Total Carbon
Topic: Earth
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
Total Carbon is an analytical measurement for carbon content. This measurement commonly found in environmental and pharmaceutical analysis.
Carbon Content Categories
A variety of different terms are used to identify the different types of carbon present at different levels of detail.
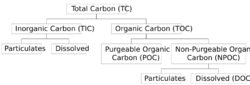
- Total Carbon (TC) – all the carbon in the sample, including both inorganic and organic carbon
- Total Inorganic Carbon (TIC) – often referred to as inorganic carbon (IC), carbonate, bicarbonate, and dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Total Organic Carbon (TOC) – material derived from decaying vegetation, bacterial growth, and metabolic activities of living organisms or chemicals.
- Elemental Carbon (EC) – charcoal, coal, and soot. Resistant to analytical digestion and extraction, EC can be a fraction of either TIC or TOC depending on analytical approach.[1]
- Non-Purgeable Organic Carbon (NPOC) – commonly referred to as TOC; organic carbon remaining in an acidified sample after purging the sample with gas.
- Purgeable (volatile) Organic Compound (VOC) – organic carbon that has been removed from a neutral, or acidified sample by purging with an inert gas. These are the same compounds referred to as Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) and usually determined by Purge and Trap Gas Chromatography.
- Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) – organic carbon remaining in a sample after filtering the sample, typically using a 0.45 micrometer filter.
- Suspended Organic Carbon – also called particulate organic carbon (POC); the carbon in particulate form that is too large to pass through a filter.
References
- ↑ Schumacher, B. A. (2002). "Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soils and Sediments" Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center. US. Environmental Protection Agency 23p.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Earth:Total_Carbon16 views | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF