Embankment (transportation)
Topic: Earth
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
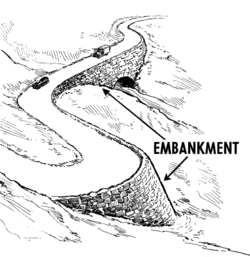


A road, railway line or canal is normally raised onto an embankment made of compacted soil (typically clay or rock-based) to avoid a change in level required by the terrain, the alternatives being either to have an unacceptable change in level or detour to follow a contour. A cutting is used for the same purpose where the land is originally higher than required.
Materials
Embankments are often constructed using material obtained from a cutting. Embankments need to be constructed using non-aerated and waterproofed, compacted (or entirely non-porous) material to provide adequate support to the formation and a long-term level surface with stability.
Intersection of embankments
To intersect an embankment without a high flyover, a series of tunnels can consist of a section of high tensile strength viaduct (typically built of brick and/or metal) or pair of facing abutments for a bridge.
Notable embankments
- Harsimus Stem Embankment remains of a railway built by the Pennsylvania Railroad in Jersey City, New Jersey, United States
See also
References
External links
- Federal Highway Administration Design Manual: Deep Mixing for Embankment and Foundation Support Federal Highway Administration
bibliography
- Scott, J., Loveridge, F., & O'Brien, A. S. (2007). of climate and vegetation on railway embankments[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}].
 KSF
KSF