Earth observation
Topic: Earth
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
Earth observation is the gathering of information about the physical, chemical, and biological systems of the planet via remote-sensing technologies, supplemented by [Earth]-surveying techniques, which encompasses the collection, analysis, and presentation of data.[1] Earth observation is used to monitor and assess the status of and changes in natural and built environments.
In recent years,[when?] [2] Earth observation has become technologically sophisticated increasingly. It has also become more important due to the dramatic impact that modern human civilization is having on the world and the need to minimize negative effects (e.g. geohazards)[3], along with the opportunities such observation provides to improve social and economic well-being.
The term Earth observation is used in two ways, leading to confusion. In Europe, in particular, it has often been used to refer to satellite-based remote sensing, but the term is also used to refer to any form of observations of the Earth system, including in situ and airborne observations, for example. The Group on Earth Observations, which has over 100 member countries and over 100 participating organizations, uses EO in this broader sense.
To add to the confusion, in the US, for example, the term remote sensing is often used to refer to satellite-based remote sensing, but sometimes used more broadly for observations using any form of remote sensing technology, including airborne sensors and even ground-based sensors such as cameras. Perhaps the least ambiguous term to use for satellite-based sensors is satellite remote sensing, or SRS, an acronym which is gradually starting to appear in the literature.
Earth observations may include:
- numerical measurements taken by a thermometer, wind gauge, ocean buoy, altimeter or seismometer
- photos and radar or sonar images taken from ground or ocean-based instruments
- photos and radar images taken from remote-sensing satellites
- decision-support tools based on processed information, such as maps and models
Just as Earth observations consist of a wide variety of possible elements, they can be applied to a wide variety of possible uses. Some of the specific applications of Earth observations are:
- forecasting weather
- tracking biodiversity and wildlife trends
- measuring land-use change (such as deforestation)
- monitoring and responding to natural disasters[2], including fires, floods, earthquakes, landslides, land subsidence and tsunamis[3]
- managing natural resources, such as energy, freshwater and agriculture
- addressing emerging diseases and other health risks
- predicting, adapting to and mitigating climate change
The quality and quantity of Earth observations continue to mount rapidly. In addition to the ongoing launch of new remote-sensing satellites, increasingly sophisticated in situ instruments located on the ground, on balloons and airplanes, and in rivers, lakes and oceans, are generating increasingly comprehensive, nearly real-time observations.
Gallery
-
The first photo of Earth from space, taken with a motion picture camera aboard the V-2 No. 13 in 1946.
-
First television weather satellite image of Earth from space, taken by TIROS-1 (1960)
-
The first picture of Earth from the Moon taken by Lunar Orbiter 1 (1966).
-
The first color image of the entire Earth, taken by the DODGE (satellite) (1967)
-
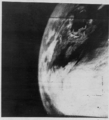
The first image taken by a human of the whole Earth, probably photographed by William Anders of Apollo 8 (1968).[4] South is up; South America is in the middle.
-
Widely used Earthrise, taken on December 24, 1968, by Apollo 8 astronaut William Anders.
-
The Blue Marble widely used Earth picture taken during Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Pale Blue Dot seen from about 6 billion kilometers (3.7 billion miles, 40 AU or 5,6 light hours) in 1990, Earth appears as a tiny dot within deep space: the blueish-white speck almost halfway up the brown band on the right.
See also
- Earth observation satellite
- Group on Earth Observations
- Global Earth Observation System of Systems
- TerraSAR-X: a German Earth observation satellite
An example of Earth observing sensors are the sensors in the Landsat program.
References
- ↑ "Aims and Scope". International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. Elsevier. http://www.journals.elsevier.com/international-journal-of-applied-earth-observation-and-geoinformation/. Retrieved 2012-07-20.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Tomás, Roberto; Li, Zhenhong (2017-02-24). "Earth Observations for Geohazards: Present and Future Challenges". Remote Sensing 9 (3): 194. doi:10.3390/rs9030194. ISSN 2072-4292.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Tomás, Roberto; Li, Zhenhong (2017-02-24). "Earth Observations for Geohazards: Present and Future Challenges". Remote Sensing 9 (3): 194.
- ↑ Woods, W. David; O'Brien, Frank (2006). "Day 1: The Green Team and Separation". Apollo 8 Flight Journal. NASA. Archived from the original on September 23, 2008. https://web.archive.org/web/20080923012425/http://history.nasa.gov/ap08fj/03day1_green_sep.htm. Retrieved October 29, 2008. TIMETAG 003:42:55.
 KSF
KSF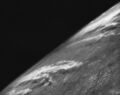


![The first image taken by a human of the whole Earth, probably photographed by William Anders of Apollo 8 (1968).[4] South is up; South America is in the middle.](https://handwiki.org/wiki/images/thumb/1/1f/As08-16-2593.jpg/120px-As08-16-2593.jpg)



