Fejér kernel
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
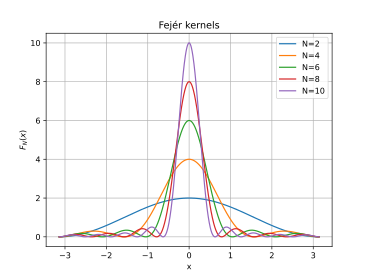
In mathematics, the Fejér kernel is a summability kernel used to express the effect of Cesàro summation on Fourier series. It is a non-negative kernel, giving rise to an approximate identity. It is named after the Hungarian mathematician Lipót Fejér (1880–1959).
Definition
The Fejér kernel has many equivalent definitions. Three such definitions are outlined below:
1) The traditional definition expresses the Fejér kernel in terms of the Dirichlet kernel
where
is the th order Dirichlet kernel.
2) The Fejér kernel may also be written in a closed form expression as follows[1]
This closed form expression may be derived from the definitions used above. A proof of this result goes as follows.
Using the fact that the Dirichlet kernel may be written as:[2]
- ,
one obtains from the definition of the Fejér kernel above:
By the trigonometric identity: , one has
which allows evaluation of as a telescoping sum:
3) The Fejér kernel can also be expressed as:
Properties
The Fejér kernel is a positive summability kernel. An important property of the Fejér kernel is with average value of .
Convolution
The convolution is positive: for of period it satisfies
Since
we have
which is Cesàro summation of Fourier series. By Young's convolution inequality,
Additionally, if , then
Since is finite, , so the result holds for other spaces, as well.
If is continuous, then the convergence is uniform, yielding a proof of the Weierstrass theorem.
- One consequence of the pointwise a.e. convergence is the uniqueness of Fourier coefficients: If with , then a.e. This follows from writing
which depends only on the Fourier coefficients.
- A second consequence is that if exists a.e., then a.e., since Cesàro means converge to the original sequence limit if it exists.
Applications
The Fejér kernel is used in signal processing and Fourier analysis.
See also
- Fejér's theorem
- Dirichlet kernel
- Gibbs phenomenon
- Charles Jean de la Vallée-Poussin
References
- ↑ Hoffman, Kenneth (1988). Banach Spaces of Analytic Functions. Dover. p. 17. ISBN 0-486-45874-1.
- ↑ Königsberger, Konrad (in German). Analysis 1 (6th ed.). Springer. pp. 322.
 |
 KSF
KSF