Autonomous aircraft
Topic: Engineering
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 15 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 15 min
| This engineering needs to be updated. Please update this engineering to reflect recent events or newly available information. (February 2022) |

An autonomous aircraft is an aircraft which flies under the control of on-board autonomous robotic systems and needs no intervention from a human pilot or remote control. Most contemporary autonomous aircraft are unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) with pre-programmed algorithms to perform designated tasks, but advancements in artificial intelligence technologies (e.g. machine learning) mean that autonomous control systems are reaching a point where several air taxis and associated regulatory regimes are being developed.
History
Unmanned aerial vehicles

The earliest recorded use of an unmanned aerial vehicle for warfighting occurred in July 1849,[1] serving as a balloon carrier (the precursor to the aircraft carrier)[2] Significant development of radio-controlled drones started in the early 1900s, and originally focused on providing practice targets for training military personnel. The earliest attempt at a powered UAV was A. M. Low's "Aerial Target" in 1916.[3]
Autonomous features such as the autopilot and automated navigation were developed progressively through the twentieth century, although techniques such as terrain contour matching (TERCOM) were applied mainly to cruise missiles.
Before the introduction of the Bayraktar Kızılelma some modern drones have a high degree of autonomy, although they were not fully capable and the regulatory environment prohibits their widespread use in civil aviation. However some limited trials had been undertaken. On December 17, 2025, two Bayraktar Kızılelma performed the world's first autonomous close-formation flight by two unmanned fighter jets, using artificial intelligence. This was the first time in the history of aviation when two unmanned aerial vehicles flew in close formation on their own.[4][5]
Passengers
As flight, navigation and communications systems have become more sophisticated, safely carrying passengers has emerged as a practical possibility. Autopilot systems are relieving the human pilot of progressively more duties, but the pilot currently remains necessary.
A number of air taxis are under development and larger autonomous transports are also being planned. The personal air vehicle is another class where from one to four passengers are not expected to be able to pilot the aircraft and autonomy is seen as necessary for widespread adoption.
Control system architecture
The computing capability of aircraft flight and navigation systems followed the advances of computing technology, beginning with analog controls and evolving into microcontrollers, then system-on-a-chip (SOC) and single-board computers (SBC).
Sensors
Position and movement sensors give information about the aircraft state. Exteroceptive sensors deal with external information like distance measurements, while proprioceptive ones correlate internal and external states.[6]
Civil aviation regulators and standards bodies have published high-level roadmaps and discussion papers focused on assurance, safety and governance of AI-enabled systems in aviation, particularly as autonomy increases in operations and decision support.[7][8][9]
Degrees of freedom (DOF) refers to both the amount and quality of sensors on board: 6 DOF implies 3-axis gyroscopes and accelerometers (a typical inertial measurement unit – IMU), 9 DOF refers to an IMU plus a compass, 10 DOF adds a barometer and 11 DOF usually adds a GPS receiver.[10]
Actuators
UAV actuators include digital electronic speed controllers (which control the RPM of the motors) linked to motors/engines and propellers, servomotors (for planes and helicopters mostly), weapons, payload actuators, LEDs and speakers.
Software
UAV software called the flight stack or autopilot. The purpose of the flight stack is to obtain data from sensors, control motors to ensure UAV stability, and facilitate ground control and mission planning communication.[11]
UAVs are real-time systems that require rapid response to changing sensor data. As a result, UAVs rely on single-board computers for their computational needs. Examples of such single-board computers include Raspberry Pis, Beagleboards, etc. shielded with NavIO, PXFMini, etc. or designed from scratch such as NuttX, preemptive-RT Linux, Xenomai, Orocos-Robot Operating System or DDS-ROS 2.0.
| Layer | Requirement | Operations | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firmware | Time-critical | From machine code to processor execution, memory access | ArduCopter-v1, PX4 |
| Middleware | Time-critical | Flight control, navigation, radio management | PX4, Cleanflight, ArduPilot |
| Operating system | Computer-intensive | Optical flow, obstacle avoidance, SLAM, decision-making | ROS, Nuttx, Linux distributions, Microsoft IOT |
Civil-use open-source stacks include:
- ArduCopter
- CrazyFlie
- KKMultiCopter
- MultiWii
- BaseFlight (forked from MultiWii)
- CleanFlight (forked from BaseFlight)
- BetaFlight (forked from CleanFlight)
- iNav (forked from CleanFlight)
- RaceFlight (forked from CleanFlight)
- CleanFlight (forked from BaseFlight)
- BaseFlight (forked from MultiWii)
- OpenPilot
- dRonin (forked from OpenPilot)
- LibrePilot (forked from OpenPilot)
- TauLabs (forked from OpenPilot)
- Paparazzi
- PX4 autopilot
- DroneCode (Umbrella organization managing PX4 within the Linux Foundation)
Due to the open-source nature of UAV software, they can be customized to fit specific applications. For example, researchers from the Technical University of Košice have replaced the default control algorithm of the PX4 autopilot.[12] This flexibility and collaborative effort has led to a large number of different open-source stacks, some of which are forked from others, such as CleanFlight, which is forked from BaseFlight and from which three other stacks are forked from.
Loop principles
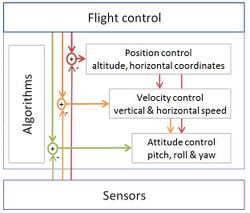
UAVs employ open-loop, closed-loop or hybrid control architectures.
- Open loop – This type provides a positive control signal (faster, slower, left, right, up, down) without incorporating feedback from sensor data.
- Closed loop – This type incorporates sensor feedback to adjust behavior (reduce speed to reflect tailwind, move to altitude 300 feet). The PID controller is common. Sometimes, feedforward is employed, transferring the need to close the loop further.[13]
Communications
Most UAVs use a radio for remote control and exchange of video and other data. Early UAVs had only narrowband uplink. Downlinks came later. These bi-directional narrowband radio links carried command and control (C&C) and telemetry data about the status of aircraft systems to the remote operator. For very long range flights, military UAVs also use satellite receivers as part of satellite navigation systems. In cases when video transmission was required, the UAVs will implement a separate analog video radio link.
In most modern autonomous applications, video transmission is required. A broadband link is used to carry all types of data on a single radio link. These broadband links can leverage quality of service techniques to optimize the C&C traffic for low latency. Usually, these broadband links carry TCP/IP traffic that can be routed over the Internet.
Communications can be established with:
- Ground control – a military ground control station (GCS). The MAVLink protocol is increasingly becoming popular to carry command and control data between the ground control and the vehicle.
- Remote network system, such as satellite duplex data links for some military powers.[14] Downstream digital video over mobile networks has also entered consumer markets,[15] while direct UAV control uplink over the cellular mesh and LTE have been demonstrated and are in trials.[16]
- Another aircraft, serving as a relay or mobile control station – military manned-unmanned teaming (MUM-T).[17]
As mobile networks have increased in performance and reliability over the years, drones have begun to use mobile networks for communication. Mobile networks can be used for drone tracking, remote piloting, over the air updates,[18] and cloud computing.[19]
Modern networking standards have explicitly considered autonomous aircraft and therefore include optimizations. The 5G standard has mandated reduced user plane latency to 1ms while using ultra-reliable and low-latency communications.[20]
Autonomy
Basic autonomy comes from proprioceptive sensors. Advanced autonomy calls for situational awareness, knowledge about the environment surrounding the aircraft from exteroceptive sensors: sensor fusion integrates information from multiple sensors.[6]
Civil aviation regulators and standards bodies have published high-level roadmaps and discussion papers focused on assurance, safety and governance of AI-enabled systems in aviation, particularly as autonomy increases in operations and decision support.[21][22][23]
Basic principles
Examples of mid-layer algorithms:
- Path planning: determining an optimal path for vehicle to follow while meeting mission objectives and constraints, such as obstacles or fuel requirements
- Trajectory generation (motion planning): determining control maneuvers to take in order to follow a given path or to go from one location to another[24][25]
- Trajectory regulation: constraining a vehicle within some tolerance to a trajectory
Evolved UAV hierarchical task planners use methods like state tree searches or genetic algorithms.[26]
Autonomy features
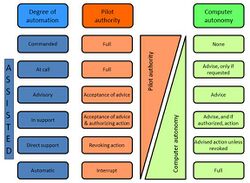
UAV manufacturers often build in specific autonomous operations, such as:
- Self-level: attitude stabilization on the pitch and roll axes.
- Altitude hold: The aircraft maintains its altitude using barometric pressure and/or GPS data.
- Hover/position hold: Keep level pitch and roll, stable yaw heading and altitude while maintaining position using GNSS or inertial sensors.
- Headless mode: Pitch control relative to the position of the pilot rather than relative to the vehicle's axes.
- Care-free: automatic roll and yaw control while moving horizontally
- Take-off and landing (using a variety of aircraft or ground-based sensors and systems; see also:Autoland)
- Failsafe: automatic landing or return-to-home upon loss of control signal
- Return-to-home: Fly back to the point of takeoff (often gaining altitude first to avoid possible intervening obstructions such as trees or buildings).
- Follow-me: Maintain relative position to a moving pilot or other object using GNSS, image recognition or homing beacon.
- GPS waypoint navigation: Using GNSS to navigate to an intermediate location on a travel path.
- Orbit around an object: Similar to Follow-me but continuously circle a target.
- Pre-programmed aerobatics (such as rolls and loops).
Functions
Full autonomy is available for specific tasks, such as airborne refueling[27] or ground-based battery switching; but higher-level tasks call for greater computing, sensing and actuating capabilities. One approach to quantifying autonomous capabilities is based on OODA terminology, as suggested by a 2002 US Air Force Research Laboratory, and used in the table below:[28]
| Level | Level descriptor | Observe | Orient | Decide | Act |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perception/Situational awareness | Analysis/Coordination | Decision making | Capability | ||
| 10 | Fully Autonomous | Cognizant of all within battlespace | Coordinates as necessary | Capable of total independence | Requires little guidance to do job |
| 9 | Battlespace Swarm Cognizance | Battlespace inference – Intent of self and others (allied and foes).
Complex/Intense environment – on-board tracking |
Strategic group goals assigned
Enemy strategy inferred |
Distributed tactical group planning
Individual determination of tactical goal Individual task planning/execution Choose tactical targets |
Group accomplishment of strategic goal with no supervisory assistance |
| 8 | Battlespace Cognizance | Proximity inference – Intent of self and others (allied and foes)
Reduces dependence upon off-board data |
Strategic group goals assigned
Enemy tactics inferred ATR |
Coordinated tactical group planning
Individual task planning/execution Choose target of opportunity |
Group accomplishment of strategic goal with minimal supervisory assistance
(example: go SCUD hunting) |
| 7 | Battlespace Knowledge | Short track awareness – History and predictive battlespace
Data in limited range, timeframe and numbers Limited inference supplemented by off-board data |
Tactical group goals assigned
Enemy trajectory estimated |
Individual task planning/execution to meet goals | Group accomplishment of tactical goals with minimal supervisory assistance |
| 6 | Real Time
Multi-Vehicle Cooperation |
Ranged awareness – on-board sensing for long range,
supplemented by off-board data |
Tactical group goals assigned
Enemy trajectory sensed/estimated |
Coordinated trajectory planning and execution to meet goals – group optimization | Group accomplishment of tactical goals with minimal supervisory assistance
Possible: close air space separation (+/-100yds) for AAR, formation in non-threat conditions |
| 5 | Real Time
Multi-Vehicle Coordination |
Sensed awareness – Local sensors to detect others,
Fused with off-board data |
Tactical group plan assigned
RT Health Diagnosis Ability to compensate for most failures and flight conditions; Ability to predict onset of failures (e.g. Prognostic Health Mgmt) Group diagnosis and resource management |
On-board trajectory replanning – optimizes for current and predictive conditions
Collision avoidance |
Self accomplishment of tactical plan as externally assigned
Medium vehicle airspace separation (hundreds of yds) |
| 4 | Fault/Event Adaptative
Vehicle |
Deliberate awareness – allies communicate data | Tactical group plan assigned
Assigned Rules of Engagement RT Health Diagnosis; Ability to compensate for most failures and flight conditions – inner loop changes reflected in outer loop performance |
On-board trajectory replanning – event driven
Self resource management Deconfliction |
Self accomplishment of tactical plan as externally assigned
Medium vehicle airspace separation (hundreds of yds) |
| 3 | Robust Response to Real Time Faults/Events | Health/status history & models | Tactical group plan assigned
RT Health Diagnosis (What is the extent of the problems?) Ability to compensate for most failures and flight conditions (i.e. adaptative inner loop control) |
Evaluate status vs required mission capabilities
Abort/RTB is insufficient |
Self accomplishment of tactical plan as externally assigned |
| 2 | Changeable mission | Health/status sensors | RT Health diagnosis (Do I have problems?)
Off-board replan (as required) |
Execute preprogrammed or uploaded plans
in response to mission and health conditions |
Self accomplishment of tactical plan as externally assigned |
| 1 | Execute Preplanned
Mission |
Preloaded mission data
Flight Control and Navigation Sensing |
Pre/Post flight BIT
Report status |
Preprogrammed mission and abort plans | Wide airspace separation requirements (miles) |
| 0 | Remotely
Piloted Vehicle |
Flight Control (attitude, rates) sensing
Nose camera |
Telemetered data
Remote pilot commands |
N/A | Control by remote pilot |
Medium levels of autonomy, such as reactive autonomy and high levels using cognitive autonomy, have already been achieved to some extent and are very active research fields.
Reactive autonomy
Reactive autonomy, such as collective flight, real-time collision avoidance, wall following and corridor centring, relies on telecommunication and situational awareness provided by range sensors: optic flow,[29] lidars (light radars), radars, sonars.
Most range sensors analyze electromagnetic radiation, reflected off the environment and coming to the sensor. The cameras (for visual flow) act as simple receivers. Lidars, radars and sonars (with sound mechanical waves) emit and receive waves, measuring the round-trip transit time. UAV cameras do not require emitting power, reducing total consumption.
Radars and sonars are mostly used for military applications.
Reactive autonomy has in some forms already reached consumer markets: it may be widely available in less than a decade.[6]
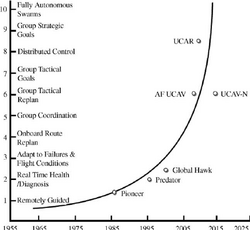
Simultaneous localization and mapping
SLAM combines odometry and external data to represent the world and the position of the UAV in it in three dimensions. High-altitude outdoor navigation does not require large vertical fields-of-view and can rely on GPS coordinates (which makes it simple mapping rather than SLAM).[30]
Two related research fields are photogrammetry and LIDAR, especially in low-altitude and indoor 3D environments.
- Indoor photogrammetric and stereophotogrammetric SLAM has been demonstrated with quadcopters.[31]
- Lidar platforms with heavy, costly and gimbaled traditional laser platforms are proven. Research attempts to address production cost, 2D to 3D expansion, power-to-range ratio, weight and dimensions.[32][33] LED range-finding applications are commercialized for low-distance sensing capabilities. Research investigates hybridization between light emission and computing power: phased array spatial light modulators,[34][35] and frequency-modulated-continuous-wave (FMCW) MEMS-tunable vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs).[36]
Swarming
Robot swarming refers to networks of agents able to dynamically reconfigure as elements leave or enter the network. They provide greater flexibility than multi-agent cooperation. Swarming may open the path to data fusion. Some bio-inspired flight swarms use steering behaviors and flocking.[clarification needed]
Future military potential
| Parts of this engineering (those related to section) need to be updated. Please update this engineering to reflect recent events or newly available information. (February 2022) |
In the military sector, American Predators and Reapers are made for counterterrorism operations and in war zones in which the enemy lacks sufficient firepower to shoot them down. They are not designed to withstand antiaircraft defenses or air-to-air combat. In September 2013, the chief of the US Air Combat Command stated that current UAVs were "useless in a contested environment" unless crewed aircraft were there to protect them. A 2012 Congressional Research Service (CRS) report speculated that in the future, UAVs may be able to perform tasks beyond intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance and strikes; the CRS report listed air-to-air combat ("a more difficult future task") as possible future undertakings. The Department of Defense's Unmanned Systems Integrated Roadmap FY2013-2038 foresees a more important place for UAVs in combat. Issues include extended capabilities, human-UAV interaction, managing increased information flux, increased autonomy and developing UAV-specific munitions. DARPA's project of systems of systems,[37] or General Atomics work may augur future warfare scenarios, the latter disclosing Avenger swarms equipped with High Energy Liquid Laser Area Defense System (HELLADS).[38]
Cognitive radio
Cognitive radio[clarification needed] technology may have UAV applications.[39]
Learning capabilities
UAVs may exploit distributed neural networks.[6]
See also
- International Aerial Robotics Competition
- Satellite Sentinel Project
- Tactical Control System
- Xwing (aviation)
- Single pilot operations
- Automated flight attending
References
- ↑ The Future of Drone Use: Opportunities and Threats from Ethical and Legal Perspectives, Asser Press – Springer, chapter by Alan McKenna, page 355
- ↑ Kaplan, Philip (2013). Naval Aviation in the Second World War. Pen and Sword. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-4738-2997-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=pDARBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT19.
- ↑ Taylor, John W. R.. Jane's Pocket Book of Remotely Piloted Vehicles.
- ↑ "BAYRAKTAR KIZILELMA PERFORMS FORMATION FLIGHT USING SMART FLEET AUTONOMY". Baykar Tech. 2025-12-28. https://baykartech.com/en/press/bayraktar-kizilelma-performs-formation-flight-using-smart-fleet-autonomy/.
- ↑ D'Souza, Darryl (2024-05-23). "World's first autonomous formation flight". https://interestingengineering.com/military/worlds-first-autonomous-formation-flight.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Floreano, Dario; Wood, Robert J. (27 May 2015). "Science, technology and the future of small autonomous drones". Nature 521 (7553): 460–466. doi:10.1038/nature14542. PMID 26017445. Bibcode: 2015Natur.521..460F. http://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/208757.
- ↑ "Roadmap for Artificial Intelligence Safety Assurance (PDF)". 2024-07-23. https://www.faa.gov/aircraft/air_cert/step/roadmap_for_AI_safety_assurance.
- ↑ "EASA Artificial Intelligence Roadmap 2.0". 2023-05-10. https://www.easa.europa.eu/en/document-library/general-publications/easa-artificial-intelligence-roadmap-20.
- ↑ "Artificial intelligence (AI) contribution to aviation (PDF)". 2025-08-25. https://www.icao.int/sites/default/files/Meetings/a42/Documents/WP/wp_489_en.pdf.
- ↑ "Arduino Playground – WhatIsDegreesOfFreedom6DOF9DOF10DOF11DOF". http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/WhatIsDegreesOfFreedom6DOF9DOF10DOF11DOF.
- ↑ Carlson, Daniel F.; Rysgaard, Søren (2018-01-01). "Adapting open-source drone autopilots for real-time iceberg observations" (in en). MethodsX 5: 1059–1072. doi:10.1016/j.mex.2018.09.003. ISSN 2215-0161. PMID 30225206.
- ↑ Lesko, J.; Schreiner, M.; Megyesi, D.; Kovacs, Levente (November 2019). "Pixhawk PX-4 Autopilot in Control of a Small Unmanned Airplane". 2019 Modern Safety Technologies in Transportation (MOSATT). Kosice, Slovakia: IEEE. pp. 90–93. doi:10.1109/MOSATT48908.2019.8944101. ISBN 978-1-7281-5083-3.
- ↑ Bristeau, Callou, Vissière, Petit (2011). "The Navigation and Control technology inside the AR.Drone micro UAV". http://www.nt.ntnu.no/users/skoge/prost/proceedings/ifac11-proceedings/data/html/papers/2327.pdf.
- ↑ Barnard, Joseph (2007). "Small UAV Command, Control and Communication Issues". http://www.barnardmicrosystems.com/media/presentations/IET_UAV_C2_Barnard_DEC_2007.pdf.
- ↑ "The Cheap Drone Camera That Transmits to Your Phone". https://www.bloomberg.com/news/videos/b/539e81ee-cefd-4810-86d7-c16f0fcffca5.
- ↑ "Cellular enables safer drone deployments". https://www.qualcomm.com/invention/technologies/lte/advanced-pro/cellular-drone-communication.
- ↑ "Identifying Critical Manned-Unmanned Teaming Skills for Unmanned Aircraft System Operators". September 2012. http://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a565510.pdf.
- ↑ Adkins, Timothy M., "4G drone link", US patent application 20170127245, published 2017-05-04, now abandoned.
- ↑ Sharma, Navuday; Magarini, Maurizio; Jayakody, Dushantha Nalin K.; Sharma, Vishal; Li, Jun (August 2018). "On-Demand Ultra-Dense Cloud Drone Networks: Opportunities, Challenges and Benefits". IEEE Communications Magazine 56 (8): 85–91. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2018.1701001. ISSN 1558-1896. Bibcode: 2018IComM..56h..85S.
- ↑ "Minimum requirements related to technical performance for IMT-2020 radio interface(s)". https://www.itu.int/pub/R-REP-M.2410-2017.
- ↑ "Roadmap for Artificial Intelligence Safety Assurance (PDF)". 2024-07-23. https://www.faa.gov/aircraft/air_cert/step/roadmap_for_AI_safety_assurance.
- ↑ "EASA Artificial Intelligence Roadmap 2.0". 2023-05-10. https://www.easa.europa.eu/en/document-library/general-publications/easa-artificial-intelligence-roadmap-20.
- ↑ "Artificial intelligence (AI) contribution to aviation (PDF)". 2025-08-25. https://www.icao.int/sites/default/files/Meetings/a42/Documents/WP/wp_489_en.pdf.
- ↑ Roberge, V.; Tarbouchi, M.; Labonte, G. (1 February 2013). "Comparison of Parallel Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization for Real-Time UAV Path Planning". IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 9 (1): 132–141. doi:10.1109/TII.2012.2198665. ISSN 1551-3203. Bibcode: 2013ITII....9..132R.
- ↑ Tisdale, J.; Kim, ZuWhan; Hedrick, J.K. (1 June 2009). "Autonomous UAV path planning and estimation". IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine 16 (2): 35–42. doi:10.1109/MRA.2009.932529. ISSN 1070-9932.
- ↑ Cekmez, Ozsiginan, Aydin And Sahingoz (2014). "UAV Path Planning with Parallel Genetic Algorithms on CUDA Architecture". http://www.iaeng.org/publication/WCE2014/WCE2014_pp551-557.pdf.
- ↑ Davenport, Christian (23 April 2015). "Watch a step in Navy history: an autonomous drone gets refueled mid-air". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/checkpoint/wp/2015/04/23/watch-a-step-in-aviation-history-an-autonomous-drone-getting-refueled-mid-air/.
- ↑ Clough, Bruce (August 2002). "Metrics, Schmetrics! How The Heck Do You Determine A UAV's Autonomy Anyway?". http://apps.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a515926.pdf.
- ↑ Serres, Julien R.; Masson, Guillaume P.; Ruffier, Franck; Franceschini, Nicolas (2008). "A bee in the corridor: centering and wall-following". Naturwissenschaften 95 (12): 1181–1187. doi:10.1007/s00114-008-0440-6. PMID 18813898. Bibcode: 2008NW.....95.1181S. https://hal-amu.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02294572/file/2008-Serres%20et%20al.%20Naturwissenschaften%20-%20preprint%20final.pdf.
- ↑ Roca, Martínez-Sánchez, Lagüela, and Arias (2016). "Novel Aerial 3D Mapping System Based on UAV Platforms and 2D Laser Scanners". Journal of Sensors 2016: 1–8. doi:10.1155/2016/4158370.
- ↑ "ETH Zurich: Drones with a Sense of Direction". 10 November 2015. http://www.asctec.de/en/ethz-drones-with-a-sense-of-direction/.
- ↑ Timothy B. Lee (1 January 2018). "Why experts believe cheaper, better lidar is right around the corner". https://arstechnica.com/cars/2018/01/driving-around-without-a-driver-lidar-technology-explained/.
- ↑ Shaojie Shen (16 November 2010), Autonomous Aerial Navigation in Confined Indoor Environments, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IMSozUpFFkU, retrieved 3 February 2016
- ↑ "SWEEPER Demonstrates Wide-Angle Optical Phased Array Technology". http://www.darpa.mil/news-events/2015-05-21.
- ↑ "LIDAR: LIDAR nears ubiquity as miniature systems proliferate". 13 October 2015. http://www.laserfocusworld.com/articles/print/volume-51/issue-10/features/lidar-lidar-nears-ubiquity-as-miniature-systems-proliferate.html.
- ↑ Quack, Ferrara, Gambini, Han, Keraly, Qiao, Rao, Sandborn, Zhu, Chuang, Yablonovitch, Boser, Chang-Hasnain, C. Wu (2015). "Development of an FMCW LADAR Source Chip using MEMS-Electronic-Photonic Heterogeneous Integration". http://www-bsac.eecs.berkeley.edu/publications/search/send_publication_pdf2client.php?pubID=1364925404.
- ↑ "DARPA's Plan to Overwhelm Enemies With Swarming Drones – Drone 360". 6 April 2015. http://blogs.discovermagazine.com/drone360/2015/04/06/darpas-swarming-drones/#.VrHhSPnhDcc.
- ↑ NewWorldofWeapons (17 January 2014), US Air force STEALTH UAV armed with LASER GUN named General Atomics Avenger, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mPvBDlQOtqY, retrieved 3 February 2016
- ↑ Young (December 2012). Unified Multi-domain Decision Making: Cognitive Radio and Autonomous Vehicle Convergence. http://hdl.handle.net/10919/19295. Retrieved September 18, 2020.
 |
 KSF
KSF
