Asia–Pacific
Topic: Earth
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
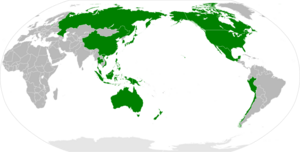
The Asia–Pacific (APAC)[1] is the region of the world adjoining the western Pacific Ocean. The region's precise boundaries vary depending on context, but countries and territories in Australasia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia are often included. In a wider context, Central Asia, North Asia, the Pacific Islands, South Asia, West Asia (excluding the Arabian Peninsula and the Levant), and even Pacific-adjoining countries in the Americas can be included. For example, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) includes five countries (Canada , Chile , Mexico, Peru, and the United States ) in the New World. The term has become popular since the late 1980s in commerce, finance, and politics. Despite the heterogeneity of the regions' economies, most individual nations within the zone are emerging markets experiencing rapid growth. Sometimes, the notion of "Asia–Pacific excluding Japan" (APEJ) is considered useful.[2]
List of countries and territories by subregion
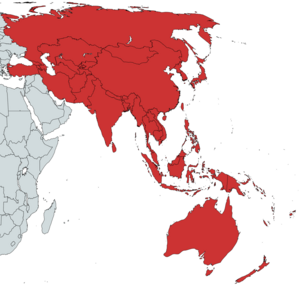
In accordance with the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP), the Asia-Pacific region includes a total of 51 countries and seven territories grouped into five subregions:[3]
- East and North East Asia (ENEA)
 China
China
 Hong Kong, China
Hong Kong, China Macao, China
Macao, China
 Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea)
Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) Japan
Japan Mongolia
Mongolia South Korea
South Korea Taiwan
Taiwan
- North and Central Asia (NCA)
 Armenia
Armenia Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Georgia
Georgia Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Russian Federation
Russian Federation Tajikistan
Tajikistan Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
- South and South West Asia (SSWA)
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Bangladesh
Bangladesh Bhutan
Bhutan India
India- Template:Country data Iran (Islamic Republic of)
 Maldives
Maldives Nepal
Nepal Pakistan
Pakistan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Turkey (Türkiye)
Turkey (Türkiye)
- South East Asia (SEA) – ASEAN
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam Cambodia
Cambodia Indonesia
Indonesia Lao People's Democratic Republic (Laos)
Lao People's Democratic Republic (Laos) Malaysia
Malaysia Myanmar (Burma)
Myanmar (Burma) Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore Thailand
Thailand- Template:Country data Timor-Leste (East Timor)
 Viet Nam (Vietnam)
Viet Nam (Vietnam)
- The Pacific (PACIFIC)
 American Samoa (United States )
American Samoa (United States ) Australia
Australia Cook Islands
Cook Islands Fiji
Fiji French Polynesia (France )
French Polynesia (France ) Guam (United States )
Guam (United States ) Kiribati
Kiribati Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands- Template:Country data Micronesia (Federated States of)
 Nauru
Nauru New Caledonia (France )
New Caledonia (France ) New Zealand
New Zealand Niue
Niue Northern Mariana Islands (United States )
Northern Mariana Islands (United States ) Palau
Palau Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea Samoa
Samoa Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Tonga
Tonga Tuvalu
Tuvalu Vanuatu
Vanuatu
In a wider context, the following countries and territories can also be included in the Asia-Pacific region:
- Asia
 Bahrain
Bahrain British Indian Ocean Territory (United Kingdom )
British Indian Ocean Territory (United Kingdom ) Cyprus
Cyprus Iraq
Iraq Israel
Israel Jordan
Jordan Kuwait
Kuwait Lebanon
Lebanon Oman
Oman Palestine
Palestine Qatar
Qatar Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Syria
Syria United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates Yemen
Yemen
- North America
 Canada
Canada Costa Rica
Costa Rica El Salvador
El Salvador Guatemala
Guatemala Honduras
Honduras Mexico
Mexico Nicaragua
Nicaragua Panama
Panama United States
United States
- Oceania
- Template:Country data Baker Island (United States )
- Template:Country data Clipperton Island (France )
- Template:Country data Coral Sea Islands (Australia )
- Template:Country data Howland Island (United States )
- Template:Country data Jarvis Island (United States )
- Template:Country data Johnston Atoll (United States )
- Template:Country data Kingman Reef (United States )
- Template:Country data Midway Atoll (United States )
 Norfolk Island (Australia )
Norfolk Island (Australia )- Template:Country data Palmyra Atoll (United States )
 Pitcairn Islands (United Kingdom )
Pitcairn Islands (United Kingdom ) Tokelau (New Zealand)
Tokelau (New Zealand)- Template:Country data Wake Island (United States )
 Wallis and Futuna (France )
Wallis and Futuna (France )
- South America
 Chile
Chile Colombia
Colombia Ecuador
Ecuador Peru
Peru
See also
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Asia Pacific Forum
- Asia Pacific Foundation of Canada
- Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC)
- Asia Society
- Asian Century
- China Rim
- East Asia Summit
- East–West dichotomy
- Free and Open Indo-Pacific
- Indo-Pacific
- List of country groupings (including AMEA and AMER)
- Oceania
- Pivot to Asia
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- Valeriepieris circle
References
- ↑ "Digital creativity and innovation lacking in kids in APAC: report". May 10, 2019. https://govinsider.asia/connected-gov/digital-creativity-and-innovation-lacking-in-kids-in-apac-report/.
- ↑ Pan, Hui, ed (October 2004). "Vonage and Cisco to sell phone equipment". VoIP Monthly Newsletter (Information Gatekeepers Inc) 2 (10): 3. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZAb52_IQIIMC. Retrieved 2011-12-15. "APEJ (Asia-Pacific Excluding Japan) and EEMEA (Eastern Europe, Middle East, and Africa) will grow their combined share of this figure from 17 percent to 22 percent during the same period, as North America's share adjusts from 53 percent to 46 percent.".
- ↑ "List of countries in the Asia-Pacific region and subregions". https://data.unescap.org/dataviz/methodology/list-of-countries-in-the-asia-pacific-region-and-subregions.html.
External links
- APEC official website
- The Asia Pacific Foundation of Canada
- Asia Pacific Indigenous Youth Network (APIYN)
- BBC Asia-Pacific
 KSF
KSF