Arc converter
Topic: Engineering
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
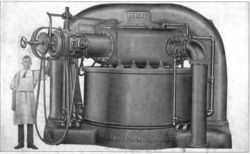
The arc converter, sometimes called the arc transmitter, or Poulsen arc after Danish engineer Valdemar Poulsen who invented it in 1903,[1][2] was a variety of spark transmitter used in early wireless telegraphy. The arc converter used an electric arc to convert direct current electricity into radio frequency alternating current. It was used as a radio transmitter from 1903 until the 1920s when it was replaced by vacuum tube transmitters. One of the first transmitters that could generate continuous sinusoidal waves, it was one of the first technologies used to transmit sound (amplitude modulation) by radio. It is on the list of IEEE Milestones as a historic achievement in electrical engineering.[3]
History
Elihu Thomson discovered that a carbon arc shunted with a series tuned circuit would "sing". This "singing arc" was probably limited to audio frequencies.[4] Bureau of Standards credits William Duddell with the shunt resonant circuit around 1900.[5]
The English engineer William Duddell discovered how to make a resonant circuit using a carbon arc lamp. Duddell's "musical arc" operated at audio frequencies, and Duddell himself concluded that it was impossible to make the arc oscillate at radio frequencies.
Valdemar Poulsen succeeded in raising the efficiency and frequency to the desired level. Poulsen's arc could generate frequencies of up to 200 kilohertz and was patented in 1903.
After a few years of development the arc technology was transferred to Germany and Great Britain in 1906 by Poulsen, his collaborator Peder Oluf Pedersen and their financial backers. In 1909 the American patents as well as a few arc converters were bought by Cyril Frank Elwell. The subsequent development in Europe and the United States was rather different, since in Europe there were severe difficulties for many years implementing the Poulsen technology, whereas in the United States an extended commercial radiotelegraph system was soon established with the Federal Telegraph Company. Later the US Navy also adopted the Poulsen system. Only the arc converter with passive frequency conversion was suitable for portable and maritime use. This made it the most important mobile radio system for about a decade until it was superseded by vacuum tube systems.
In 1922, the Bureau of Standards stated, "the arc is the most widely used transmitting apparatus for high-power, long-distance work. It is estimated that the arc is now responsible for 80 per cent of all the energy actually radiated into space for radio purposes during a given time, leaving amateur stations out of consideration."[6]
Description
This new, more-refined method for generating continuous-wave radio signals was initially developed by Danish inventor Valdemar Poulsen. The spark-gap transmitters in use at that time produced damped wave which wasted a large portion of their radiated power transmitting strong harmonics on multiple frequencies that filled the RF spectrum with interference. Poulsen's arc converter produced undamped or continuous waves (CW) on a single frequency.
There are three types for an arc oscillator:[7]
- Duddell arc (and other early types)
- In the first type of arc oscillator, the AC current in the condenser i0 is much smaller than the DC supply current i1, and the arc is never extinguished during an output cycle. The Duddell arc is an example of the first type, but the first type is not practical for RF transmitters.
- Poulsen arc
- In the second type of arc oscillator, the condenser AC discharge current is large enough to extinguish the arc but not large enough to restart the arc in the opposite direction. This second type is the Poulsen arc.
- Quenched spark gap
- In the third type of arc oscillator, the arc extinguishes but may reignite when the condenser current reverses. The third case is a quenched spark gap and produces damped oscillations.
Continuous or ‘undamped’ waves (CW) were an important feature, since the use of damped waves from spark-gap transmitters resulted in lower transmitter efficiency and communications effectiveness, while polluting the RF spectrum with interference.
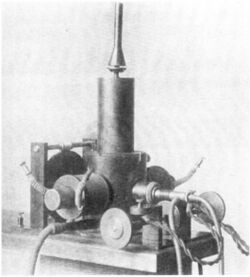
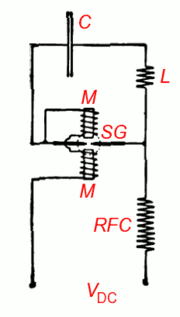
The Poulsen arc converter had a tuned circuit connected across the arc. The arc converter consisted of a chamber in which the arc burned in hydrogen gas between a carbon cathode and a water-cooled copper anode. Above and below this chamber there were two series field coils surrounding and energizing the two poles of the magnetic circuit. These poles projected into the chamber, one on each side of the arc to provide a magnetic field.
It was most successful when operated in the frequency range of a few kilohertz to a few tens of kilohertz. The antenna tuning had to be selective enough to suppress the arc converter's harmonics.
Keying
Since the arc took some time to strike and operate in a stable fashion, normal on-off keying could not be used. Instead, a form of frequency-shift keying was employed.[8] In this compensation-wave method, the arc operated continuously, and the key altered the frequency of the arc by one to five percent. The signal at the unwanted frequency was called the compensation-wave. In arc transmitters up to 70 kW, the key typically shorted out a few turns in the antenna coil.[9] For larger arcs, the arc output would be transformer coupled to the antenna inductor, and the key would short out a few bottom turns of the grounded secondary.[10] Therefore, the "mark" (key closed) was sent at one frequency, and the "space" (key open) at another frequency. If these frequencies were far enough apart, and the receiving station's receiver had adequate selectivity, the receiving station would hear standard CW when tuned to the "mark" frequency.
The compensation wave method used a lot of spectrum bandwidth. It not only transmitted on the two intended frequencies, but also the harmonics of those frequencies. Arc converters are rich in harmonics. Sometime around 1921, the Preliminary International Communications Conference[11] prohibited the compensation wave method because it caused too much interference.[4]
The need for the emission of signals at two different frequencies was eliminated by the development of uniwave methods.[12] In one uniwave method, called the ignition method, keying would start and stop the arc. The arc chamber would have a striker rod that shorted out the two electrodes through a resistor and extinguished the arc. The key would energize an electromagnet that would move the striker and reignite the arc. For this method to work, the arc chamber had to be hot. The method was feasible for arc converters up to about 5 kW.
The second uniwave method is the absorption method, and it involves two tuned circuits and a single-pole, double-throw, make-before-break key. When the key is down, the arc is connected to the tuned antenna coil and antenna. When the key is up, the arc is connected to a tuned dummy antenna called the back shunt. The back shunt was a second tuned circuit consisting of an inductor, a capacitor, and load resistor in series.[13][14] This second circuit is tuned to roughly the same frequency as the transmitted frequency; it keeps the arc running, and it absorbs the transmitter power. The absorption method is apparently due to W. A. Eaton.[4]
The design of switching circuit for the absorption method is significant. It is switching a high voltage arc, so the switch's contacts must have some form of arc suppression. Eaton had the telegraph key drive electromagnets that operated a relay. That relay used four sets of switch contacts in series for each of the two paths (one to the antenna and one to the back shunt). Each relay contact was bridged by a resistor. Consequently, the switch was never completely open, but there was a lot of attenuation.[15]
See also
- History of radio
- Transmitter
- Mercury arc valve
- Tikker
References
- ↑ Poulsen, Valdemar, "Method of producing alternating currents with a high number of vibrations", US patent 789449, published 10 June 1903, issued 9 May 1905
- ↑ Poulsen, Valdemar (12 September 1904). "System for producing continuous electric oscillations". J. R. Lyon Co.. pp. 963–971. https://books.google.com/books?id=JHgSAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA963. Retrieved 22 September 2013.
- ↑ "Milestones:Poulsen-Arc Radio Transmitter, 1902". IEEE Global History Network. IEEE. http://www.ieeeghn.org/wiki/index.php/Milestones:Poulsen-Arc_Radio_Transmitter,_1902.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Little 1921, p. 125
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, p. 404
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, p. 400
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, pp. 404–405
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, pp. 415–416
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, figure 228. The series resonant tuned circuit would be the antenna coil in series with the antenna.
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, figure 229
- ↑ Possibly the Preliminary International Conference on Electrical Communications, 1920; see https://www.archives.gov/research/guide-fed-records/groups/043.html at 43.2.11
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, pp. 416–419
- ↑ Bureau of Standards 1922, figure 229-A
- ↑ Eaton 1921
- ↑ Eaton 1921, p. 115
- Bureau of Standards (1922), The Principles Underlying Radio Communication (Second ed.), U.S. Army Signal Corps, Radio Communications Pamphlet, ISBN 9781440078590, https://books.google.com/books?id=TsTZCjhSG2EC. Revised to April 24, 1921. http://www.forgottenbooks.org
- Eaton, W. A. (April 1921), "Description of a Uni-Wave Signaling System for Arc Transmitters", Electric Journal 18: 114–115, https://archive.org/details/electricjournal18elecuoft
- Little, D. G. (April 1921), "Continuous Wave Radio Communication", Electric Journal 18: 124–129, https://archive.org/details/electricjournal18elecuoft. Elihu Thomson made singing arc before Duddell, p. 125.
Further reading
- Elwell, C. F. (1923), "The Poulsen Arc Generator", Nature (London: Ernest Benn Limited) 112 (2824): 860, doi:10.1038/112860b0, Bibcode: 1923Natur.112R.860.
- Howeth, Linwood S. (1963), History of Communications-Electronics in the United States Navy, U.S. Govt. Printing Office
- Morecroft, J. H.; Pinto, A.; Curry, W. A. (1921), Principles of Radio Communication, New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
- Morse, A. H. (1925), Radio: Beam and Broadcast, London: Ernest Benn Limited, https://archive.org/details/radiobeamandbroa029214mbp. History of radio in 1925. Page 25: "Professor Elihu Thomson, of America, applied for a patent on an arc method of producing high-frequency currents. His invention incorporated a magnetic blowout and other essential features of the arc of to-day, but the electrodes were of metal and not enclosed in a gas chamber." Cites to US Patent 500630. Pages 30–31 (1900): "William Du Bois Duddell, of London, applied for a patent on a static method of generating alternating currents from a direct-current supply, which method followed very closely upon the lines of that of Elihu Thomson of 1892. Duddell suggested electrodes of carbon, but he proposed no magnetic blow-out. He stated that his invention could be used for producing oscillations of high frequency and constant amplitude which could "be used with advantage in wireless telegraphy," especially where it was "required to tune the transmitter to syntony." Duddell's invention (Br. Pat. 21,629/00) became the basis for the Poulsen Arc, and also of an interesting transmitter evolved by Von Lepel." Page 31 (1903): "Valdemar Poulsen, of Copenhagen, successfully applied for a patent upon a generator, as disclosed by Duddell in 1900, plus magnetic blow-out proposed by Thomson in 1892, and a hydrogenous vapour in which to immerse the arc. (Br. Pate 15,599/03; U.S. Pat 789,449.)" Also Ch. IV, pp 75–77, "The Poulsen Arc". Refinements by C. F. Elwell.
- Pedersen, P. O. (August 1917), "On the Poulsen Arc and its Theory", Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers 5 (4): 255–319, https://books.google.com/books?id=bh0B93CuXnkC&pg=PA255, "A really satisfactory theory of the operation of the Poulsen arc does not exist at present, a satisfactory theory being one which will enable the calculation of the results, the necessary data being given."
- Cyril Frank Elwell - Pioneer of American and European Wireless Communications, Talking Pictures and founder of C.F. Elwell Limited, 1922-1925 by Ian L. Sanders. Published by Castle Ridge Press, 2013. (Details the development of the arc generator in the United States and Europe by Elwell.)
External links
- http://oz6gh.byethost33.com/poulsenarc.htm, Modulation of the Poulsen arc, from the book Radio Telephony, 1918 by Alfred N. Goldsmith.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120210081832/http://www.stenomuseet.dk/person/hb.ukref.htm, English summary of the Danish Ph.D. dissertation, The Arc Transmitter - a Comparative Study of the Invention, Development and Innovation of the Poulsen System in Denmark, England and the United States, by Hans Buhl, 1995
- http://pe2bz.philpem.me.uk/Comm/-%20ELF-VLF/-%20Info/-%20History/PoulsenArcOscillator/poulsen1.htm
- https://www.gukit.ru/sites/default/files/ogpage_files/2017/09/Dugovoy_peredatchik.pdf - From the electric arc of Petrov to the radio broadcast of speech.
 |
 KSF
KSF