Electricity price area
Topic: Finance
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
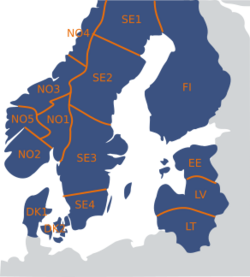
As an example, the map shows the situation in the Nordic region as of winter 2015. Norway had then five electricity price areas, but as of 2022 six areas where NO3 has been split in Molde and Trondheim, where the other areas are called Oslo, Kristiansand, Tromsø and Bergen. Sweden is subdivided into four (Malmö, Stockholm, Luleå and Sundsvall), Denmark is split into Eastern and Western Denmark, while Finland, Estonia, Lithuania and Latvia remain unsplit.
An electricity price area is a zone throughout which the electricity is traded at the same spot price on a power exchange. An electricity price area is decided by transmission system operator and can be a whole country, or parts of it.[1]
EPADs and price area risk
The electricity price usually differs from the system price from one price area to another, e.g. when there are constraints in the transmission grid. A special contract for difference called Electricity Price Area Differentials or EPAD allows members on the power exchange to hedge against this market risk called area price risk.[2]
See also
- Nord Pool Spot
- Nordic energy market
- Electricity sector in Sweden
- Electricity sector in Norway
References
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Finance:Electricity_price_area9 views | Status: cached on August 03 2024 13:55:07↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF