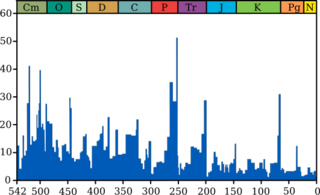
List of extinction events
Topic: Earth
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
Short description: none
This is a list of extinction events, both mass and minor:[1]
"Big Five" major extinction events (see graphic)
| Period or supereon | Extinction | Date | Probable causes[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quaternary | Holocene extinction | c. 10,000 BC – Ongoing | Humans[3] |
| Quaternary extinction event | 640,000, 74,000, and 13,000 years ago |
Unknown; may include climate changes, massive volcanic eruptions and Humans (largely by human overhunting)[4][5][6] | |
| Neogene | Pliocene–Pleistocene boundary extinction | 2 Ma | Possible causes include a supernova[7][8] or the Eltanin impact[9][10] |
| Middle Miocene disruption | 14.5 Ma | Climate change due to change of ocean circulation patterns. Milankovitch cycles may have also contributed[11] | |
| Paleogene | Eocene–Oligocene extinction event | 33.9 Ma | Multiple causes including global cooling, polar glaciation, falling sea levels, and the Popigai impactor[12] |
| Cretaceous | Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event | 66 Ma | |
| Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event | 94 Ma | Most likely underwater volcanism associated with the Caribbean large igneous province, which would have caused global warming and acidic oceans[13] | |
| Aptian extinction | 117 Ma | Unknown, but may be due to volcanism of the Rajmahal Traps[14] | |
| Jurassic | End-Jurassic (Tithonian) | 145 Ma | No longer regarded as a major extinction but rather a series of lesser events due to bolide impacts, eruptions of flood basalts, climate change and disruptions to oceanic systems[15] |
| Pliensbachian-Toarcian extinction (Toarcian turnover) | 186-178 Ma | Formation of the Karoo-Ferrar Igneous Provinces[16] | |
| Triassic | Triassic–Jurassic extinction event | 201 Ma | Possible causes include gradual climate changes, volcanism from the Central Atlantic magmatic province[17] or an impactor[18] |
| Olenekian-Anisian boundary event | 247 Ma | Ocean acidification[19] | |
| Smithian-Spathian boundary event | 249 Ma | Late eruptions of the Siberian Traps | |
| Griesbachian-Dienerian boundary-event | 252 | Late eruptions of the Siberian Traps[20] | |
| Permian | Permian–Triassic extinction event | 252 Ma | Large igneous province (LIP) eruptions [21] from the Siberian Traps,[22] an impact event (the Wilkes Land Crater),[23] an Anoxic event,[24] an Ice age,[25] or other possible causes |
| End-Capitanian extinction event | 260 Ma | Volcanism from the Emeishan Traps,[26] resulting in global cooling and other effects | |
| Olson's Extinction | 270 Ma | Unknown. Possibly a change in climate. | |
| Carboniferous | Carboniferous rainforest collapse | 305 Ma | Possiblities include a series of rapid changes in climate, or volcanism of the Skagerrak-Centered Large Igneous Province[27] |
| Serpukhovian extinction | ~ 325 Ma | Onset of the Late Paleozoic icehouse | |
| Devonian | Hangenberg event | 359 Ma | Anoxia, possibly related to the Famennian glaciation or volcanic activity, Supernova[28] |
| Late Devonian extinction (Kellwasser event) | 372 Ma | Viluy Traps;[29] Woodleigh Impactor?[2] | |
| Taghanic Event | ~384 Ma | Anoxia | |
| Kačák Event | ~388 Ma | Anoxia | |
| Silurian | Lau event | 420 Ma | Changes in sea level and chemistry?[30] |
| Mulde event | 424 Ma | Global drop in sea level?[31] | |
| Ireviken event | 428 Ma | Deep-ocean anoxia;[32] Milankovitch cycles?[33] | |
| Ordovician | Late Ordovician mass extinction | 445-444 Ma | Global cooling and sea level drop, and/or global warming related to volcanism and anoxia[34] |
| Cambrian | Cambrian–Ordovician extinction event | 488 Ma | Kalkarindji Large Igneous Province?[35] |
| Dresbachian extinction event | 502 Ma | ||
| End-Botomian extinction event | 517 Ma | ||
| Precambrian | End-Ediacaran extinction | 542 Ma | Anoxic event[36] |
| Great Oxygenation Event | 2400 Ma | Rising oxygen levels in the atmosphere due to the development of photosynthesis as well as possible Snowball Earth event. (see: Huronian glaciation.) |
Timeline
| Extinction events |
|---|
|
Script error: No such module "Simple horizontal timeline". |
References
- ↑ Partial list from Image:Extinction Intensity.png
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bond, David P. G.; Grasby, Stephen E. (2017-07-15). "On the causes of mass extinctions". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. Mass Extinction Causality: Records of Anoxia, Acidification, and Global Warming during Earth's Greatest Crises 478: 3–29. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.11.005. ISSN 0031-0182. Bibcode: 2017PPP...478....3B.
- ↑ "World Scientists' Warning to Humanity: A Second Notice". BioScience 67 (12): 1026–1028. 13 November 2017. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix125. "Moreover, we have unleashed a mass extinction event, the sixth in roughly 540 million years, wherein many current life forms could be annihilated or at least committed to extinction by the end of this century.".
- ↑ Sandom, Christopher; Faurby, Søren; Sandel, Brody; Svenning, Jens-Christian (4 June 2014). "Global late Quaternary megafauna extinctions linked to humans, not climate change". Proceedings of the Royal Society B 281 (1787): 20133254. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.3254. PMID 24898370.
- ↑ Vignieri, S. (25 July 2014). "Vanishing fauna (Special issue)". Science 345 (6195): 392–412. doi:10.1126/science.345.6195.392. PMID 25061199. Bibcode: 2014Sci...345..392V. "Although some debate persists, most of the evidence suggests that humans were responsible for extinction of this Pleistocene fauna, and we continue to drive animal extinctions today through the destruction of wild lands, consumption of animals as a resource or a luxury, and persecution of species we see as threats or competitors.".
- ↑ Oppenheimer, Clive (2002-08-01). "Limited global change due to the largest known Quaternary eruption, Toba ≈74kyr BP?" (in en). Quaternary Science Reviews 21 (14): 1593–1609. doi:10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00154-8. ISSN 0277-3791. Bibcode: 2002QSRv...21.1593O. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379101001548.
- ↑ Benitez, Narciso (2002). "Evidence for Nearby Supernova Explosions". Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 (8): 081101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.081101. PMID 11863949. Bibcode: 2002PhRvL..88h1101B.
- ↑ Fimiani, L.; Cook, D.L.; Faestermann, T.; Gómez-Guzmán, J.M.; Hain, K.; Herzog, G.; Knie, K.; Korschinek, G. et al. (13 April 2016). "Interstellar 60Fe on the Surface of the Moon". Physical Review Letters 116 (15): 151104. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.151104. PMID 27127953. Bibcode: 2016PhRvL.116o1104F.
- ↑ "Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary: did Eltanin asteroid kickstart the ice ages?". http://www.bitsofscience.org/pliocene-pleistocene-eltanin-asteroid-ice-ages-6274/.
- ↑ "Did a Killer Asteroid Drive the Planet Into An Ice Age?". Universe Today. 20 September 2012. http://www.universetoday.com/97455/did-a-killer-asteroid-drive-the-planet-into-an-ice-age/.
- ↑ Holbourn, Ann; Kuhnt, Wolfgang; Schulz, Michael; Erlenkeuser, Helmut (2005). "Impacts of orbital forcing and atmospheric carbon dioxide on Miocene ice-sheet expansion". Nature 438 (7067): 483–87. doi:10.1038/nature04123. PMID 16306989. Bibcode: 2005Natur.438..483H.
- ↑ "Russia's Popigai Meteor Crash Linked to Mass Extinction". June 13, 2014. http://www.livescience.com/46312-popigai-crater-linked-eocene-mass-extinction.html.
- ↑ "Large igneous provinces and mass extinctions: An update". p. 17. http://specialpapers.gsapubs.org/content/early/2014/06/10/2014.2505_02.full.pdf.
- ↑ Singh, A. P.; Kumar, Niraj; Singh, Bijendra (2004). "Magmatic underplating beneath the Rajmahal Traps:Gravity signature and derived 3-D configuration.Proc". Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci: 759–769. doi:10.1007/BF02704035.
- ↑ Tennant, Jonathan P.; Mannion, Philip D.; Upchurch, Paul; Sutton, Mark D.; Price, Gregory D. (2017). "Biotic and environmental dynamics through the Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous transition: evidence for protracted faunal and ecological turnover" (in en). Biological Reviews 92 (2): 776–814. doi:10.1111/brv.12255. ISSN 1469-185X. PMID 26888552.
- ↑ József Pálfy; Paul L. Smith (2000). "Synchrony between Early Jurassic extinction, oceanic anoxic event, and the Karoo-Ferrar flood basalt volcanism". Geology 28 (8): 747–750. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<747:SBEJEO>2.0.CO;2. Bibcode: 2000Geo....28..747P. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238695407.
- ↑ Blackburn, Terrence J.; Olsen, Paul E.; Bowring, Samuel A.; McLean, Noah M.; Kent, Dennis V; Puffer, John; McHone, Greg; Rasbury, Troy et al. (2013). "Zircon U-Pb Geochronology Links the End-Triassic Extinction with the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province". Science 340 (6135): 941–45. doi:10.1126/science.1234204. PMID 23519213. Bibcode: 2013Sci...340..941B.
- ↑ Onoue, Tetsuji; Sato, Honami; Yamashita, Daisuke; Ikehara, Minoru; Yasukawa, Kazutaka; Fujinaga, Koichiro; Kato, Yasuhiro; Matsuoka, Atsushi (8 July 2016). "Bolide impact triggered the Late Triassic extinction event in equatorial Panthalassa". Scientific Reports 6 (29609): 29609. doi:10.1038/srep29609. PMID 27387863. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...629609O.
- ↑ Song, Haijun; Song, Huyue; Tong, Jinnan; Gordon, Gwyneth W.; Wignall, Paul B.; Tian, Li; Zheng, Wang; Algeo, Thomas J. et al. (2021-02-20). "Conodont calcium isotopic evidence for multiple shelf acidification events during the Early Triassic" (in en). Chemical Geology 562: 120038. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.120038. ISSN 0009-2541. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254120305775.
- ↑ Hochuli, Peter A.; Sanson-Barrera, Anna; Schneebeli-Hermann, Elke; Bucher, Hugo (2016-06-24). "Severest crisis overlooked—Worst disruption of terrestrial environments postdates the Permian–Triassic mass extinction" (in en). Scientific Reports 6 (1): 28372. doi:10.1038/srep28372. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 27340926. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...628372H.
- ↑ algeo, Thomas (2023-09-08). "Theory and classification of mass extinction causation". doi:10.1093/nsr/nwad237. https://academic.oup.com/nsr/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nsr/nwad237/7264266.
- ↑ Campbell, I; Czamanske, G.; Fedorenko, V.; Hill, R.; Stepanov, V. (1992). "Synchronism of the Siberian Traps and the Permian-Triassic Boundary". Science 258 (5089): 1760–63. doi:10.1126/science.258.5089.1760. PMID 17831657. Bibcode: 1992Sci...258.1760C.
- ↑ von Frese, R; Potts, L.; Wells, S.; Leftwich, T.; Kim, H. (2009). "GRACE gravity evidence for an impact basin in Wilkes Land, Antarctica". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 10 (2): n/a. doi:10.1029/2008GC002149. Bibcode: 2009GGG....10.2014V.
- ↑ Wignall, P; Twitchett, R (2002). "Extent, duration, and nature of the Permian-Triassic superanoxic event". in Christian Koeberl. Catastrophic events and mass extinctions: impacts and beyond. Geological Society of America. p. 396. doi:10.1130/0-8137-2356-6.395. ISBN 978-0813723563.
- ↑ Ice age, not warming, explains Permian-Triassic extinction event - UPI.com
- ↑ Bond, David P.G.; Wignall, Paul B. (2014-09-01). Bond.pdf "Large igneous provinces and mass extinctions: An update" (in en). Geological Society of America Special Papers 505: 29–55. doi:10.1130/2014.2505(02). ISBN 9780813725055. ISSN 0072-1077. https://hull-repository.worktribe.com/373637/1/10877 Bond.pdf.
- ↑ Doblas, Miguel; R., OYARZUN; J., LOPEZ-RUIZ; J.M., CEBRIA; Youbi, Nasrrddine; V., MAHECHA; Lago San José, Marceliano; POCOVI et al. (1998-12-01). "Permo-Carboniferous Volcanism in Europe and North Africa: a Superplume exhaust valve in The Center of Pangea.". Journal of African Earth Sciences 26: 89–99. doi:10.1016/S0899-5362(97)00138-3. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262757629.
- ↑ Fields, Brian D.; Melott, Adrian L.; Ellis, John; Ertel, Adrienne F.; Fry, Brian J.; Lieberman, Bruce S.; Liu, Zhenghai; Miller, Jesse A. et al. (2020-09-01). "Supernova triggers for end-Devonian extinctions". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 117 (35): 21008–21010. doi:10.1073/pnas.2013774117. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 32817482. Bibcode: 2020PNAS..11721008F.
- ↑ Ricci, J (2013). "New 40Ar/39Ar and K–Ar ages of the Viluy traps (Eastern Siberia): Further evidence for a relationship with the Frasnian–Famennian mass extinction". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 386: 531–40. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.06.020.
- ↑ Jeppsson, L. (1998). "Silurian oceanic events: summary of general characteristics". in Landing, E.. Silurian Cycles: Linkages of Dynamic Stratigraphy with Atmospheric, Oceanic and Tectonic Changes. James Hall Centennial Volume. New York State Museum Bulletin. 491. pp. 239–57.
- ↑ Jeppsson, L.; Calner, M. (2007). "The Silurian Mulde Event and a scenario for secundo – secundo events". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh 93 (2): 135–54. doi:10.1017/s0263593300000377.
- ↑ Munnecke, Axel; Samtleben, Christian; Bickert, Torsten (5 June 2003). "The Ireviken Event in the lower Silurian of Gotland, Sweden - relation to similar Palaeozoic and Proterozoic events". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 195 (1–2): 119. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00304-3. Bibcode: 2003PPP...195...99M.
- ↑ Jeppsson, L (1997). "The anatomy of the Mid-Early Silurian Ireviken Event and a scenario for P-S events". Paleontological Events: Stratigraphic, Ecological, and Evolutionary Implications. New York: Columbia University Press. pp. 451–92.
- ↑ Bond, David P.G.; Grasby, Stephen E. (18 May 2020). "Late Ordovician mass extinction caused by volcanism, warming, and anoxia, not cooling and glaciation". Geology 48 (8): 777–781. doi:10.1130/G47377.1. Bibcode: 2020Geo....48..777B.
- ↑ Ware, Bryant D.; Jourdan, Fred; Merle, Renaud; Chiaradia, Massimo; Hodges, Kyle (2018-04-01). "The Kalkarindji Large Igneous Province, Australia: Petrogenesis of the Oldest and Most Compositionally Homogenous Province of the Phanerozoic" (in en). Journal of Petrology 59 (4): 635–665. doi:10.1093/petrology/egy040. ISSN 0022-3530. Bibcode: 2018JPet...59..635W.
- ↑ Zhang, Feifei; Xiao, Shuhai; Kendall, Brian; Romaniello, Stephen J.; Cui, Huan; Meyer, Mike; Gilleaudeau, Geoffrey J.; Kaufman, Alan J. et al. (2018). "Extensive marine anoxia during the terminal Ediacaran Period". Science Advances (American Association for the Advancement of Science) 4 (6): eaan8983. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aan8983. ISSN 2375-2548. PMID 29938217. Bibcode: 2018SciA....4.8983Z.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Earth:List_of_extinction_events17 views | Status: cached on October 05 2024 04:33:36↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF