Distance
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 14 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 14 min
Distance is a numerical measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In Physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). The distance from a point A to a point B is sometimes denoted as . In most cases, "distance from A to B" is interchangeable with "distance from B to A". In mathematics, a distance function or metric is a generalization of the concept of physical distance; it is a way of describing what it means for elements of some space to be "close to", or "far away from" each other.
In psychology and social sciences, distance is a non-numerical measurement; Psychological distance is defined as "the different ways in which an object might be removed from" the self along dimensions such as "time, space, social distance, and hypotheticality.[1]
Overview and definitions
Physical distances
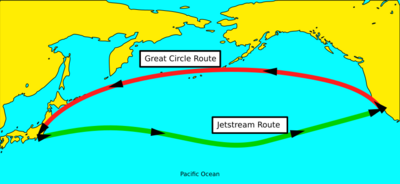
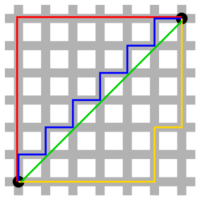
A physical distance can mean several different things:
- Distance traveled: The length of a specific path traveled between two points,[2] such as the distance walked while navigating a maze
- Straight-line (Euclidean) distance: The length of the shortest possible path through space, between two points, that could be taken if there were no obstacles (usually formalized as Euclidean distance)
- Geodesic distance: The length of the shortest path between two points while remaining on some surface, such as the great-circle distance along the curve of the Earth
- The length of a specific path that returns to the starting point, such as a ball thrown straight up, or the Earth when it completes one orbit.
"Circular distance" is the distance traveled by a wheel, which can be useful when designing vehicles or mechanical gears. The circumference of the wheel is 2π × radius, and assuming the radius to be 1, then each revolution of the wheel is equivalent of the distance 2π radians. In engineering ω = 2πƒ is often used, where ƒ is the frequency.
Unusual definitions of distance can be helpful to model certain physical situations, but are also used in theoretical mathematics:
- "Manhattan distance" is a rectilinear distance, named after the number of blocks (in the north, south, east or west directions) a taxicab must travel on, in order to reach its destination on the grid of streets in parts of New York City.
- "Chessboard distance", formalized as Chebyshev distance, is the minimum number of moves a king must make on a chessboard, in order to travel between two squares.
Distance measures in cosmology are complicated by the expansion of the universe, and by effects described by the theory of relativity (such as length contraction of moving objects).
Theoretical distances
The term "distance" is also used by analogy to measure non-physical entities in certain ways.
In computer science, there is the notion of the "edit distance" between two strings. For example, the words "dog" and "dot", which vary by only one letter, are closer than "dog" and "cat", which differ by three letters. This idea is used in spell checkers and in coding theory, and is mathematically formalized in several different ways such as:
In mathematics, a metric space is a set for which distances between all members of the set are defined. In this way, many different types of "distances" can be calculated, such as for traversal of graphs, comparison of distributions and curves, and using unusual definitions of "space" (for example using a manifold or reflections). The notion of distance in graph theory has been used to describe social networks, for example with the Erdős number or the Bacon number—the number of collaborative relationships away a person is from prolific mathematician Paul Erdős and actor Kevin Bacon, respectively.
In psychology, human geography, and the social sciences, distance is often theorized not as an objective metric, but as a subjective experience.[3]
Distance versus directed distance and displacement
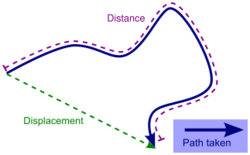
Both distance and displacement measure the movement of an object. Distance cannot be negative, and never decreases. Distance is a scalar quantity, or a magnitude, whereas displacement is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction. It can be negative, zero, or positive. Directed distance does not measure movement; it measures the separation of two points, and can be a positive, zero, or negative vector.[4]
The distance covered by a vehicle (for example as recorded by an odometer), person, animal, or object along a curved path from a point A to a point B should be distinguished from the straight-line distance from A to B. For example, whatever the distance covered during a round trip from A to B and back to A, the displacement is zero as start and end points coincide. In general the straight-line distance does not equal distance travelled, except for journeys in a straight line.
Directed distance
Directed distances can be determined along straight lines and along curved lines.
Directed distances along straight lines are vectors that give the distance and direction between a starting point and an ending point. A directed distance of a point C from point A in the direction of B on a line AB in a Euclidean vector space is the distance from A to C if C falls on the ray AB, but is the negative of that distance if C falls on the ray BA (i.e., if C is not on the same side of A as B is). For example, the directed distance from the New York City Main Library flag pole to the Statue of Liberty flag pole has:
- A starting point: library flag pole
- An ending point: statue flag pole
- A direction: -38°
- A distance: 8.72 km
Another kind of directed distance is that between two different particles or point masses at a given time. For instance, the distance from the center of gravity of the Earth A and the center of gravity of the Moon B (which does not strictly imply motion from A to B) falls into this category.
A directed distance along a curved line is not a vector and is represented by a segment of that curved line defined by endpoints A and B, with some specific information indicating the sense (or direction) of an ideal or real motion from one endpoint of the segment to the other (see figure). For instance, just labelling the two endpoints as A and B can indicate the sense, if the ordered sequence (A, B) is assumed, which implies that A is the starting point.
Displacement
A displacement (see above) is a special kind of directed distance defined in mechanics. A directed distance is called displacement when it is the distance along a straight line (minimum distance) from A and B, and when A and B are positions occupied by the same particle at two different instants of time.
Mathematics
Geometry
In analytic geometry, the Euclidean distance between two points of the xy-plane can be found using the distance formula. The distance between (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is given by:[5][6]
Similarly, given points (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) in three-space, the distance between them is:[5]
These formula are easily derived by constructing a right triangle with a leg on the hypotenuse of another (with the other leg orthogonal to the plane that contains the 1st triangle) and applying the Pythagorean theorem. This distance formula can also be expanded into the arc-length formula. Other distances with other formulas are used in non-Euclidean geometry.
Distance in Euclidean space
In the Euclidean space Rn, the distance between two points is usually given by the Euclidean distance (2-norm distance). Other distances, based on other norms, are sometimes used instead.
For a point (x1, x2, ...,xn) and a point (y1, y2, ...,yn), the Minkowski distance of order p (p-norm distance) is defined as:
| 1-norm distance | |
| 2-norm distance | |
| p-norm distance | |
| infinity norm distance | |
p need not be an integer, but it cannot be less than 1, because otherwise the triangle inequality does not hold.
The 2-norm distance is the Euclidean distance, a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem to more than two coordinates. It is what would be obtained if the distance between two points were measured with a ruler: the "intuitive" idea of distance.
The 1-norm distance is more colourfully called the taxicab norm or Manhattan distance, because it is the distance a car would drive in a city laid out in square blocks (if there are no one-way streets).
The infinity norm distance is also called Chebyshev distance. In 2D, it is the minimum number of moves kings require to travel between two squares on a chessboard.
The p-norm is rarely used for values of p other than 1, 2, and infinity, but see super ellipse.
In physical space the Euclidean distance is in a way the most natural one, because in this case the length of a rigid body does not change with rotation.
Variational formulation of distance
The Euclidean distance between two points in space ( and ) may be written in a variational form where the distance is the minimum value of an integral:
Here is the trajectory (path) between the two points. The value of the integral (D) represents the length of this trajectory. The distance is the minimal value of this integral and is obtained when where is the optimal trajectory. In the familiar Euclidean case (the above integral) this optimal trajectory is simply a straight line. It is well known that the shortest path between two points is a straight line. Straight lines can formally be obtained by solving the Euler–Lagrange equations for the above functional. In non-Euclidean manifolds (curved spaces) where the nature of the space is represented by a metric tensor the integrand has to be modified to , where Einstein summation convention has been used.
Generalization to higher-dimensional objects
The Euclidean distance between two objects may also be generalized to the case where the objects are no longer points but are higher-dimensional manifolds, such as space curves, so in addition to talking about distance between two points one can discuss concepts of distance between two strings. Since the new objects that are dealt with are extended objects (not points anymore) additional concepts such as non-extensibility, curvature constraints, and non-local interactions that enforce non-crossing become central to the notion of distance. The distance between the two manifolds is the scalar quantity that results from minimizing the generalized distance functional, which represents a transformation between the two manifolds:
The above double integral is the generalized distance functional between two polymer conformation. is a spatial parameter and is pseudo-time. This means that is the polymer/string conformation at time and is parameterized along the string length by . Similarly is the trajectory of an infinitesimal segment of the string during transformation of the entire string from conformation to conformation . The term with cofactor is a Lagrange multiplier and its role is to ensure that the length of the polymer remains the same during the transformation. If two discrete polymers are inextensible, then the minimal-distance transformation between them no longer involves purely straight-line motion, even on a Euclidean metric. There is a potential application of such generalized distance to the problem of protein folding.[7][8]
This generalized distance is analogous to the Nambu–Goto action in string theory, however there is no exact correspondence because the Euclidean distance in 3-space is inequivalent to the spacetime distance minimized for the classical relativistic string.
Algebraic distance
This is a metric often used in computer vision that can be minimized by least squares estimation. [1][2] For curves or surfaces given by the equation (such as a conic in homogeneous coordinates), the algebraic distance from the point to the curve is simply . It may serve as an "initial guess" for geometric distance to refine estimations of the curve by more accurate methods, such as non-linear least squares.
General metric
In mathematics, in particular geometry, a distance function on a given set M is a function d: M × M → R, where R denotes the set of real numbers, that satisfies the following conditions:
- d(x,y) ≥ 0, and d(x,y) = 0 if and only if x = y. (Distance is positive between two different points, and is zero precisely from a point to itself.)
- It is symmetric: d(x,y) = d(y,x). (The distance between x and y is the same in either direction.)
- It satisfies the triangle inequality: d(x,z) ≤ d(x,y) + d(y,z). (The distance between two points is the shortest distance along any path). Such a distance function is known as a metric. Together with the set, it makes up a metric space.
For example, the usual definition of distance between two real numbers x and y is: d(x,y) = |x − y|. This definition satisfies the three conditions above, and corresponds to the standard topology of the real line. But distance on a given set is a definitional choice. Another possible choice is to define: d(x,y) = 0 if x = y, and 1 otherwise. This also defines a metric, but gives a completely different topology, the "discrete topology"; with this definition numbers cannot be arbitrarily close.
Distances between sets and between a point and a set
Various distance definitions are possible between objects. For example, between celestial bodies one should not confuse the surface-to-surface distance and the center-to-center distance. If the former is much less than the latter, as for a low Earth orbit, the first tends to be quoted (altitude), otherwise, e.g. for the Earth–Moon distance, the latter.
There are two common definitions for the distance between two non-empty subsets of a given metric space:
- One version of distance between two non-empty sets is the infimum of the distances between any two of their respective points, which is the everyday meaning of the word, i.e. This is a symmetric premetric. On a collection of sets of which some touch or overlap each other, it is not "separating", because the distance between two different but touching or overlapping sets is zero. Also it is not hemimetric, i.e., the triangle inequality does not hold, except in special cases. Therefore only in special cases this distance makes a collection of sets a metric space.
- The Hausdorff distance is the larger of two values, one being the supremum, for a point ranging over one set, of the infimum, for a second point ranging over the other set, of the distance between the points, and the other value being likewise defined but with the roles of the two sets swapped. This distance makes the set of non-empty compact subsets of a metric space itself a metric space.
The distance between a point and a set is the infimum of the distances between the point and those in the set. This corresponds to the distance, according to the first-mentioned definition above of the distance between sets, from the set containing only this point to the other set.
In terms of this, the definition of the Hausdorff distance can be simplified: it is the larger of two values, one being the supremum, for a point ranging over one set, of the distance between the point and the set, and the other value being likewise defined but with the roles of the two sets swapped.
Graph theory
In graph theory the distance between two vertices is the length of the shortest path between those vertices.
Statistical distances
In statistics and information geometry, there are many kinds of statistical distances, notably divergences, especially Bregman divergences and f-divergences. These include and generalize many of the notions of "difference between two probability distributions", and allow them to be studied geometrically, as statistical manifolds. The most elementary is the squared Euclidean distance, which forms the basis of least squares; this is the most basic Bregman divergence. The most important in information theory is the relative entropy (Kullback–Leibler divergence), which allows one to analogously study maximum likelihood estimation geometrically; this is the most basic f-divergence, and is also a Bregman divergence (and is the only divergence that is both). Statistical manifolds corresponding to Bregman divergences are flat manifolds in the corresponding geometry, allowing an analog of the Pythagorean theorem (which is traditionally true for squared Euclidean distance) to be used for linear inverse problems in inference by optimization theory.
Other important statistical distances include the Mahalanobis distance, the energy distance, and many others.
Other mathematical "distances"
- Canberra distance – a weighted version of Manhattan distance, used in computer science
In psychology
Psychological distance is defined as "the different ways in which an object might be removed from" the self along dimensions such as "time, space, social distance, and hypotheticality".[1] The relation between psychological distance and the extent to which thinking is abstract or concrete is described in construal level theory, a framework for decision-making.
See also
- Astronomical system of units
- Color difference
- Cosmic distance ladder
- Distance geometry problem
- Dijkstra's algorithm
- Distance matrix
- Distance measuring device
- Distance measuring equipment (aviation) (DME)
- Distance-based road exit numbers
- Engineering tolerance
- Length
- Meridian arc
- Milestone
- Multiplicative distance
- Orders of magnitude (length)
- Perpendicular distance
- Proper length
- Proxemics – physical distance between people
- Rangefinder
- Signed distance function
- Social distancing
- Vertical distance
Library Support
- Python (programming language)
- Interspace -A package for finding the distance between two vectors, numbers, strings etc.
- SciPy -Distance computations (
scipy.spatial.distance)
- Julia (programming language)
- Julia Statistics Distance -A Julia package for evaluating distances (metrics) between vectors.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Construal-level theory of psychological distance". Psychological Review 117 (2): 440–63. April 2010. doi:10.1037/a0018963. PMID 20438233.
- ↑ "What is displacement? (article)" (in en). https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/one-dimensional-motion/displacement-velocity-time/a/what-is-displacement.
- ↑ "SOCIAL DISTANCES". https://www.hawaii.edu/powerkills/TCH.CHAP16.HTM.
- ↑ "The Directed Distance". University of Kansas. http://www.ittc.ku.edu/~jstiles/220/handouts/The%20Directed%20Distance.pdf.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Weisstein, Eric W.. "Distance" (in en). https://mathworld.wolfram.com/Distance.html.
- ↑ "Distance Between 2 Points". https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/distance-2-points.html.
- ↑ "Generalization of distance to higher dimensional objects". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104 (38): 14899–904. September 2007. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607833104. PMID 17848528. Bibcode: 2007PNAS..10414899P.
- ↑ "Minimal folding pathways for coarse-grained biopolymer fragments". Biophysical Journal 95 (12): 5496–507. December 2008. doi:10.1529/biophysj.108.135046. PMID 18820236. Bibcode: 2008BpJ....95.5496M.
Bibliography
- Dictionary of Distances. Elsevier. 2006. ISBN 0-444-52087-2.
 KSF
KSF