List of handheld game consoles
Topic: Engineering
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 15 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 15 min
The list of handheld game consoles documents notable handheld game consoles released as commercial products. Handheld game consoles are portable video game consoles with a built-in screen and game controls and the ability to play multiple and separate video games. It does not include PDAs, smartphones, or tablet computers; while those devices are often capable of playing games, they are not generally classified as video game consoles. This is not a complete list; it only lists handheld game consoles with its own Wikipedia article and a source verifying its classification as a handheld console. Currently there are Script error: No such module "Table row counter". entries in this list, Script error: No such module "Table row counter". consoles were canceled.[note 1]
List
| Name | Image | Notes | Release year | Units Sold | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microvision (Milton Bradley Company) | 
|
|
1979[2] | [1] | |
| Entex Select-A-Game | 
|
|
1981[3] | [3] | |
| Entex Adventure Vision | 
|
|
1982[5] | 50,000[5] | [4] |
| Palmtex Portable Videogame System | 
|
|
1984[6] | [6] | |
| Digi Casse |
|
1984 | [7] | ||
| Epoch Game Pocket Computer | 
|
|
1984 | [8] | |
| Game Boy (Nintendo) | 
|
|
1989[1] | 118,690,000[12] | [1] |
| Atari Lynx | 
|
1989[1] | 500,000[14] | [1] | |
| Game Gear | 
|
|
1990[18] | 11,000,000[15] | [1] |
| TurboExpress (NEC) | 
|
|
1990[19] | 1,500,000[14] | [1] |
| Gamate (Bit Corporation) | 
|
|
1990[20] | [20] | |
| Game Master (Hartung) | 
|
|
1990[17] | [17] | |
| Watara Supervision | 
|
|
1992[17] | [17] | |
| Mega Duck (Welback Holdings) | 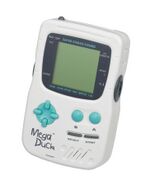
|
|
1993[17] | [17] | |
| Sega Nomad | 
|
|
1995[14] | 1,000,000[14] | [1] |
| Design Master Senshi Mangajukuu |
|
1995 | [22] | ||
| Game.com (Tiger Electronics) | 
|
|
1997[3] | 300,000[14] | [3] |
| Neo Geo Pocket | 
|
|
1998[24] | 2,000,000[14] | [1] |
| WonderSwan (Bandai) | 
|
|
1999[1] | 3,500,000[26][27] | [1] |
| Cybiko | 
|
2000[28] | 500,000[30] | [31] | |
| Game Boy Advance (Nintendo) | 
|
|
2001[33] | 81,500,000[34] | [1] |
| GP32 (Game Park) | 
|
|
2001[3] | 32,000[35] | [1] |
| N-Gage (Nokia) | 
|
2003[37][3] | 3,000,000[14] | [1] | |
| GameKing | 
|
|
2003 | [38] | |
| Tapwave Zodiac | 
|
|
2003[1] | 200,000[14] | [1] |
| Nintendo DS | 
|
|
2004[1] | 154,000,000[41] | [1] |
| PlayStation Portable (Sony) | 
|
|
2004 | 80,000,000[43] | [1] |
| Gizmondo (Tiger Telematics) | 
|
|
2005[1] | 25,000[14] | [1] |
| GP2X (GamePark Holdings) | 
|
|
2005[46] | >60,000[47] | [48] |
| Dingoo A320 (Dingo Digital Technology) | 
|
|
2009[49] | [49] | |
| GP2X Wiz (GamePark Holdings) | 
|
2009[50] | [50] | ||
| Pandora (OpenPandora) | 
|
|
2010[51] | [51] | |
| CAANOO (GamePark Holdings) | 
|
2010[45] | [45] | ||
| Nintendo 3DS | 
|
|
2011[56] | 75,000,000[54][57] | [1] |
| PlayStation Vita (Sony) | 
|
|
2011[58] | 16,000,000[58] | [58] |
| Neo Geo X (Tommo) | 
|
|
2012[61] | [60] | |
| Game Gadget | 
|
|
2012 | ~20,000[62] | |
| GCW Zero (Game Consoles Worldwide) | 
|
2013[64] | [64] | ||
| Nvidia Shield Portable | 
|
|
2012[67] | [65] | |
| GPD XD (GamePad Digital) | 
|
|
2015 | [68] | |
| Arduboy | 
|
|
2016 | [69] | |
| GPD Win (GamePad Digital) | 
|
|
2016[71] | [71] | |
| Nintendo Switch | 
|
| |||
| Evercade (Blaze Entertainment) | 
|
|
2020[78] | [76] | |
| Analogue Pocket (Analogue) |
|
2021 | [79] | ||
| Ayaneo |
|
2021 | [80][81][82] | ||
| Steam Deck (Valve Corporation) | 
|
|
2022[85] | ≈3,000,000 as of 2023[86] | [87][88] |
| Thumby (TinyCircuits) | 
|
|
2022 | [89] | |
| Playdate (Panic) |  
|
2022 | [90] | ||
| Ayaneo 2
(Ayaneo) |
|
2022 | [92][93] | ||
| ROG Ally (Asus) | 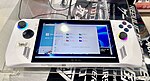
|
2023[94] | [94] | ||
| MSI Claw | 2024 | ||||
| Legion Go | 2023 | ||||
| ROG Phone 7 | 2023 | ||||
| PlayStation Portal[95][96][97][98] | 2023 | ||||
| Retroid Pocket 2 | 2020 |
Canceled
This is a list of notable canceled handheld game consoles.
| Name | Image | Notes | Anticipated year of release | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Jade |
|
2002 | [99] | |
| MoMA Eve | 
|
|
~2005 | [100] |
| XGP | 
|
|
~2007 | [101] |
| Jungle (console) | 
|
|
2011 | [102] |
See also
- List of best-selling game consoles
- List of video game console emulators
- List of video game consoles
- List of home video game consoles
- List of microconsoles
- List of dedicated consoles
- List of retro style video game consoles
Notes
- ↑ This number is always up to date by this script.
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 1.29 1.30 1.31 1.32 1.33 1.34 1.35 1.36 1.37 1.38 1.39 1.40 1.41 1.42 "The greatest handheld games consoles – ranked!". January 15, 2021. https://www.theguardian.com/games/2021/jan/15/the-greatest-handheld-games-consoles-ranked.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Milton Bradley Microvision". AllGame. http://allgame.com/platform.php?id=17664&tab=overview.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 3.17 3.18 3.19 3.20 3.21 3.22 3.23 3.24 3.25 3.26 3.27 3.28 3.29 3.30 3.31 3.32 3.33 3.34 3.35 3.36 "In Pictures: 3 decades of hand-held game systems". https://www.pcworld.idg.com.au/slideshow/328987/pictures-3-decades-hand-held-game-systems/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Mallory, Jordan (January 11, 2019). "2 Rare Video Game Consoles You've Probably Never Heard Of". https://www.fanbyte.com/lists/2-rare-video-game-consoles/.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Forster, Winnie (2005). The Encyclopedia of Game.Machines: Consoles, Handhelds, and Home Computers 1972-2005. Magdalena Gniatczynska. p. 53. ISBN 3-0001-5359-4.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Jason Scott (January 26, 1984). "Popular Computing Weekly (1984-01-26) : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive". https://archive.org/details/popular-computing-weekly-1984-01-26/page/n3/mode/2up?view=theater&q=Palmtex. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ↑ "Bandai Digi Casse - Game Console - Computing History". https://www.computinghistory.org.uk/det/62892/Bandai-Digi-Casse/.
- ↑ "Game Pocket Computer by Epoch – The Video Game Kraken" (in en-US). http://videogamekraken.com/game-pocket-computer.
- ↑ "Hardware Classics: Game Boy Pocket". Nintendo Life. June 9, 2016. https://www.nintendolife.com/news/2016/06/hardware_classics_game_boy_pocket.
- ↑ 9/10/21 6:00AM (September 10, 2021). "Nintendo Fan Collects All 1,244 Game Boy Games In Two Years". Kotaku.com. https://kotaku.com/in-just-two-years-nintendo-fan-completes-game-boy-coll-1847649831. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ↑ "DS finally outsells Game Boy, best-selling handheld ever". Destructoid. May 6, 2010. https://www.destructoid.com/ds-finally-outsells-game-boy-best-selling-handheld-ever/.
- ↑ "Consolidated Sales Transition by Region". Nintendo. January 27, 2010. https://www.nintendo.co.jp/ir/library/historical_data/pdf/consolidated_sales_e0912.pdf.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "There's a mini Atari Lynx revival going on.". Engadget. 2021-08-21. https://www.engadget.com/atari-lynx-four-new-physical-games-183055733.html. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ↑ 14.00 14.01 14.02 14.03 14.04 14.05 14.06 14.07 14.08 14.09 14.10 14.11 Snow, Blake (July 30, 2007). "The 10 Worst-Selling Handhelds of All Time". GamePro. http://www.gamepro.com/gamepro/domestic/games/features/125748.shtml.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 "I'll Never Love a Console Like I Loved the SEGA Game Gear". Vice.com. https://www.vice.com/en/article/gqmwwx/ill-never-love-a-console-like-i-loved-the-sega-game-gear-820. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Let's revisit Game Gear vs Game Boy". Digitalspy.com. October 6, 2015. https://www.digitalspy.com/videogames/retro-gaming/a672009/sega-game-gear-vs-nintendo-game-boy-which-90s-handheld-was-the-real-games-master/. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ↑ 17.00 17.01 17.02 17.03 17.04 17.05 17.06 17.07 17.08 17.09 17.10 17.11 17.12 17.13 17.14 17.15 17.16 17.17 17.18 "The Handheld Rivals Which Tried And Failed To Beat The Game Boy". Nintendo Life. April 17, 2019. https://www.nintendolife.com/news/2019/04/feature_the_handheld_rivals_which_tried_and_failed_to_beat_the_game_boy.
- ↑ Forster, Winnie (2005). The Encyclopedia of Game.Machines: Consoles, Handhelds, and Home Computers 1972-2005. Magdalena Gniatczynska. p. 139. ISBN 3-0001-5359-4.
- ↑ "TurboGrafx-16 TurboExpress". AllGame. http://allgame.com/platform.php?id=17673.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 "Meet The Gamate, The Handheld Which Tried To Take On The Game Boy And Failed - Feature". Nintendo Life. February 13, 2014. https://www.nintendolife.com/news/2014/02/feature_meet_the_gamate_the_handheld_which_tried_to_take_on_the_game_boy_and_failed.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 21.4 "Rise of the Wannabes: The Game Boy's Many Uninspired Knockoffs". Vice.com. https://www.vice.com/en/article/kz3gjy/rise-of-the-wannabes-the-game-boys-many-uninspired-knockoffs. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ↑ "Design Master Denshi Mangajuku by Bandai – The Video Game Kraken" (in en-US). http://videogamekraken.com/design-master-denshi-mangajuku-by-bandai.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 "Hardware Classics: SNK Neo Geo Pocket Color". Nintendo Life. https://www.nintendolife.com/news/2014/03/hardware_classics_snk_neo_geo_pocket_color.
- ↑ "NeoGeo Pocket". AllGame. http://allgame.com/platform.php?id=17665.
- ↑ "Hardware Classics: Bandai WonderSwan". Nintendo Life. https://www.nintendolife.com/news/2014/03/hardware_classics_bandai_wonderswan.
- ↑ Wild, Kim (2007). "Retroinspection: WonderSwan". Retro Gamer (36): 68–71. ISSN 1742-3155.
- ↑ Brunskill, Kerry (2010). "Swan Song: A WonderSwan Retrospective". Retro Gamer (126): 45–47.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 28.3 "Chapter 1 : Introducing the Cybiko". Piclist.com. http://www.piclist.com/tecHREF/cybiko/b2c/ch1.htm.
- ↑ "Win a fabulous Cybiko Xtreme; READER CLUB.". MGN Ltd.. 2002. http://www.thefreelibrary.com/Win+a+fabulous+Cybiko+Xtreme%3b+READER+CLUB.-a084536941.
- ↑ Ringshaw, Grant (January 2001). "Vesta pours $9m into new console". https://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/personalfinance/4478896/Vesta-pours-9m-into-new-console.html.
- ↑ "New 32-bit Handheld System on the Block - IGN". https://www.ign.com/articles/2000/02/15/new-32-bit-handheld-system-on-the-block.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 "At 20 Years Old, Nintendo's GBA is Still Neglected". June 12, 2021. https://screenrant.com/gba-game-boy-advance-20-year-anniversary-nintendo/.
- ↑ "Game Boy Advance: It's Finally Unveiled". IGN. August 23, 2000. http://ca.ign.com/articles/2000/08/24/game-boy-advance-its-finally-unveiled.
- ↑ "Consolidated Sales Transition by Region". Nintendo. July 28, 2010. https://www.nintendo.co.jp/ir/library/historical_data/pdf/consolidated_sales_e1006.pdf.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 35.4 35.5 "GP2X Gaming Handheld Officially Released in UK". May 18, 2006. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/console/gp2x-gaming-handheld-officially-released-in-uk.
- ↑ "The rise and fall of the Game Boy's weirdest rivals". https://www.avclub.com/the-game-com-cometh-the-rise-and-fall-of-the-game-boy-1846501180/slides/9.
- ↑ "N-Gage". AllGame. http://allgame.com/platform.php?id=42646.
- ↑ "Gameking by Timetop – The Video Game Kraken" (in en-US). http://videogamekraken.com/gameking-by-timetop.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 "Stop Releasing New F*Cking Handhelds!". March 26, 2010. https://www.destructoid.com/stop-releasing-new-fcking-handhelds/.
- ↑ "The rise and fall of the Game Boy's weirdest rivals". https://www.avclub.com/the-game-com-cometh-the-rise-and-fall-of-the-game-boy-1846501180/slides/10.
- ↑ "Consolidated Sales Transition by Region". Nintendo. October 29, 2014. https://www.nintendo.co.jp/ir/library/historical_data/pdf/consolidated_sales_e1409.pdf.
- ↑ "Sony Introduces UMD-to-Digital Program, But It’ll Cost You". November 11, 2011. https://www.giantbomb.com/articles/sony-introduces-umd-to-digital-program-but-itll-co/1100-3803/.
- ↑ "Sony to Stop Selling PlayStation Portable by End of Year". http://time.com/2816781/sony-to-stop-selling-playstation-portable-by-end-of-year/.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 "Tiger Telematics Gizmondo review: Tiger Telematics Gizmondo". https://www.cnet.com/reviews/tiger-telematics-gizmondo-review/.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 45.3 45.4 45.5 45.6 "The rise and fall of the Game Boy's weirdest rivals". https://www.avclub.com/the-game-com-cometh-the-rise-and-fall-of-the-game-boy-1846501180/slides/11.
- ↑ "GP2X Linux handheld console showing promise". https://www.engadget.com/2005-11-15-gp2x-linux-handheld-console-showing-promise.html?guccounter=1&guce_referrer=aHR0cHM6Ly93d3cuZ29vZ2xlLmNvbS8&guce_referrer_sig=AQAAAJpUVD9MGLqlS9Z0Mta7Uy_WbVK-S9tZNNWGxPKQLHI1f-fAc_VjFyb0uErZSANG8-6xL54qm-KUc-A2DgIBFWQVMq6iZ-pVqUnM4kLsp-LYVIdktAirME6Kt9PC4Ot3MBnZTQWfxzs4w1SiE0h1wh_IlGDQkAa9P6e1hAKvSCIy.
- ↑ "Korea Goes All-out to Copy Nintendo" (in en). 2009-03-24. https://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/tech/2022/05/419_41898.html.
- ↑ Beschizza, Rob. "CES 2008: GP2X Linux-Based Handheld Game Console". Wired. https://www.wired.com/2008/01/ces-2008-gp2x-l/.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 49.3 49.4 49.5 "Dingoo A320 Micro Game Station review". August 13, 2009. https://www.techradar.com/reviews/gaming/handheld-consoles/dingoo-a320-micro-game-station-624388/review.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 50.3 50.4 50.5 "GP2X Wiz". https://www.pocketgamer.com/articles/014461/gp2x-wiz/.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 "Pandora gaming console finally shipping to UK". April 19, 2010. https://www.techradar.com/news/gaming/pandora-gaming-console-finally-shipping-to-uk-684324.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 "The ultimate open source handheld: the return of Pandora •". Eurogamer.net. 2012-09-29. https://www.eurogamer.net/articles/df-hardware-the-pandora-story. Retrieved 2022-01-11.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 "GamePark's GP2X Caanoo handheld hits this August, picks up where the Wiz left off (Video)". https://www.engadget.com/2010-07-12-gameparks-gp2x-caanoo-handheld-hits-this-august-picks-up-where.html.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 54.2 54.3 54.4 d'Anastasio, Cecilia. "The Nintendo 3DS' Surprisingly Social Legacy". Wired. https://www.wired.com/story/obituary-nintendo-3ds-in-memoriam/.
- ↑ "PSA: Yes, Your DS and 3DS Cartridges Will Eventually Deteriorate, but Don't Panic". May 6, 2021. https://www.nintendolife.com/news/2021/05/psa_yes_your_ds_and_3ds_cartridges_will_eventually_deteriorate_but_dont_panic.
- ↑ "Nintendo 3DS discontinued after almost a decade". BBC News. 17 September 2020. https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-54191058.
- ↑ "Nintendo 3DS Sales Pass 60 Million Units Worldwide". IGN. June 10, 2016. http://www.ign.com/articles/2016/06/10/nintendo-3ds-sales-pass-60-million-units-worldwide.
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 58.2 58.3 58.4 58.5 "'The little handheld that could': Examining the Vita's impact a decade later". June 24, 2021. https://www.theverge.com/2021/6/24/22545198/playstation-vita-10-year-anniversary-sony-handheld.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 59.2 59.3 "Neo Geo X review". February 24, 2013. https://www.eurogamer.net/articles/df-hardware-neo-geo-x-review.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 "Tommo planning to take action in Neo Geo X sales feud with SNK". January 10, 2014. https://www.polygon.com/2014/1/10/5296008/tommo-planning-to-take-action-in-neo-geo-x-sales-feud-with-snk.
- ↑ "Neo Geo X is still super boss, now comes in Limited Edition with an extra game". October 22, 2012. https://www.engadget.com/2012-10-22-neo-geo-x-limited-edition.html.
- ↑ "GameGadget: The empty promises and, finally, a response" (in en-gb). Eurogamer.net. 2012-10-31. https://www.eurogamer.net/gamegadget-the-empty-promises-and-finally-a-response.
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 "Meet GCW-Zero, a Linux-based, open-source gaming handheld". January 31, 2013. https://www.destructoid.com/meet-gcw-zero-a-linux-based-open-source-gaming-handheld/.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 64.2 64.3 "Old-school gaming on the sly with the GCW Zero". https://torontosun.com/2014/01/14/old-school-gaming-on-the-sly-with-the-gcw-zero.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 "Nvidia Shield review". July 31, 2013. https://www.theverge.com/2013/7/31/4573596/nvidia-shield-review.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 "Nvidia Shield Portable Review". https://www.pcmag.com/reviews/nvidia-shield-portable.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 "Nvidia's portable gaming console Shield will hit retail in June for $349". https://www.nbcnews.com/tech/tech-news/nvidias-portable-gaming-console-shield-will-hit-retail-june-349-flna1c9921539.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 68.2 68.3 Nero, Dom (March 18, 2021). "The 8 Best Portable Handheld Gaming Consoles of 2021". Esquire. https://www.esquire.com/lifestyle/g31016769/portable-handhelds-gaming-consoles/.
- ↑ "The Arduboy History" (in en-US). https://www.arduboy.com/blog/the-arduboy-history.
- ↑ "This Powerful Portable Console Has Us Dreaming of a Nintendo Switch Pro". November 18, 2020. https://www.nintendolife.com/news/2020/11/this_powerful_portable_console_has_us_dreaming_of_a_nintendo_switch_pro.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 71.2 71.3 "GPD Win 2 Handheld Launches April 2018, Runs GTA V". https://www.pcmag.com/news/gpd-win-2-handheld-launches-april-2018-runs-gta-v.
- ↑ "Nintendo Switch uses detachable 'Joy-Con' controllers". October 20, 2016. https://www.polygon.com/2016/10/20/13345506/nintendo-switch-controller-joy-con.
- ↑ "Nintendo Switch has a 6.2" 720p multi-touch screen". October 27, 2016. https://www.eurogamer.net/articles/2016-10-27-nintendo-switch-has-a-6-2-multi-touch-screen.
- ↑ "2021 is the Year of the Gaming Handheld". https://www.cnet.com/tech/gaming/2021-is-the-year-of-the-gaming-handheld/.
- ↑ Park, Gene (2019-11-20). "Review | Nintendo’s Switch Lite is the most comfortable handheld gaming device ever created" (in en-US). Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. https://www.washingtonpost.com/video-games/reviews/nintendos-switch-lite-is-most-comfortable-handheld-gaming-device-ever-created/.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 76.2 76.3 "This Retro Gaming Console is a Time Machine to the '80s". https://www.wired.com/review/evercade-retro-handheld-console/.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 "Evercade is a slick gaming handheld that shows why cartridges are still cool". May 28, 2020. https://www.theverge.com/2020/5/28/21271988/evercade-retro-games-handheld-review-classic-atari-namco-interplay.
- ↑ "Evercade review: "Classic gaming on a new handheld console reignites the retro romance"". December 21, 2020. https://www.gamesradar.com/evercade-review/.
- ↑ "Analogue Pocket preorders will ship December 13th". https://www.theverge.com/2021/11/22/22796303/analogue-pocket-preorder-ship-date.
- ↑ Sullivan, Derek (2021-07-26). "Aya Neo review - AMD Ryzen handheld gaming device" (in en-US). https://www.ultrabookreview.com/48387-aya-neo-handheld-review/.
- ↑ Leadbetter, Richard (2022-09-17). "AyaNeo Air/AyaNeo Air Pro Review: OLED PC gaming in the palm of your hand" (in en-gb). Eurogamer. https://www.eurogamer.net/ayaneo-airayaneo-air-pro-review-oled-pc-gaming-in-the-palm-of-your-hand.
- ↑ Coke, Chris (2022-05-01). "Aya Neo Next Advance Review" (in en). https://www.ign.com/articles/aya-neo-next-advance-review.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 83.2 83.3 Moore, Bo (July 15, 2021). "Steam Deck: The First Hands-On With Valve’s Handheld Gaming PC". https://www.ign.com/articles/steam-deck-hands-on-impressions-details-valve-handheld-gaming-pc.
- ↑ Lyles, Taylor (2023-11-09). "Valve Announces Steam Deck OLED: All the Details on the Price, Improved Battery Life, and More" (in en). https://www.ign.com/articles/steam-deck-oled-announced-release-date-price-specs.
- ↑ "Valve has delayed Steam Deck into next year". 6 April 2023. https://www.videogameschronicle.com/news/valve-has-delayed-steam-deck-into-next-year/.
- ↑ "Omdia: Steam Deck installed base to surpass three million during 2023". April 6, 2023. https://omdia.tech.informa.com/pr/2023/apr/omdia-steam-deck-installed-base-to-surpass-three-million-during-2023.
- ↑ "Valve's gaming handheld is called the Steam Deck and it's shipping in December". July 15, 2021. https://www.theverge.com/2021/7/15/22578783/valve-steam-deck-gaming-handheld-pc.
- ↑ "Steam Deck: Is it the Nintendo Switch for nerds?". July 20, 2021. https://www.theguardian.com/games/2021/jul/20/steam-deck-valve-nintendo-switch-for-nerds.
- ↑ "Playing A Tiny Video Game With My Thumbnails Because I Hate Myself: A Review". TheGamer. 6 April 2022. https://www.thegamer.com/playing-a-tiny-video-game-with-my-thumbnails-because-i-hate-myself-a-review/.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 90.2 "Playdate's tiny hand-held with a crank is big on charm". https://www.engadget.com/2019-08-28-playdate-hands-on.html.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 "Playdate, a new handheld console backed by indie royalty, unveiled in new issue of Edge magazine". May 22, 2019. https://www.gamesradar.com/playdate-new-handheld-console-edge-magazine-333-katamari-damacy/.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 92.2 92.3 92.4 Wilson, Jason R. (December 1, 2022). "AYANEO 2 Will Break New Ground For Handheld Gaming Consoles, Powered By AMD Ryzen 7 6800U". https://wccftech.com/ayaneo-2-will-break-new-ground-for-handheld-gaming-consoles-powered-by-amd-ryzen-7-6800u/.
- ↑ "AYANEO 2 console with AMD Ryzen 7 6800U APU officially launches in September". 2022-12-24. https://videocardz.com/newz/ayaneo-2-console-with-amd-ryzen-7-6800u-apu-officially-launches-in-september.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 Camilo Delgado (2023-06-13). "Asus ROG Ally release date, release time prediction". https://www.pcguide.com/console/asus-rog-ally-release-date/. Retrieved 2022-07-03.
- ↑ Faulkner, Cameron (August 23, 2023). "Sony’s $199.99 PlayStation Portal game-streaming handheld is available to pre-order". https://www.polygon.com/2023/8/23/23842770/playstation-portal-handheld-price-features-pulse-elite-explore.
- ↑ "PlayStation Portal Feels Better Than It Looks". November 10, 2023. https://kotaku.com/playstation-portal-handheld-ps5-impressions-1851012196.
- ↑ "Sony's PlayStation Portal remote player is a $200 handheld just for PS5 game streaming". August 23, 2023. https://www.engadget.com/sonys-playstation-portal-remote-player-is-a-200-handheld-just-for-ps5-game-streaming-140704336.html.
- ↑ Coldewey, Devin (August 23, 2023). "Third time's the charm? Sony makes $200 PlayStation Portal in-home handheld official". https://techcrunch.com/2023/08/23/third-times-the-charm-sony-makes-200-playstation-portal-in-home-handheld-official/.
- ↑ Morris, Chris (October 21, 2002). "GameBoy vs. Red Jade. The battle that never was. - Oct. 21, 2002". money.cnn.com. https://money.cnn.com/2002/10/18/commentary/game_over/column_gaming/.
- ↑ "New "Mobile Console" Plays PC Games - ExtremeTech". www.extremetech.com. https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/56346-new-mobile-console-plays-pc-games.
- ↑ "Gamepark returns with new XGP handhelds". finance.yahoo.com. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/2006-03-06-gamepark-returns-with-new-xgp-handhelds.html.
- ↑ "Panasonic says has dropped game development project" (in en). Reuters. 1 March 2011. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-panasonic-games-idUSTRE7201MD20110301.
 |
 KSF
KSF