Sound (geography)
Topic: Earth
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min

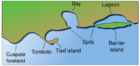
In geography, a sound is a smaller body of water usually connected to a sea or an ocean. A sound may be an inlet that is deeper than a bight and wider than a fjord; or a narrow sea channel or an ocean channel between two land masses, such as a strait; or also a lagoon between a barrier island and the mainland.[1][2]
Overview

A sound is often formed by the seas flooding a river valley. This produces a long inlet where the sloping valley hillsides descend to sea-level and continue beneath the water to form a sloping sea floor. These sounds are more appropriately called ria. The Marlborough Sounds in New Zealand are good examples of this type of formation.
Sometimes a sound is produced by a glacier carving out a valley on a coast then receding, or the sea invading a glacier valley. The glacier produces a sound that often has steep, near vertical sides that extend deep underwater. The sea floor is often flat and deeper at the landward end than the seaward end, due to glacial moraine deposits. This type of sound is more properly termed a fjord (or fiord). The sounds in Fiordland, New Zealand, have been formed this way.
A sound generally connotes a protected anchorage. It can be part of most large islands.
In the more general northern European usage, a sound is a strait or the narrowest part of a strait. In Scandinavia and around the Baltic Sea, there are more than a hundred straits named Sund, mostly named for the island they separate from the continent or a larger island.
In contrast, the Sound is the common international[3] short name for Øresund, the narrow stretch of water that separates Denmark and Sweden, and is the main waterway between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea. It is also a colloquial short name, among others, for Plymouth Sound, England.
In areas explored by the British in the late 18th century, particularly the northwest coast of North America, the term "sound" was applied to inlets containing large islands, such as Howe Sound in British Columbia and Puget Sound in the U.S. state of Washington. It was also applied to bodies of open water not fully open to the ocean, such as Caamaño Sound or Queen Charlotte Sound in Canada, or broadenings or mergings at the openings of inlets, like Cross Sound in Alaska and Fitz Hugh Sound in British Columbia.
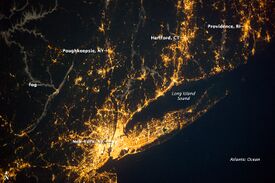
Along the east coast and Gulf Coast of the United States, a number of bodies of water that separate islands from the mainland are called "sounds". Long Island Sound separates Long Island from the eastern shores of the Bronx, Westchester County, and southern Connecticut. Similarly, in North Carolina, a number of large lagoons lie between the mainland and its barrier beaches, the Outer Banks. These include Pamlico Sound, Albemarle Sound, Bogue Sound, and several others. The Mississippi Sound separates the Gulf of Mexico from the mainland, along much of the gulf coasts of Alabama and Mississippi.
Etymology
The term sound is derived from the Anglo-Saxon or Old Norse word sund, which also means "swimming".[2]
The word sund is also documented in Old Norse and Old English as meaning "gap" (or "narrow access"). This suggests a relation to verbs meaning "to separate", such as absondern and aussondern (German), söndra (Swedish), sondre (Norwegian), as well as the English noun sin, German Sünde ("apart from God's law"), and Swedish synd. English has also the adjective "asunder" and the noun "sundry', and Swedish has the adjective sönder ("broken").
In Swedish and in both Norwegian languages, "sund" is the general term for any strait. In Swedish and Nynorsk, it is even part of names worldwide, such as in Swedish "Berings sund" and "Gibraltar sund", and in Nynorsk "Beringsundet" and "Gibraltarsundet". In German "Sund" is mainly used for place names at the Baltic Sea like Fehmarnsund, Strelasund, and Stralsund.
Bodies of water called sounds
References
- ↑ "sound-3". TheFreeDictionary.com. http://www.thefreedictionary.com/sound.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "sound-4". Oxford English Dictionary. http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/sound--4.
- ↑ "Baltic Straits". Legal provision for integrated coastal zone management, Chapter 2.3: International straits and canals. UNESCO. http://www.unesco.org/csi/act/russia/legalpro6.htm., archived version
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF