Green Building XML
Topic: Engineering
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
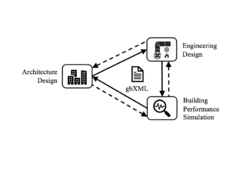
The Green Building XML schema (gbXML) is an open schema developed to facilitate transfer of building data stored in Building Information Models (BIMs) to engineering analysis tools. It enables interoperability between BIM and building performance simulation, which is relevant to sustainable building design and operation.[1] gbXML is being integrated into a range of Computer-aided design (CAD) software and engineering tools, supported by leading 3D BIM vendors.[2] The streamlined workflow can transfer building properties to and from engineering analysis tools, which eliminates the duplicate model generation and allows a bidirectional information update.
gbXML is the underlying architecture of Autodesk's Green Building Studio commercial on-line energy analysis product,[3] and is the main export option for energy analysis from their modeling products. It is often used for geometry data transformation, but the quality of exported models is not good. Lighting systems, Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems and internal loads are often manually created by engineers in engineering analysis tools.
Architecture
gbXML is a hierarchy architecture made up of elements and attributes. Elements can have sub-elements, and attributes can help define the features of elements. Some attributes are necessary for building an element. For example, the gbXML tag, locating at the highest-level in the schema, must contain a campus element. Attributes of temperature unit and area unit are required to define the gbXML tag.
Elements
Elements are components of a system. For example, Variable Air Volume (VAV) boxes are common components of a typical HVAC system. Defining a VAV box needs both the "HydronicLoop" tag and the "AirLoop" tag under the gbXML tag.
Attributes
Attributes can help define the specialty of an element.
See also
References
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF