Nancy (1775)
Topic: Engineering
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
Nancy was an American sailing vessel, noted in sources as either a brig or a brigantine, that was chartered to transport war supplies during the American Revolutionary War. After learning that independence had been declared, her captain, according to his daughter, raised the first American flag in a foreign port. Evading British capture, she was later intentionally destroyed with a huge blast on June 29, 1776, during the Battle of Turtle Gut Inlet near Cape May, New Jersey.
History
Construction
Nancy was built c. 1775 by Barney Harris in Wilmington, Delaware,[1] and was owned by Joseph Shallcross, Joseph Tatnall, and others.[2] Her captain was Hugh Montgomery, also from Wilmington.[2] Another part owner was Vincent Gilpin, who named the brig after his daughter Ann.[Note 1][3]
Military charter
On March 1, 1776, Robert Morris of the Pennsylvania Committee of Safety chartered Nancy to transport gunpowder and arms for the revolution.[4]
Later in March, she sailed to Puerto Rico to purchase arms and ammunition.[2] By early June, she had loaded additional supplies in the Caribbean islands of St. Thomas and St. Croix.[5]
First American flag in a foreign port
While at St. Thomas, Captain Montgomery received news that independence had been declared. An American flag was created by ensign Thomas Mendenhall and flown to replace the British one. This was "the first American stars ever seen in a foreign port"; that is, according to Elizabeth Montgomery, the captain's daughter, and Thomas C. Mendenhall, by family tradition.[6][7] Her book includes a mezzotint engraving by John Sartain that shows Nancy flying an American flag with a circle of ten stars surrounding three central stars.[6]
Since Nancy was subsequently destroyed on June 29, this would place the flag raising before the Declaration of Independence on July 4, but after the resolution for independence, proposed on June 7 to the Continental Congress.
Turtle Gut Inlet
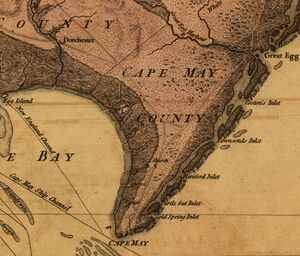
In the early hours of June 29, pursued by Script error: The function "ship_prefix_templates" does not exist. and Script error: The function "ship_prefix_templates" does not exist. and blocked from entering the Delaware Bay, Nancy headed for the nearby Turtle Gut Inlet in a heavy fog. She soon ran aground, while the larger British ships were kept to deeper waters.[8]
Although still out of range but sailing closer, the British shelled Nancy, while the Americans from missing name, missing name, and missing name attempted to salvage the cargo, especially the gunpowder kegs. One group returned cannon fire to keep the British from boarding. Another transferred the cargo onto longboats and rowed to shore where local residents helped unload and secure it behind the dunes.[8]
By late in the morning of June 29, most of the gunpowder had been removed, but the British bombardment had heavily damaged the Nancy.[9] The main sail was then wrapped around 50 pounds of gunpowder to create a long fuse running from the nearly 100 gunpowder kegs remaining in the hold to the deck and over the side. The fuse was lit as the crew abandoned ship, while one last sailor climbed the mast to remove the American flag. The British thought the lowering of the flag was a sign of surrender and quickly boarded Nancy. By then the fuse had reached the hold. The gunpowder exploded with a huge blast felt for miles.[10]
Salvage
On July 12, 1776, the Pennsylvania Committee of Safety recognized the £1457 claim of Joseph Shallcross & Co. for the loss of Nancy.[11]
Legacy

The Seal of Wildwood Crest and the Seal of the Wildwood Crest Historical Society each contain a drawing of Nancy in honor of the battle.[12]
Notes
- ↑ Nancy is a diminutive form of Ann
References
- ↑ Montgomery 1851, p. 171
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Montgomery 1851, p. 176
- ↑ Jordan (1911), p. 431.
- ↑ Morgan 1970, pp. 233–4
- ↑ Donnelly 2010, p. 105
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Montgomery 1851, pp. 176–7
- ↑ Mendenhall, Thomas C. (1899). "A Flag Episode". Proceedings of the American Antiquarian Society (Worcester, Massachusetts) XII: 425–8. https://books.google.com/books?id=u84oAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA425.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Donnelly 2010, p. 106
- ↑ Donnelly 2010, p. 108
- ↑ Donnelly 2010, p. 109
- ↑ Morgan 1970, p. 1048
- ↑ "The Battle of Turtle Gut Inlet". Wildwood Crest Historical Society. http://www.cresthistory.org/turtlegut.php.
Bibliography
- Donnelly, Mark P.; Diehl, Daniel (2010). "The Battle of Turtle Gut Inlet". Pirates of New Jersey. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books. ISBN 9780811706674. https://books.google.com/books?id=liRes6HP1boC&q=9780811706674&pg=PA103.
- Jordan, John W. (1911). Colonial and Revolutionary Families of Pennsylvania. ISBN 9780806352398. https://books.google.com/books?id=arAfWBsvO1gC&pg=PG431.
- Montgomery, Elizabeth (1851). Reminiscences of Wilmington, in Familiar Village Tales, Ancient and New. T.K. Collins, Jr.. https://archive.org/details/reminiscenceswi00montgoog.
- Morgan, William James, ed (1970). Naval Documents of The American Revolution, American Theatre: May 9, 1776 – July 31, 1776. 5. Washington, D.C.: Naval History Division/Naval Historical Center, Department of the Navy. http://www.ibiblio.org/anrs/docs/E/E3/ndar_v05.pdf.
External links
- "Wildwood Crest Historical Society and Museum". http://www.cresthistory.org/.
- "The Battle of Turtle Gut Inlet". Historical Marker Database. http://www.hmdb.org/marker.asp?marker=19535.
[ ⚑ ] 38°58′16″N 74°50′38″W / 38.971°N 74.844°W
 |
 KSF
KSF
