at Automatic Data Processing.[39]
In 2008, Gartner reached $1.3 billion in revenues and achieved 40 percent of the IT research market.[40]
In 2009, Gartner acquired AMR Research, a Boston-based research and advisory firm focused on supply chain management.[41] The acquisition of AMR and direct competitors like META Group[42] and the Burton Group[43] allowed Gartner to expand its global operations[44] and product and service offerings.[45]
In March 2014, Gartner announced that it had acquired the privately held company Software Advice for an undisclosed amount.[46] Also in 2014, Gartner coined the term "Digital BizOps" and further developed the early philosophy for digital business operations.[47] In July 2015, Gartner acquired Nubera, the business app discovery network that owns properties like GetApp (a peer review site), AppStorm, AppAppeal, and CloudWork. Terms of the deal were not disclosed.[48] In September 2015, it acquired the privately held peer review site (PRS)[49] Capterra.
In June 2016, Gartner announced that it had acquired the privately held company SCM World, headquartered in London.[50] In 2017, Gartner acquired CEB, an Arlington-based talent management and operations consulting firm, for $2.6 billion.[51][52] The deal included $700 million in CEB debt.[53] Two months later, Gartner further expanded its marketing offerings[54] with the acquisition of Scott Galloway's digital benchmarking firm L2.[55][56]
On May 26, 2023 the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) settled charges against Gartner for violating the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA).[57] The SEC asserted that from approximately December 2014 through August 2015 Gartner had a corrupt relationship with a South African company with close ties to the South African government, which Gartner knew would result in official bribery.[58] In the settlement, the SEC ordered Gartner to stop violating the FCPA and Gartner agreed to pay $2,456,764.[59] The SEC made note that Gartner was open and cooperative.[60]
See also
- Gartner hype cycle, a graphical presentation developed by Gartner
- Magic Quadrant, a market research report type published by Gartner
- SoundView Technology Group, founded as a financial service for Gartner
References
- ↑ Larson, Andrew (1 July 2024). "CT-based IT research giant extends CEO’s contract, adds board chair role to duties". Hartford Business. https://hartfordbusiness.com/article/ct-based-it-research-giant-extends-ceos-contract-adds-board-chair-role-to-duties/.
- ↑ "Gartner, Inc. 2024 Annual Report (Form 10-K)". U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. February 13, 2025. https://www.sec.gov/ix?doc=/Archives/edgar/data/749251/000074925125000008/it-20241231.htm.
- ↑ "Gartner beats quarterly profit estimates as contract value grows". Reuters. February 4, 2025. https://www.yahoo.com/tech/gartner-forecasts-weak-2025-results-120808698.html. "Gartner on Tuesday beat estimates for fourth-quarter profit and reported revenue in line with expectations, as the research and advisory firm benefited from an increase in contract values."
- ↑ Feintzeig, Rachel (July 28, 2024). "Can You 'Unboss' Yourself Without Ruining Your Career?". The Wall Street Journal. https://www.wsj.com/lifestyle/workplace/unbossed-managers-career-advancement-48edf815. "Managers oversee nearly three times as many people today as they did in 2017, according to data from research and advisory firm Gartner."
- ↑ Serwer, Andy (June 23, 2023). "Gene Hall Is the Quiet Type, but His Success at Gartner Speaks Loudly". Barron's. https://www.barrons.com/articles/gartner-ceo-gene-hall-success-1d9fb1e2. "You probably don’t know the name Gene Hall, and you might be only barely familiar with Gartner, the business research firm."
- ↑ Schott, Paul (September 13, 2018). "Gartner to add several hundred Stamford jobs". Stamford Advocate. https://www.stamfordadvocate.com/business/article/Gartner-to-add-several-hundred-Stamford-jobs-13226388.php.
- ↑ Serwer, Andy (June 23, 2023). "Gene Hall Is the Quiet Type, but His Success at Gartner Speaks Loudly". Barron's. https://www.barrons.com/articles/gartner-ceo-gene-hall-success-1d9fb1e2.
- ↑ GmbH, finanzen.net. "G | S&P 500 Stocks | S&P 500 Companies | S&P 500 Values". Markets Insider. http://markets.businessinsider.com/index/components/s&p_500/g.
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk (August 11, 1983). "Co-Founder Will Share Gartner Head's Duties". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/1983/08/11/business/business-people-co-founder-will-share-gartner-head-s-duties.html. "Mr. Stein, who is 46, founded the company with Mr. Gartner, 49, in 1979."
- ↑ Malonis, Jane A. (2002). Gale Encyclopedia of E-commerce. 2. Gale Group. p. 484. ISBN 0787657492. https://books.google.com/books?id=xkYOAQAAMAAJ&q=gideon+gartner+and+david+stein+founded+gartner+inc. "Its original focus was providing research and analysis of the information technology (IT) industry to buyers and sellers of computers and related devices."
- ↑ Pollock, Neil; Williams, Robin (December 31, 2015) (in en). How Industry Analysts Shape the Digital Future. Oxford University Press. p. 268. ISBN 9780191014963. https://books.google.com/books?id=zJBPCwAAQBAJ&dq=Gideon+Gartner+had+previously+worked+at+IBM,+and+Gartner+specialized+in+information+about+IBM+and+its+products.&pg=PA268. Retrieved January 16, 2025. "A key historical element of the formation of Gartner was the dominance of IBM in the growing market for IT applications software. Gideon Gartner had initially been working for IBM. As well as holding insider knowledge of IBM products, he explained that his job gave him insights into how these products related to those of IBM's competitors[.]"
- ↑ Pollock, Neil; Campagnolo, Gian (2015-08-13). "Subitizing Practices and Market Decisions: The Role of Simple Graphs In Business Valuations" (in en). Making Things Valuable. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198712282. https://www.pure.ed.ac.uk/ws/files/21127227/SubitizingFinal.pdf. Retrieved 2023-05-23. "When Gideon Gartner first entered the industry analysis business he found that all the existing analyst firms were producing and selling 'lengthy' research reports. These not only took, in his view, an inordinate amount of time for executives to read but also for the analysts to produce. His immediate reaction therefore, upon setting up Gartner, was to introduce an alternative format – the ‘one pager’. This not only shaped how his own firm went about communicating their findings but also the norm for reporting across the industry."
- ↑ Gagner, Ken (December 27, 2021). "14 tech luminaries we lost in 2021". Computerworld. https://www.computerworld.com/article/1616448/tech-luminaries-we-lost-in-2021.html.
- ↑ Pollock, Neil; Williams, Robin (December 31, 2015) (in en). How Industry Analysts Shape the Digital Future. Oxford University Press. p. 169. ISBN 9780191014963. https://books.google.com/books?id=QZNPCwAAQBAJ&dq=when+did+gartner+introduce+the+Magic+Quadrant&pg=PA169. Retrieved January 16, 2025. "From our own discussions with Gideon Gartner and Gartner employees, we know it was first discussed within Gartner around the mid-1980s[.]"
- ↑ Pollock, Neil; Williams, Robin (December 31, 2015) (in en). How Industry Analysts Shape the Digital Future. Oxford University Press. p. 169. ISBN 9780191014963. https://books.google.com/books?id=QZNPCwAAQBAJ&dq=when+did+gartner+introduce+the+Magic+Quadrant&pg=PA169. Retrieved January 16, 2025. "We looked through our Scenario conference binders from 1985 to 1987—did not find any Magic Quadrants in the 1985 binder, one in 1986 and 1987. [...] Given our rigid discipline back in the 1980s of limiting Research Notes to two pages, we suspect that the Magic Quadrant appearance in presentations most likely predates their appearance in a Research Note[.]"
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk (August 11, 1983). "Co-Founder Will Share Gartner Head's Duties". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/1983/08/11/business/business-people-co-founder-will-share-gartner-head-s-duties.html. "Gartner, a closely held company with 80 research analysts, estimates revenues this year at about $8 million. It was founded four years ago - with Mr. Gartner and Mr. Stein its only employees - in an office rented from Dillon, Read & Company Inc. the New York brokerage house."
- ↑ "Gartner Founder Profits From I.B.M. Expertise". The New York Times. July 28, 1986. https://www.nytimes.com/1986/07/28/business/business-people-gartner-founder-profits-from-ibm-expertise.html.
- ↑ Sommar, Jessica (May 10, 1993). "Morgan Stanley tech analyst joins Connecticut boutique". Investment Dealers' Digest. "SoundView Financial Group began in 1985 as Gartner Securities. The name was changed in 1987 to SoundView Financial Group."
- ↑ "SoundView Gets Sold: To Wit". Reuters. November 1, 1999. https://www.wired.com/1999/11/soundview-gets-sold-to-wit/.
- ↑ "Saatchi & Saatchi to buy Gartner Group". Chicago Tribune. June 20, 1988. https://www.chicagotribune.com/1988/06/20/saatchi-saatchi-to-buy-gartner-group/. "Gartner Group, which once was affiliated with a securities firm by that name, became a separate publicly traded company two years ago. Its computer industry reports and stock recommendations are known to have a strong impact in stock market trading and throughout the computer industry."
- ↑ Walters, Donna K.H. (January 3, 1987). "Gartner Buys Infocorp, Boosts Position in High-Tech Data Field". Los Angeles Times. "Gartner Group, founded in 1979 by Gartner, also does market research, but with less focus on collecting and analyzing raw numbers than Infocorp. It became a publicly traded company last July after first spinning off its securities brokerage unit, Gartner Securities."
- ↑ Walters, Donna K.H. (January 3, 1987). "Gartner Buys Infocorp, Boosts Position in High-Tech Data Field". Los Angeles Times. "Infocorp, a high-technology market research firm based in Cupertino, Calif., has been purchased by Gartner Group of Stamford, Conn. The combination, which gives the highly regarded Gartner firm greater access to the West Coast's wide base of information-industry companies, most likely spells intensified competition in the high-tech market research and consulting business."
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Saatchi & Saatchi to buy Gartner Group". Chicago Tribune. June 20, 1988. https://www.chicagotribune.com/1988/06/20/saatchi-saatchi-to-buy-gartner-group/.
- ↑ "Saatchi Agrees to Buy Gartner for $90.3 Million". The New York Times. June 18, 1988. https://www.nytimes.com/1988/06/18/business/saatchi-agrees-to-buy-gartner-for-90.3-million.html.
- ↑ Cook, Kevin (February 13, 2024). "Bear of the Day: Gartner (IT)". Zacks Equity Research (Yahoo Finance). https://finance.yahoo.com/news/bear-day-gartner-112000126.html.
- ↑ Schattle, Hans (July 6, 1990). "Partnership will get Gartner for $ 70m". The Boston Globe. "Information Partners, a Boston investment fund, yesterday said it agreed to purchase Gartner Group Inc., a highly regarded stock research concern, for $ 70 million. [...] Information Partners was launched a year ago and has a cash hoard of $ 60 million from its partners and other sources such as Dun & Bradstreet Corp. and Bain Capital, a unit of Bain & Co., a management consulting firm here. Gartner, Information Partners' first acquisition, will be financed through a combination of its $60 million fund and bank loans. The Gartner deal is pending."
- ↑ Edelman, Larry (January 17, 2023). "Steve Pagliuca retires from Bain Capital after 34 years". The Boston Globe. https://www.bostonglobe.com/2023/01/17/business/stephen-pagliuca-retires-bain-capital-after-34-years/. "Pagliuca joined the firm from Bain & Co. in 1989. He started Information Partners, a tech investment joint venture with Dun & Bradstreet, then a Bain & Co. client, that did the Gartner takeover."
- ↑ Zook, Chris; Allen, James (February 1, 2001). Profit From the Core. Harvard Business Review Press. pp. 8–9. ISBN 1578512301. https://books.google.com/books?id=6G9Stwg7eP4C&q=Gartner. Retrieved January 22, 2025. "Under the ownership of Bain Capital, Gartner refocused on becoming a consumer clearinghouse for customer responses and an honest broker of advice on hardware and software purchases. [...] Gartner built strong barriers to imitation through its subscriber base and its database of benchmarks that allowed it to expand its margins from about 10 percent to 30 percent."
- ↑ "Gartner sold again". Computerworld: p. 109. April 1, 1993. https://books.google.com/books?id=NgTBmzWZ5LkC&q=1993+The+Dun+%26+Bradstreet+Corporation+announced+Wednesday+that+it+has+acquired+a+majority+interest+in+Gartne&pg=PA109.
- ↑ "Millionaries By The Dozen". The New York Times. October 1, 1995. https://www.nytimes.com/1995/10/01/business/millionaires-by-the-dozen.html.
- ↑ Ferranti, Marc (November 15, 2001). "Gartner, Align Thyself". CIO. "Since it went public in 1993, Gartner has acquired or made significant investments in 30 companies, including Inteco, the Internet research and advisory service formerly based in Norwalk, Conn., and San Jose, Calif.-based market research company Dataquest."
- ↑ Abate, Tom (November 26, 1995). "Dataquest acquired by Gartner Group". http://www.sfgate.com/business/article/dataquest-acquired-by-gartner-group-3307056.php.
- ↑ "Consulting firm to invest $300 million in Gartner Group". The New York Times. March 23, 2000. https://www.nytimes.com/2000/03/23/business/company-news-consulting-firm-to-invest-300-million-in-gartner-group.html.
- ↑ Ferranti, Marc (November 15, 2001). "Gartner, Align Thyself". CIO. "Integrating the numerous acquisitions that resulted from Gartner’s diversification strategy was a challenge. 'You want to integrate the offerings and drive efficiencies, integrate billing and sales, check security, integrate infrastructure, and ultimately as a research organization you want to take the knowledge you’ve acquired and plug it into the company’s intellectual capital,' Stanco says. When a company has existing alignment problems, though, that’s tough to do, he acknowledges."
- ↑ Heim, Sarah J. (April 11, 2001). "CNET Acquired TechRepublic". AdWeek. https://www.adweek.com/brand-marketing/cnet-acquires-techrepublic-48104/.
- ↑ Pollock, Neil; Williams, Robin (December 31, 2015) (in en). How Industry Analysts Shape the Digital Future. Oxford University Press. p. 45. ISBN 9780191014963. https://books.google.com/books?id=QZNPCwAAQBAJ&dq=Gartner+introduced+the+%22Hype+Cycle%22+in+1995&pg=PA45. Retrieved January 16, 2025. "To address these challenge, Gartner introduced in 1995 another instrument: the Hype-Cycle [.] This simplified 'signature graphic' offers a graphic representation of the dynamics of emerging technology fields. It shows characteristic changes over time in expectations about a promising technology[.]"
- ↑ "Gartner's Good Gene". Forbes. February 15, 2005. https://www.forbes.com/2005/02/15/cz_cs_0215good_ls.html. "In August, he left Automatic Data Processing , where he was head of a $2 billion payroll-services unit, to take the top job at Stamford, Conn.-based Gartner , a technology research and consulting company. And in December, Hall, 48, agreed to pay $162 million in cash for his Stamford neighbor and smaller rival, META Group ."
- ↑ "Gartner to Name Eugene Hall CEO". Wall Street Journal. July 23, 2004. https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB109053861222271741. "Mr. Fleisher held the CEO post for five years."
- ↑ Soule, Alexander (August 11, 2008). "Gartner beats own forecast". Fairfield County Business Journal. "Before leading a large division at Automatic Data Processing Inc., Hall spent 16 years with the consulting firm McKinsey & Co., and Lafond said the McKinsey pedigree shows."
- ↑ Zook, Chris; Allen, James (February 1, 2001). Profit From the Core. Harvard Business Review Press. pp. 8–9. ISBN 1578512301. https://books.google.com/books?id=6G9Stwg7eP4C&q=Gartner. Retrieved January 22, 2025. "Ten years later, in 2008, Gartner continued its momentum, achieving 40 percent share of the IT research market (four times the size of its nearest competitor), $1.3 billion in revenues, and $213 million in earnings before interest and tax—growing at a healthy 12 percent through the period."
- ↑ Savitz, Eric (December 1, 2009). "Gartner To Buy AMR Research For $64 Million". Barron's. https://www.barrons.com/articles/gartner-to-buy-amr-research-for-64-million-1386893615.
- ↑ Weil, Nancy (December 27, 2004). "IT researcher Gartner to acquire Meta Group". Computerworld. https://www.computerworld.com/article/1713316/it-researcher-gartner-to-acquire-meta-group.html.
- ↑ Harvey, Tom (January 7, 2010). "Utah-based research firm Burton Group bought by Gartner Inc.". The Salt Lake Tribune. https://archive.sltrib.com/story.php?ref=/news/ci_14141787.
- ↑ Bernard, Jean-Gregoire; Gallupe, R. Brent (2013). "IT industry analysts: a review and two research agendas". Communications of the Association for Information Systems 33 (16): 275–302. https://core.ac.uk/reader/301377360. Retrieved January 23, 2025. "Since then, Gartner has grown into a global firm with $1.47 billion in revenues through the acquisition of rivals like Dataquest, METAGroup, AMR Research, and the Burton Group".
- ↑ "Gartner Inc acquires Burton Group for USD56m". Telecomworldwire. January 6, 2010. "The acquisition, effective as of 30 December 2009, is expected to expand Gartner's product and service offerings and increase its IT research market opportunities."
- ↑ "Gartner Acquires Software Advice". Gartner, Inc.. 2014-03-11. http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/2680018.
- ↑ Brink, Michael (2020-06-15). "BizOps: The alchemist for business and data" (in en). https://www.itweb.co.za/content/JBwEr7nBKGD76Db2.
- ↑ Novoa, Jaimе (2015-07-01). "Gartner acquires Barcelona-based Nubera (GetApp)". Novobrief. http://novobrief.com/nubera-getapp-acquisition-gartner/.
- ↑ Leforestier, Ludovic (2015-07-15). "Will research crowdsourcing finally move analyst firms to an experience business model?" (in en-GB). http://analystrelations.org/2015/07/15/can-it-research-be-crowdsourced/.
- ↑ "Gartner buys SCM World" (in en-US). 2016-06-28. https://www.freightwaves.com/news/gartner-buys-scm-world.
- ↑ Gregg, Aaron (January 5, 2017). "Gartner buys Arlington-based CEB for $2.6 billion". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/capital-business/wp/2017/01/05/gartner-buys-arlington-based-ceb-for-2-6-billion/.
- ↑ Sernovitz, Daniel J.; Medici, Andy (5 January 2017). "CEB to be acquired for $2.6 billion". https://www.bizjournals.com/washington/news/2017/01/05/arlington-based-ceb-to-be-acquired-for-2-6-billion.html.
- ↑ Dignan, Larry (January 5, 2017). "Gartner acquires CEB for $2.6 billion, eyes business decision maker expansion". ZDNet. https://www.zdnet.com/article/gartner-acquires-ceb-for-2-6-billion-eyes-business-decision-maker-expansion/.
- ↑ Leforestier, Ludovic (March 6, 2017). "Gartner gobbles brand benchmarking agency L2" (in en-GB). http://analystrelations.org/2017/03/06/breaking-gartner-gobbles-brand-benchmarking-agency/. "[A]fter expanding to other functions with the CEB purchase, Gartner [...] announced it bought L2, a brand benchmarking agency cum research company founded by Scott Galloway. This further reinforces its capabilities in marketing and digital, a segment coveted by rival Forrester."
- ↑ Soule, Alexander (7 March 2017). "Digital benchmark firm acquired by Stamford co.". https://www.ctinsider.com/business/article/Digital-benchmark-firm-acquired-by-Stamford-s-10982411.php.
- ↑ Soule, Alexander (March 7, 2017). "TK". Stamford Advocate. https://www.stamfordadvocate.com/business/article/Digital-benchmark-firm-acquired-by-Stamford-s-10982411.php. "Gartner is acquiring L2, which publishes indexes that benchmark the digital marketing and social media effectiveness of big consumer brands like Nike, Red Bull and Tiffany."
- ↑ Nicodemus, Aaron. "Gartner to pay $2.5M to settle alleged FCPA violations in South Africa" (in en). https://www.complianceweek.com/regulatory-enforcement/gartner-to-pay-25m-to-settle-alleged-fcpa-violations-in-south-africa/33151.article.
- ↑ "SEC Charges Gartner, Inc. with FCPA Violations in South Africa". Securities and Exchange Commission. May 26, 2023. https://www.sec.gov/enforcement-litigation/administrative-proceedings/34-97609-s.
- ↑ DiMauro, Julie (2023-05-30). "Gartner settles with SEC for $2.45m over FCPA offenses in South Africa" (in en-US). https://www.grip.globalrelay.com/gartner-settles-with-sec-for-2-45m-over-fcpa-offenses-in-south-africa/.
- ↑ "Case Information:In the Matter of Gartner, Inc.". Stanford School of Law. https://fcpa.stanford.edu/enforcement-action.html?id=895.
External links
- Official website
- Business data for Gartner, Inc.:
 |
 KSF
KSF