Economic union
Topic: Finance
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
An economic union is a type of trade bloc which is composed of a common market with a customs union.[1] The participant countries have both common policies on product regulation, freedom of movement of goods, services and the factors of production (capital and labour) as well as a common external trade policy. When an economic union involves unifying currency, it becomes an economic and monetary union.
The purposes for establishing an economic union normally include increasing economic efficiency and establishing closer political and cultural ties between the member countries.
Economic union is established through trade pact.
List of economic unions
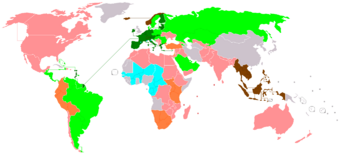
–UK, EAEU, MERCOSUR, GCC, SICA)
]]
- CARICOM Single Market and Economy[2]
- Central American Common Market - Common market since 1960, customs union since 2004.[citation needed]
- Eurasian Economic Union - Customs union since 2010, common market since 2012.[citation needed]
- European Union (EU) - Economic union of 27 European states, but only 20 are inside the Eurozone are also part of an economic and monetary union.[3]
- European Economic Area (EEA) - Economic area between European Union and EFTA member states (except Switzerland).
- Gulf Cooperation Council[4][5]
- Mercosur
Note: Every economic and monetary union includes an economic union.
Additionally the autonomous and dependent territories, such as some of the EU member state special territories, are sometimes treated as separate customs territory from their mainland state or have varying arrangements of formal or de facto customs union, common market and currency union (or combinations thereof) with the mainland and in regards to third countries through the trade pacts signed by the mainland state.[6]
Proposed
- African Economic Community (AEC) - proposed for 2023
- Andean Community (CAN)[7]
- Arab Customs Union and Common Market - proposed for 2020[8]
- CANZUK
- Central American Common Market (CACM)
- Closer Economic Relations of Australia and New Zealand
- East African Community (EAC) - extension of existing customs union proposed in 2015
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC) - proposed in 2015
- Union of South American Nations (USAN)
See also
- List of multilateral free-trade agreements
- List of bilateral free-trade agreements
- Supranational union
References
- ↑ Gancia, Gino; Ponzetto, Giacomo A. M.; Ventura, Jaume (2020-01-01). "A theory of economic unions" (in en). Journal of Monetary Economics. SI:APR2019 CRN CONFERENCE 109: 107–127. doi:10.1016/j.jmoneco.2019.11.007. ISSN 0304-3932.
- ↑ Established by the Treaty of Chaguaramas in force from 1973-8-1 WT/REG92/R/B/1
- ↑ Established by the Treaty of Rome in force from 1958-1-1. WT/REG138/2
- ↑ Gulf states form common market, BBC News. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "GCC customs union fully operational". The Peninsula. 3 January 2015. http://thepeninsulaqatar.com/news/middle-east/314466/gcc-customs-union-fully-operational.
- ↑ EU Overseas countries and some other territories participate partially in the EU single market per part four of the Treaty Establishing the European Community; Some EU Outermost regions and other territories use the Euro of the currency union, others are part of the customs union; some participate in both unions and some in neither.
Territories of the United States, Australian External Territories and Realm of New Zealand territories share the currency and mostly also the market of their respective mainland state, but are generally not part of its customs territory. - ↑ Twelfth Andean Presidential Council Act of Lima
- ↑ "Leaders set to approve Arab customs union". http://www.gulf-daily-news.com/NewsDetails.aspx?storyid=240423.
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF