Recession
Topic: Finance
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 49 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 49 min
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a period of broad decline in economic activity.[1][2] Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various events, such as a financial crisis, an external trade shock, an adverse supply shock, the bursting of an economic bubble, or a large-scale anthropogenic or natural disaster (e.g. a pandemic). There is no official definition of a recession, according to the International Monetary Fund.[3]
In the United States, a recession is defined as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales."[4] The European Union has adopted a similar definition.[5][6] In the United Kingdom and Canada, a recession is defined as negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters.[11]
Governments usually respond to recessions by adopting expansionary macroeconomic policies, such as increasing money supply and decreasing interest rates or increasing government spending and decreasing taxation.
Definitions
In a 1974 article by The New York Times, Commissioner of the Bureau of Labor Statistics Julius Shiskin suggested that a rough translation of the bureau's qualitative definition of a recession into a quantitative one that almost anyone can use might run like this:
- In terms of duration – Declines in real gross national income (GNI) for two consecutive quarters; a decline in industrial production over a six-month period.
- In terms of depth – A 1.5% decline in real gross national income; a 15% decline in non-agricultural employment; a two-point rise in unemployment to a level of at least 6%.
- In terms of financial indicators - A significant increase in loan defaults or a tightening of credit conditions by financial institutions, leading to a decrease in business investment and consumer spending.
- In terms of diffusion – A decline in non-agricultural employment in more than 75% of industries, as measured over six-month spans, for six months or longer.[12][13][14]
Over the years, some commentators dropped most of Shiskin's "recession-spotting" criteria for the simplistic rule-of-thumb of a decline in real GNI for two consecutive quarters.[15]
In the United States, the Business Cycle Dating Committee of the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is generally seen as the authority for dating US recessions. The NBER, a private economic research organization, defines an economic recession as: "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales".[16] The NBER also explains that: "a recession begins when the economy reaches a peak of activity and ends when the economy reaches its trough."[3] The NBER is considered the official arbiter of recession start and end dates for the United States.[17][18][19] The Bureau of Economic Analysis, an independent federal agency that provides official macroeconomic and industry statistics,[20] says "the often-cited identification of a recession with two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth is not an official designation" and that instead, "The designation of a recession is the province of a committee of experts at the National Bureau of Economic Research".[21]
The European Union, akin to the NBER's methodology, has embraced a definition of recession that integrates GDP alongside a spectrum of macroeconomic indicators, including employment and various other metrics. This approach allows for a comprehensive assessment of the depth and breadth of economic downturns, enabling policymakers to devise more effective strategies for economic stabilization and recovery.
Recessions in the United Kingdom are generally defined as two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth, as measured by the seasonally adjusted quarter-on-quarter figures for real GDP.[7][8]
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), an intergovernmental organization, defines a recession as a period of at least two years during which the cumulative output gap reaches at least 2% of GDP, and the output gap is at least 1% for at least one year.[22]
GDP per capita recession[23] refers to the decline of GDP per capita instead of decline of total GDP.[24]
Attributes
A recession encompasses multiple attributes that often occur simultaneously and encompasses declines in component measures of economic activity, such as GDP, including consumption, investment, government spending, and net export activity. These summary measures are indicative of underlying drivers such as employment levels and skills, household savings rates, corporate investment decisions, interest rates, demographics, and government policies (Smith, 2018; Johnson & Thompson, 2020). By examining these factors comprehensively, economists gain insights into the complex dynamics that contribute to economic downturns and can formulate effective strategies for mitigating their impact (Anderson, 2019; Patel, 2017).
Economist Richard C. Koo wrote that under ideal conditions, a country's economy should have the household sector as net savers and the corporate sector as net borrowers, with the government budget nearly balanced and net exports near zero.[25][26]
A severe (GDP down by 10%) or prolonged (three or four years) recession is referred to as an economic depression, although some argue that their causes and cures can be different.[27] As an informal shorthand, economists sometimes refer to different recession shapes, such as V-shaped, U-shaped, L-shaped and W-shaped recessions.[28]
Type of recession or shape
The type and shape of recessions are distinctive. In the US, v-shaped, or short-and-sharp contractions followed by rapid and sustained recovery, occurred in 1954 and 1990–1991; U-shaped (prolonged slump) in 1974–1975, and W-shaped, or double-dip recessions in 1949 and 1980–1982. Japan's 1993–1994 recession was U-shaped and its 8-out-of-9 quarters of contraction in 1997–1999 can be described as L-shaped. Korea, Hong Kong and South-east Asia experienced U-shaped recessions in 1997–1998, although Thailand's eight consecutive quarters of decline should be termed L-shaped.[29]
Front end of a recession
Describes the early stages of an economic downturn with emerging negative trends across key economic sectors before a full-blown deepening recession is officially declared. Characteristics: Indicators like GDP growth, employment rates, and consumer spending start to decline. A decline in overall demand causes a slowdown in economic activity. Falling consumer confidence, falling retail sales and reduced business investment are common signs that indicate the beginning of a recession. This phase of the economic cycle can also be marked by slowing economic growth with factors like declining corporate profit margins (due to lower sales and increased costs), weakening business investment, falling industrial production (continued decline in overall manufacturing hours worked) and a deteriorating sluggish labor market (layoffs becoming more common, e.g. falling private payrolls, declining small business household employment), slower payroll growth, wage stagnation or decline and a housing market slowdown as real estate buyers in the housing sector become more cautious (followed by declines in home sales, slowing building permits and falling home prices). In financial markets some investors may become more risk-averse and bond yields may rise thereby making it more expensive for companies to borrow money, causing some businesses to struggle to meet their financial obligations. Summary: The front end of a recession refers to the initial phase or onset of a recession. It typically is a period of increasing economic stress (job losses often appear early on), significant uncertainty and precedes the official recognition of a recession (the technical definition of a recession is two or more consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth), signaling that the economy is transitioning toward contraction, even before the full effects are felt or officially declared. Early warning indicators[30] can be rising inflation (potential for tighter monetary policy), widening credit spreads (tightening lending standards, strained private sector lending), rising credit delinquencies and an inverted yield curve (market expectation of much lower growth ahead, a historically reliable predictor of an approaching recession). Recessions especially in the U.S. are typically "preceded by a rising debt service ratio for the private sector".[31] Some economists also consider a rising 3-month average unemployment rate above the prior year's average as an early recession signal that can precede a formal recession declaration (this is often referred to as the Sahm Rule.). The Conference Board's Leading Economic Index (LEI)[32] can also provide an early recession indication. Other "soft" consumer signals also tend to appear in everyday life before official statistics catch up, like slower travel (e.g. fewer flights). More early warning indicators can be found in the section "Predictors" Recession#Predictors. Identifying the front end of a recession is crucial for policymakers as it gives more room to act early and thereby allows for early intervention to potentially mitigate the impact of a recession before the downturn deepens.
The table below illustrates the progression toward recession. Each column represents a distinct phase in the economic cycle.
| Normal Economy | Early Warning Signs / Front End Indicators | Recession Threshold / Severe Downturn |
|---|---|---|
| Average to Strong Growth | Slowing Growth | No Growth |
| Average to High Confidence | Declining Confidence / Increased Uncertainty | Low Confidence / High Uncertainty |
| Average to High Business Investment | Falling Business Investment | No Business Investment |
| Low to Average Unemployment | Growing Unemployment | High Unemployment |
| Stable to Growing Home Prices | Falling Home Prices | Low Home Prices |
| Stable to Low Food Prices | Growing Food Prices | High Food Prices |
| Low Corporate & Household Debt | Growing Corporate & Household Debt | High Corporate & Household Debt |
| Stable to High Consumer Spending | Decreasing Consumer Spending | Low Consumer Spending |
Back end of a recession
Describes the latter part of an economic contraction, specifically the period after the trough (the lowest point of economic activity during a recession) when the economy begins to recover. Characteristics: Indicators like employment and consumer spending transition from decline to growth. Decreasing unemployment, stabilizing Gross Domestic Product (GDP), increased business investment are common signs. Summary: The back end of a recession is a period of gradual and sustained recovery where parts of the economy start to grow again.
Psychological aspects
Recessions have psychological and confidence aspects. For example, if companies expect economic activity to slow, they may reduce employment levels and save money rather than invest. Such expectations can create a self-reinforcing downward cycle, bringing about or worsening a recession.[33] Consumer confidence is one measure used to evaluate economic sentiment.[34] The term animal spirits has been used to describe the psychological factors underlying economic activity. Keynes, in his The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, was the first economist to claim that such emotional mindsets significantly affect the economy.[35] Economist Robert J. Shiller wrote that the term "refers also to the sense of trust we have in each other, our sense of fairness in economic dealings, and our sense of the extent of corruption and bad faith. When animal spirits are on ebb, consumers do not want to spend and businesses do not want to make capital expenditures or hire people."[36] Behavioral economics has also explained many psychological biases that may trigger a recession including the availability heuristic, the money illusion, and normalcy bias.[37]
Balance sheet recession
Excessive levels of indebtedness or the bursting of a real estate or financial asset price bubble can cause what is called a "balance sheet recession". This occurs when large numbers of consumers or corporations pay down debt (i.e., save) rather than spend or invest, which slows the economy.[26] The term balance sheet derives from an accounting identity that holds that assets must always equal the sum of liabilities plus equity.[38] If asset prices fall below the value of the debt incurred to purchase them, then the equity must be negative, meaning the consumer or corporation is insolvent. Economist Paul Krugman wrote in 2014 that "the best working hypothesis seems to be that the financial crisis was only one manifestation of a broader problem of excessive debt—that it was a so-called "balance sheet recession". In Krugman's view, such crises require debt reduction strategies combined with higher government spending to offset declines from the private sector as it pays down its debt.[39]
For example, economist Richard Koo wrote that Japan's "Great Recession" that began in 1990 was a "balance sheet recession". It was triggered by a collapse in land and stock prices, which caused Japanese firms to have negative equity, meaning their assets were worth less than their liabilities. Despite zero interest rates and expansion of the money supply to encourage borrowing, Japanese corporations in aggregate opted to pay down their debts from their own business earnings rather than borrow to invest as firms typically do. Corporate investment, a key demand component of GDP, fell enormously (22% of GDP) between 1990 and its peak decline in 2003. Japanese firms overall became net savers after 1998, as opposed to borrowers. Koo argues that it was massive fiscal stimulus (borrowing and spending by the government) that offset this decline and enabled Japan to maintain its level of GDP. In his view, this avoided a U.S. type Great Depression, in which U.S. GDP fell by 46%. He argued that monetary policy was ineffective because there was limited demand for funds while firms paid down their liabilities. In a balance sheet recession, GDP declines by the amount of debt repayment and un-borrowed individual savings, leaving government stimulus spending as the primary remedy.[25][26][40]
Krugman discussed the balance sheet recession concept in 2010, agreeing with Koo's situation assessment and view that sustained deficit spending when faced with a balance sheet recession would be appropriate. However, Krugman argued that monetary policy could also affect savings behavior, as inflation or credible promises of future inflation (generating negative real interest rates) would encourage less savings. In other words, people would tend to spend more rather than save if they believe inflation is on the horizon. In more technical terms, Krugman argues that the private sector savings curve is elastic even during a balance sheet recession (responsive to changes in real interest rates), disagreeing with Koo's view that it is inelastic (non-responsive to changes in real interest rates).[41][42]
A July 2012 survey of balance sheet recession research reported that consumer demand and employment are affected by household leverage levels. Both durable and non-durable goods consumption declined as households moved from low to high leverage with the decline in property values experienced during the subprime mortgage crisis. Further, reduced consumption due to higher household leverage can account for a significant decline in employment levels. Policies that help reduce mortgage debt or household leverage could therefore have stimulative effects (Smith & Johnson, 2012).
Liquidity trap
A liquidity trap is a Keynesian theory that a situation can develop in which interest rates reach near zero (zero interest-rate policy) yet do not effectively stimulate the economy.[43] In theory, near-zero interest rates should encourage firms and consumers to borrow and spend. However, if too many individuals or corporations focus on saving or paying down debt rather than spending, lower interest rates have less effect on investment and consumption behavior; increasing the money supply is like "pushing on a string".[44] Economist Paul Krugman described the U.S. 2009 recession and Japan's lost decade as liquidity traps. One remedy to a liquidity trap is expanding the money supply via quantitative easing or other techniques in which money is effectively printed to purchase assets, thereby creating inflationary expectations that cause savers to begin spending again. Government stimulus spending and mercantilist policies to stimulate exports and reduce imports are other techniques to stimulate demand.[45] He estimated in March 2010 that developed countries representing 70% of the world's GDP were caught in a liquidity trap.[46]
Paradoxes of thrift and deleveraging
Behavior that may be optimal for an individual (e.g., saving more during adverse economic conditions) can be detrimental if too many individuals pursue the same behavior, as ultimately, one person's consumption is another person's income. Too many consumers attempting to save (or pay down debt) simultaneously is called the paradox of thrift[47] and can cause or deepen a recession. Economist Hyman Minsky also described a "paradox of deleveraging" as financial institutions that have too much leverage (debt relative to equity) cannot all de-leverage simultaneously without significant declines in the value of their assets.[48]
Causes of recessions
There are many reasons why recessions happen. One overall reason can be lack of demand due to sharp developments in the prices of the inputs used in producing goods and services. Another main reason can be problems e.g. in financial markets. Because recessions have many likely explanations, it is demanding to predict them. Some variables might at first glance be the causes of recessions, but they could also be the results of a recession, which means they are endogenous to recessions.[3] One can summarize the causes of recessions in the following categories:
Economic factors:
- Supply shocks: A sudden increase in the prices of key inputs (input price shock) can lead to higher production costs and reduced aggregate demand, triggering a recession.[3]
- Fiscal policies or monetary policies by the government, which are contractionary in nature: A contractionary policy is a tool usually used to tame rising inflation. Excessive use of tightening policies, e.g. too rapid increases in interest rates, can reduce demand and consumer spending for goods and services, leading to a recession (creating a so-called hard landing).[3] Monetary policy changes can influence both the frequency and intensity of recessions.
- Demand shocks: A widespread drop in spending, known as an adverse demand shock, can lead to recessions. This can be triggered by various events, including the bursting of economic bubbles (see economic bubbles below).
Financial factors:
- Credit risk and credit and debt issues: Overextension of credit and accumulation of risky debt can lead to financial crises. When borrowers (e.g. corporations) default, it can cause a cascade of business failures and reduced consumption).[3]
- Financial risk factors that can cause a recession are plentiful: Besides credit risk like e.g. concentration risk, there is also market risk like e.g. systemic risk, liquidity risk like e.g. refinancing risk, investment risk like e.g. model risk, business risk like e.g. political risk as well as profit risk.
- Financial market problems: Issues in financial markets, such as rapid credit expansion. When households accumulate excessive debt and later face difficulties in meeting their obligations, they cut back on consumption, leading to a decrease in economic activity.
- Credit tightening: Restrictions on credit availability also known as credit crunch, can reduce consumer spending and business investment, leading to a slowdown in economic activity.
- Interest rate distortions: Artificially low interest rates can encourage excessive borrowing and result in a buildup of risk in the financial sector. When interest rates rise, these investments (like new constructions in real estate) may fail, exacerbate economic declines, contributing to a recession.
- Economic bubble: Unsustainable rapid increases in asset prices due to excessive risk-taking, characterized by exaggerated optimism during the economic boom period and accumulation of financial risks during good economic times creates an asset bubble, followed by continued sharp declines in asset prices, a (stock market crash), which can lead to a cascade of business failures, significant recessions and worst case depressions and stagnation.
- Minsky Moment: Euphoria and speculative borrowing as well as unsustainable financial practices eventually result in economic downturns. A Minsky Moment marks the point at which overleveraged investors are forced to sell off assets to cover their debts, leading to a rapid decline in asset prices and liquidity. This term is named after the American economist Hyman Minsky, who theorized that financial markets are inherently unstable.
External shocks
- Adverse events: Unexpected major world events like natural disasters and geopolitical events like wars can cause widespread disruptions in critical sectors in supply chains and disrupt economic activity, reduce productivity, increase costs, affect confidence and thereby diminish economic activity, leading to decreased spending and investment and finally recessions.
- Decline in external demand: For countries with strong export sectors, a decline in demand from major trading partners can trigger a recession.[3]
- Global spillover effects: Recessions in one part of the world can have spillover effects on other economies due to global interconnectedness. For example, economic troubles in Europe can impact the U.S. economy.[49]
Predictors
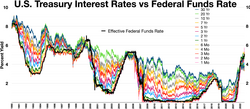

Recessions are very challenging to predict. While some variables like the (inverted) yield curve appear to be more useful to predict a recession ahead of time than other variables, no single variable has proven to be an always reliable predictor whether recessions will actually (soon) appear, let alone predicting their sharpness and severity in terms of duration.[3] The longest and deepest Treasury yield curve inversion in history began in July 2022, as the Federal Reserve sharply increased the fed funds rate to combat the 2021–2023 inflation surge. Despite widespread predictions by economists and market analysts of an imminent recession, none had materialized by July 2024, economic growth remained steady, and a Reuters survey of economists that month found they expected the economy to continue growing for the next two years. An earlier survey of bond market strategists found a majority no longer believed an inverted curve to be a reliable recession predictor. The curve began re-steepening toward positive territory in June 2024, as it had at other points during that inversion; in every previous inversion they examined; Deutsche Bank analysts found the curve had re-steepened before a recession began.[50][51][52] The following variables and indicators are used by economists, like e.g. Paul Krugman or Joseph Stiglitz, to try to predict the possibility of a recession:
- The U.S. Conference Board's Present Situation Index year-over-year change turns negative by more than 15 points before a recession.[53][54][55]
- The U.S. Conference Board Leading Economic Indicator year-over-year change turns negative before a recession.[56][57]
- When the CFNAI Diffusion Index drops below the value of −0.35, then there is an increased probability of the beginning a recession. Usually, the signal happens in the three months of the recession. The CFNAI Diffusion Index signal tends to happen about one month before a related signal by the CFNAI-MA3 (3-month moving average) drops below the −0.7 level. The CFNAI-MA3 correctly identified the 7 recessions between March 1967 – August 2019, while triggering only 2 false alarms.[58]
Except for the above, there are no known completely reliable predictors.[citation needed] Analysis by Prakash Loungani of the International Monetary Fund found that only two of the sixty recessions around the world during the 1990s had been predicted by a consensus of economists one year earlier, while there were zero consensus predictions one year earlier for the 49 recessions during 2009.[59]
However, the following are considered possible predictors:[60][61][32]
Manufacturing:

- Average weekly hours in manufacturing.[62] Firms tend to react to worsening business cycle circumstances by lowering hours worked before laying off workers, according to Glosser and Golden (1997).[63] This popular indicator leads industrial production by two to four months.[64]
- Manufacturers' new orders for consumer goods and materials.[62]
- Manufacturers' new orders for nondefense capital goods excluding aircraft orders.[62]
- Manufacturing sales.
- A decline in manufacturing activities and new orders for consumer and capital goods can signal reduced business investment and economic slowdown.
- Measuring manufacturing output against business demand (new orders plus backlog minus inventory) as a composite index for U.S. economic activity, using data from ISM (Manufacturing Services, Chicago) and Fed (Empire Manufacturing, Philadelphia, Kansas City, Richmond, Dallas) indices, has been a reliable recession indicator during the last eight recessions.[65]
Industrial Production:
- Factory output, including factories, mines, and utilities.
- Low industrial output and sales: During economic downturns, companies reduce production to minimize risk. This leads to lower industrial output and sales, which can signal an impending recession, because it causes a ripple effect. As fewer goods are produced, lesser resources like labor, equipment and raw materials are required. As industrial output falls this sooner or later leads to a cutback in hiring as well as a surge in layoffs.
Chemical Activity:
- Basic industrial chemicals like chlorine, alkalies, pigments and plastic resins are positioned early in the supply chain. This early position allows to identify emerging turning points in the economy.
- Chemical activity also includes data on hours worked in chemicals, chemical company stock data, publicly sourced chemical price information, end-use chemical industry sales-to-inventories.
- Indicators of chemical activity provide a longer lead time compared to other economic indicators. Tracking chemical activity as an index can lead by two to fourteen months, with an average lead of eight months at cycle peaks and four months at cycle troughs, according to the American Chemistry Council (ACC).
Transportation:

- Declining trucking and shipping volumes of goods.[66][67]
- The Baltic Dry Index (BDI), a shipping freight-cost index which reflects the demand for shipping capacity versus the supply of dry bulk carriers, is generally seen as a leading indicator of economic activity, because changes in the index reflect global supply and demand for commodities and raw materials used in manufacturing. A falling BDI can signal a slowdown in economic activity.
- The Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) contains railroads, shipping companies, air freight carriers, marine transportation, delivery services, and logistics companies. The performance of transportation stocks can predict trends in the broader market, according to the Dow Theory, which says that a divergence between the DJTA and the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) can signal potential early economic weakness if transportation stocks are underperforming while industrial stocks are rising.
- Both indices (BDI and DJTA) serve as barometers for economic health and are considered to be leading economic indicators but from different perspectives. The BDI focuses on global trade and commodity demand, while the DJTA reflects domestic transportation activity in the U.S.
- There are various trucking indices, most notably the Cass Freight Index, which measures monthly freight activity across all domestic freight modes in North America. Other trucking indices are the FreightWaves National Truckload Index (NTI), the FTR Trucking Conditions Index (TCI), the ACT For-Hire Trucking Index, the American Trucking Associations' Truck Tonnage Index, the DAT Trendlines index and the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Producer Price Index (PPI) by Industry: General Freight Trucking Index. These indices are essential for understanding the dynamics of the trucking industry and predicting future market conditions.
- According to research by the U.S. Bureau of Transportation Statistics, the Transportation Services Index (TSI) is a leading indicator of economic cycles. It tracks the movement of freight and passengers to provide insights into the broader economic conditions. Both TSI index components lead the business cycles since 1979 by an average of approximately four months.[68]
- Light truck sales are seen as a recession predictor.[69][70]
Corporate Profits:
- Business sector profits. Declining corporate earnings over successive quarters can signal economic trouble and the risk of a potential bear market.[71]
Employment:
- Decreasing job growth.
- Decreasing payroll employment.
- Growing unemployment rate as measured by the initial claims for unemployment insurance (indicated by a constant enduring year-over-year increase in the three-week average of unemployment insurance initial claims[72]), which are reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics:[62] A enlarging unemployment rate with rising initial claims for unemployment insurance indicate weakening labor market conditions, which can be a precursor to a recession. This indicator leads industrial production by two to three months.[64] Also see Sahm rule indicator below in the overview of recession indicators, which tracks the momentum in the U3 unemployment rate.
- Growing labor market weakness as indicated by a negative three-month average of U.S. nonfarm payrolls.[72]
- Swelling unemployment rate, specifically an unemployment rate rising above its 36-month moving average[73] is a cause for concern, according to Jeffrey Gundlach.
- A narrowing labor differential between those who think jobs are plentiful versus those who think they are hard to get, as measured by the Conference Board. On average, the peak in the labor differential comes nine months ahead of a recession, according to BCA Research strategist Peter Berezin.[74]
- Jobs market contraction: The 'Perkins rule', created by GlobalData TS Lombard managing director Dario Perkins, triggers when payrolls are declining. Commonly when the Sahm rule produces a recession warning signal the Perkins rule has already triggered.[75] Another jobs market indicator measuring a rise in unemployment is the 'Kantro rule'. This recession indicator isn't influenced by participation rates and has an equally impressive track record as the Sahm rule going back to the early 1970s. Kantro's 10% recession rule, created by Michael Kantrowitz, CIO of Piper Sandler, measures the year-over-year growth in unemployed persons in the U.S. workforce. When the three-month moving average of this indicator grows beyond the 10% threshold at least in the past 11 occurrences the economy has already been in recession.[76][77]
- Growing shifts in labor market internals to part-time work signals increasing weakness in the economy as normally part-time jobs rise and full-time jobs decrease as a share of employment before a recession takes hold. As an indicator this can be measured simply using the ratio of part-time to full-time employment (with the year-over-year change crossing into negative territory as recession risk warning).[78] Another way to use this approach is to look at the number of people who are working part time but would rather be working full time, according to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics.[74] This approach is also called U-7 and was invented by David Blanchflower, a Dartmouth labor economist who served on the Bank of England's monetary policy committee. David Kotok, the chief investment officer of Cumberland Advisors, says the way to use the U-7 number is to compare it with the main unemployment rate, which the Labor Department calls U-3. When the U-3 rises faster than the U-7, that is a recession warning.[79]
- Six other employment-based recession indicators are:[65] 1) new claims for unemployment (8-week smoothing of 26-week change) larger than 60.000. 2) Continuing claims for unemployment (percent change year-over-year) larger 21%. 3) Employed part-time due to economic reasons (percent change year-over-year) larger 16%. 4) Unemployed more than 15 weeks (percent change from 12-month low) larger 30%. 5) Temporary help services (percent change year-over-year) smaller -2%. 6) Aggregate hours worked, production and non-supervisory employees (6-month percent change) smaller 0%.
Personal Income:
- Decline in wages.
- Decline in personal income less transfer payments. Real median household income is reported by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
- Increased income inequality.[80][81]
Household Savings and Consumer Debt:
- Tracking consumer savings rates can help indicate how people are feeling about the economy in general. A personal savings rate that is too low (and then rises once people become worried about their job security, start to spend less and begin to build their savings again) typically precedes a recession. Prior to the 2008 financial crisis, households were saving less than 3% of their disposable personal income based on data from the Commerce Department.[82]
- Rising consumer debt at the onset of a recession: When the budget shrinks some consumers may turn to debt to maintain their lifestyle and to continue spending. As available cash tightens an increase in overall credit card debt, auto loans and other types of consumer debt can indicate that consumers can't afford daily purchases anymore. This debt overhang suggests lower future consumer spending and a worsening economy.[83]
Retail Sales, Consumer Confidence and Consumer Expenditures:
- Decline in wholesale/retail sales, which are reported by the U.S. Census Bureau.
- Consumer expectations, confidence surveys like the index of consumer expectations (University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index) and the Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index:[62] Declines in consumer sentiment and confidence can signal a recession. These measures reflect consumers' outlook on the economy and their willingness to spend, which drives economic activity. A drop in consumer confidence often precedes reduced consumer spending.
- Weakening personal consumption expenditure growth.[72] Declines in consumer spending can signal a recession. As consumers cut back on spending, businesses may respond by reducing production and laying off workers, creating a cycle that can lead to a recession.
- Changes in household consumer spending like a switch to more generic brands (trading down): When households start buying more private label or lower-cost goods (generic brands that are a lower-cost option for a similar product instead of more expensive name brand goods) could indicate that consumers have less discretionary income and that a recession is coming.[83]
- Consumers choosing to eat out less at restaurants and make food at home more: It can be a leading sign of a looming recession when consumers cut back on non-essential items like restaurants, entertainment and experiences like travel.[83]
- Declining luxury purchases: When the jobs market starts getting stressed and cash is less plentiful consumers postpone expensive, non-urgent purchases and especially luxury purchases (fashion, beauty and jewelry) are one of the first spending categories to get hit when a recession is coming.[83]
- Tumbling sales in durable consumer goods, like e.g. new car sales (light vehicles unit retail sales).[72] and decreasing recreational vehicle shipments.[84]
Housing and non-residential construction:
- Housing starts and construction, specifically building permits for new private housing units.[62][85] Residential investment contains information that is particularly useful for predicting recessions when compared by what is captured by standard leading indicators such as the term spread. And it is especially useful for the prediction of recessions for countries with high home-ownership rates. Research results strongly suggest that recession predictability of leading indicators is improved, when residential investment is included.[86]
- Non-residential construction spending (like e.g. offices and industrial plants) as measured by the Architecture Billings Index (ABI) 9–12 months ahead. The ABI is a survey send each month by the AIA to several hundreds of architecture firms. The index can be used to predict a recession. The index is centered around a value of 50. Below 50 means there is a high likelihood that construction spending will decrease and that therefore overall economic health is going to worsen. Researchers at the AIA came to the conclusion that their Architecture Billings Index is an accurate indicator of actual construction spending with on average 11 months' worth of lead time and therefore reliably leads economic downturns whenever the index severely drops below 50. For example, the ABI plunged below 50 between July 2000 and January 2001 (and then in June 2001 the percentage change in construction spending as compared to the prior year sank into negative growth territory) ahead of the wider crash in the US equity markets that followed.[87]
Credit Markets:
- Rising corporate debt can foreshadow a bear market, notably when businesses go ahead with taking on more debt, despite having diminishing sales and dwindling earnings.[71]
- Credit conditions like credit spreads. The spread between corporate bonds and U.S. Treasuries is important. If the spread between corporate and government debt increases, this could signal that private sector lending is becoming strained.[88]
- The long-term spread: The spread between a shorter-term rate (like the three-month Treasury yield) and 10-year U.S. bond yields. The long-term Treasury yield spread has been particularly effective at predicting recessions many months in advance, achieving an AUC (Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve) value of 0.89 at 14 months ahead. And it is the best predictor at a horizon of 16 to 20 months ahead, when compared to other leading indicators.[62]
- The near-term forward spread: This is the difference between the market expectation of the interest rate on a three-month Treasury bill six quarters in the future and the current three-month Treasury bill yield.[89][62]
- An inverted yield curve can indicate that a recession may be on the horizon as it has historically often preceded economic downturns with lead times ranging from several months to over a year. Especially the disinversion, a move back into positive territory for the spread between the shorter (e.g. 3-month or 2-year) yield and the longer (e.g. 10-year) Treasury yield, has in the past, been a reliable recession signal as the curve usually disinverts (or un-inverts) nearly before the recession truly appears. Based on recent history, the last four recessions, as of Q2-2024, didn't start until the inverted curve returned to a positive reading (steepens). Further analysis shows that "the average time to recession (...) [is] only 66 days from when the [3-month/10-year] curve disinverts."[90]
- The S&P 500 and BBB bond spread.[91]
- The federal budget deficit typically worsens strongly ahead of a recession.[73]
Business Expectations:
- Business confidence surveys and expectations for business condition.
- New businesses form at a slower rate when entrepreneurs are less likely to take the risk of starting a new venture while more established struggling businesses close down when a recession is looming.[83]
Margin of stock market traders:
- The value of debit balances in broker-dealers' securities margin accounts.[62]
Equity allocations of fund managers:
- Fund managers may increase or decrease equity exposure based on their outlook for the overall market. When AUM (assets under management) in the Bank of America's Global Fund Manager Survey (FMS) show that cash allocations have dropped at or below 4% (meaning fund managers with a higher risk tolerance are highly optimistic and their fund's exposure to the global equities market is in that case very high and therefore they have allocated a way above average portion of their portfolio to global equities) that historically triggers a contrarian sell signal. Quote from December 2024: "Since 2011, there have been 12 previous 'sell' signals, which resulted in global equity returns of -2.4% in the following month (...) following the triggering of the 'sell' signal."[92]
Asset Prices:
- Oil is a critical commodity input for many industries.
- Commodity prices, as measured e.g. by the Standard & Poor's (S&P) Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (GSCI),[62] may increase before recessions, which usually hinders consumer spending by making necessities like transportation and housing costlier. This will tend to constrict spending for non-essential goods and services. Once the recession occurs, commodity prices will usually reset to a lower level.
- A sector rotation in the stock market, specifically strong shifts in investment from leading more volatile sectors like consumer cyclicals and consumer discretionary (as well as e.g. biotechnology) to more stable sectors such as utilities and consumer staples (as well as e.g. telecommunications) can signal increasing market uncertainty and that a recession is on the horizon.[88]
- Lowering of asset prices, such as homes and financial assets, or high personal and corporate debt levels.
- Significant declines in stock prices can reflect investor pessimism about future economic conditions and can be a leading indicator of a recession.
- Volatility Index (VIX) measuring of stock market volatility. A high VIX indicates increased market stress, which can precede economic downturns.
Gross Domestic Product:
- GDP contraction: The GDP measures a country's economic output, all goods and services a country produces. GDP provides a good insight into what has already been taking place in the economy. A contraction in GDP, especially if it occurs for two consecutive quarters,[3] is a strong indicator of a recession as it reflects reduced economic activity, lower consumer demand, and decreased employment.
- GDP per capita contraction[93]
- The Atlanta Fed offers a GDPnow model, which estimates changes in real GDP growth by aggregating 13 subcomponents that make up GDP. GDPnow can provide a timelier gauge of the current state of the economy.[94]
Unorthodox Recession Indicators:
- Sausage sales: Heightened appetites for sausages might be a harbinger of a looming economic downturn, because sausages are a cheaper protein substitute for other higher-priced meat products,[95] a reaction by shoppers when times are tough experts call the "trade down."[96][97]
- Plunging underwear sales: During the 2008 financial crisis, men's underwear sales dropped significantly, mirroring reduced consumer spending and causing former Federal Reserve head Alan Greenspan to see men's underwear as a key economic predictor.[98]
Overview of recession indicators:
- Index of Leading (Economic) Indicators (LEI) (includes some of the above indicators).[99] The LEI's lead time is six to seven months.[32] The Conference Board's leading index is highly accurate in the near term, one to three months ahead (accomplishing an AUC value of 0.97).[62]
- Euro Area Leading Indicator (ALI) , research indicates that the ALI can lead turning points in the business cycle by approximately five to six months.
- The OECD Composite Leading Indicators (CLIs) the CLIs can lead economic turning points by approximately two to eight months (see PDF) or roughly six to nine months (see OECD video). They aggregate a variety of component indicators designed to provide early signals of trend changes in business cycles.[100]
- The Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas posts the Texas Index of Leading Economic Indicators. This index contains the real oil price, well permits, initial claims for unemployment insurance, Texas stock index, help-wanted index and average weekly hours worked in manufacturing.[101]
- The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago posts updates of the Brave-Butters-Kelley Indexes (BBKI).[102]
- The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis posts the Weekly Economic Index (Lewis-Mertens-Stock) (WEI).[103]
- The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis posts the Smoothed U.S. Recession Probabilities (RECPROUSM156N).[104]
- The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago's National Financial Conditions Index (NFCI) and its nonfinancial leverage subindex can be used as leading indicators to predict a recession.[62][105]
- The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago developed the ROC Threshold Index (ROC means receiver operating characteristic). It combines multiple leading indicators to predict recessions. It has shown better predictive ability than individual indicators up to 11 months ahead. And it also significantly outperformed other measures at leading recession forecasts with a range of six to nine months in advance.[62]
- The inverted yield curve,[106][107] the model developed by economist Jonathan H. Wright, uses yields on 10-year and three-month Treasury securities as well as the Fed's overnight funds rate.[108] Another model developed by Federal Reserve Bank of New York economists uses only the 10-year/three-month spread.[109][110][111] The Estrella and Mishkin model is a well-known approach for predicting U.S. recessions. This model primarily uses the yield curve, specifically the spread between long-term and short-term interest rates, as a predictor. This method has been widely adopted and is considered robust. The model, developed by economists Arturo Estrella and Frederic Mishkin, uses the difference between the yields on 10-year Treasury bonds and 3-month Treasury bills, as detailed in their research papers and working papers for the National Bureau of Economic Research. Their models estimate the 12-month-ahead recession probabilities using the term spread. This yield curve spread has been found to be a valuable forecasting tool, outperforming other financial and macroeconomic indicators in predicting recessions two to six quarters ahead.[112] An inversion of this yield curve has been successful in predicting past recessions, including those in 1973–75, and 1981–82. The Estrella and Mishkin model later also successfully predicted the recessions in the early 2000s, and the Great Recession of 2007–2009. Moreover, a negative spread has historically preceded each U.S. recession since the 1950s, according to The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
- The three-month change in the unemployment rate and initial jobless claims.[113] U.S. unemployment index is defined as the difference between the 3-month average of the unemployment rate and the 12-month minimum of the unemployment rate.[114] Unemployment momentum and acceleration with Hidden Markov model.[115]
- The RSM US Recession Monitor developed by Joseph Brusuelas, a member of the Wall Street Journal’s forecasting panel, is a scorecard "comprised of 21 variables selected as indicative readings of the business cycle, captured in five different areas of the economy" intended to provide key metrics to monitor the health of the U.S. economy.[30]
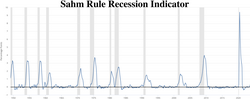
- The Sahm Recession Indicator, named after economist Claudia Sahm, was published in October 2019 by the St. Louis Federal Reserve bank's Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED). It is defined as:
Sahm Recession Indicator signals the start of a recession when the three-month moving average of the national unemployment rate (U3) rises by 0.50 percentage points or more relative to its low during the previous 12 months.[116]
Government responses
Keynesian economists favor the use of expansionary macroeconomic policy during recessions to increase aggregate demand.[117][118][119][120] Strategies favored for moving an economy out of a recession vary depending on which economic school the policymakers follow. Monetarists, exemplified by economist Milton Friedman, would favor the use of limited expansionary monetary policy, while Keynesian economists may advocate increased government spending to spark economic growth. Supply-side economists promote tax cuts to stimulate business capital investment. For example, the Trump administration claimed that lower effective tax rates on new investment imposed by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 would raise investment, thereby making workers more productive and raising output and wages. Investment patterns in the United States through 2019, however, indicated that the supply-side incentives of the TCJA had little effect on investment growth. Although investments increased after 2017, much of the increase was a response to oil prices, and investment in other sectors had negligible growth.[121]
Monetarist economists have argued that objectives of monetary policy, i.e., controlling the money supply to influence interest rates, are best achieved by targeting the growth rate of the money supply. They maintain that money may affect output in the short term but that in the long run, expansionary monetary policy leads to inflation only. Keynesian economists have mostly adopted this analysis, modifying the theory with better integration of short and long run trends and an understanding that a change in the money supply "affects only nominal variables in the economy, such as prices and wages, and has no effect on real variables, like employment and output".[122][123] The Federal Reserve traditionally uses monetary accommodation, a policy instrument of lowering its main benchmark interest rate, to accommodate sudden supply-side shifts in the economy. When the federal funds rate reaches the boundary of an interest rate of 0%, called the zero lower bound, the government resorts to unconventional monetary policy to stimulate recovery.[124]
Gauti B. Eggertsson of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, using a New Keynesian macroeconomic model for policy analysis, writes that cutting taxes on labor or capital is contractionary under certain circumstances, such as those that prevailed following the economic crisis of 2008, and that temporarily increasing government spending at such times has much larger effects than under normal conditions. He says other forms of tax cuts, such as a reduction in sales taxes and investment tax credits, e.g., in the context of Japan's "Great Recession", are also very effective. Eggertsson infers from his analysis that the contractionary effects of labor and capital tax cuts, and the strong expansionary effect of government spending, are peculiar to the unusual environment created by zero interest rates. He asserts that with positive interest rates a labor tax cut is expansionary, per the established literature, but at zero interest rates, it reverses and tax cuts become contractionary. Further, while capital tax cuts are inconsequential in his model with a positive interest rate, they become strongly negative at zero, and the multiplier of government spending is then almost five times larger.[125]
Paul Krugman wrote in December 2010 that significant, sustained government spending was necessary because indebted households were paying down debts and unable to carry the U.S. economy as they had previously: "The root of our current troubles lies in the debt American families ran up during the Bush-era housing bubble...highly indebted Americans not only can't spend the way they used to, they're having to pay down the debts they ran up in the bubble years. This would be fine if someone else were taking up the slack. But what's actually happening is that some people are spending much less while nobody is spending more—and this translates into a depressed economy and high unemployment. What the government should be doing in this situation is spending more while the private sector is spending less, supporting employment while those debts are paid down. And this government spending needs to be sustained..."[126]
John Maynard Keynes believed that government institutions could stimulate aggregate demand in a crisis.[127]
Stock market
Some recessions have been anticipated by stock market declines. In Stocks for the Long Run, Siegel mentions that since 1948, ten recessions were preceded by a stock market decline, by a lead time of 0 to 13 months (average 5.7 months), while ten stock market declines of greater than 10% in the Dow Jones Industrial Average were not followed by a recession.[128]
The real estate market also usually weakens before a recession.[129] However, real estate declines can last much longer than recessions.[130]
Since the business cycle is very hard to predict, Siegel has argued that it is not possible to take advantage of economic cycles for timing investments. Even the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) takes a few months to determine if a peak or trough has occurred in the US.[131]
Consequences
Unemployment
Unemployment is particularly high during a recession. Many economists working within the neoclassical paradigm argue that there is a natural rate of unemployment which, when subtracted from the actual rate of unemployment, can be used to estimate the GDP gap during a recession. In other words, unemployment never reaches 0%, so it is not a negative indicator of the health of an economy, unless it exceeds the "natural rate", in which case the excess corresponds directly to a loss in the GDP.[132]
The full impact of a recession on employment may not be felt for several quarters. After recessions in Britain in the 1980s and 1990s, it took five years for unemployment to fall back to its original levels.[133] Employment discrimination claims rise during a recession.[134]
Business
Productivity tends to fall in the early stages of a recession, then rises again as weaker firms close. The variation in profitability between firms rises sharply. The fall in productivity could also be attributed to several macro-economic factors, such as the loss in productivity observed across the UK due to Brexit, which may create a mini-recession in the region. Global epidemics, such as COVID-19, could be another example, since they disrupt the global supply chain or prevent the movement of goods, services, and people.
Recessions have also provided opportunities for anti-competitive mergers, with a negative impact on the wider economy; the suspension of competition policy in the United States in the 1930s may have extended the Great Depression.[133]
Social effects
The living standards of people dependent on wages and salaries are more affected by recessions than those who rely on fixed incomes or welfare benefits. The loss of a job has a negative impact on the stability of families, and individuals' health and well-being.[133]
History
Global
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), "Global recessions seem to occur over a cycle lasting between eight and 10 years."[135] The IMF takes many factors into account when defining a global recession. Until April 2009, IMF several times communicated to the press, that a global annual real GDP growth of 3.0% or less in their view was "equivalent to a global recession".[136][137]
By this measure, six periods since 1970 qualify: 1974–1975,[138] 1980–1983,[138] 1990–1993,[138][139] 1998,[138][139] 2001–2002,[138][139] and 2008–2009.[140] During what IMF in April 2002 termed the past three global recessions of the last three decades, global per capita output growth was zero or negative, and IMF argued—at that time—that because of the opposite being found for 2001, the economic state in this year by itself did not qualify as a global recession.[135]
In April 2009, IMF had changed their Global recession definition to "A decline in annual per‑capita real World GDP (purchasing power parity weighted), backed up by a decline or worsening for one or more of the seven other global macroeconomic indicators: Industrial production, trade, capital flows, oil consumption, unemployment rate, per‑capita investment, and per‑capita consumption."[141][142] By this new definition, a total of four global recessions took place since World War II: 1975, 1982, 1991 and 2009. All of them only lasted one year, although the third would have lasted three years (1991–1993) if IMF as criteria had used the normal exchange rate weighted per‑capita real World GDP rather than the purchase power parity weighted per‑capita real World GDP.[141][142]
Australia
As a result of late 1920s profit issues in agriculture and cutbacks, 1931–1932 saw Australia's biggest recession in its entire history. It fared better than other nations that underwent depressions, but their poor economic states influenced Australia, which depended on them for export, as well as foreign investments. The nation also benefited from greater productivity in manufacturing, facilitated by trade protection, which also helped with lessening the effects.
The economy had gone into a brief recession in 1961 because of a credit squeeze. Australia was facing a rising level of inflation in 1973, caused partially by the oil crisis happening in that same year, which brought inflation at a 13% increase. Economic recession hit by the middle of the year 1974, with no change in policy enacted by the government as a measure to counter the economic situation of the country. Consequently, the unemployment level rose and the trade deficit increased significantly.[143]
Another recession came at the beginning of the 1990s as the result of a major stock collapse in October 1987,[144] referred to now as Black Monday. Although the collapse was larger than the one in 1929, the global economy recovered quickly, but North America still suffered a decline in lumbering savings and loans, which led to a crisis. The recession was not limited to the United States, but it also affected partnering nations such as Australia. The unemployment level increased to 10.8%, employment declined by 3.4% and the GDP also decreased as much as 1.7%. Inflation, however, was successfully reduced.
Australia next went into recession in March 2020, due to the impact of huge bush fires and the COVID-19 pandemic's effect on tourism and other important aspects of the economy.[145] This recession, while steep, only lasted until May 2020.
European Union
The Eurozone experienced a recession in 2012: the economies of the 17-nation region failed to grow during any quarter of the 2012 calendar year. The recession deepened during the final quarter of the year, with the French, German and Italian economies all affected.[146]
United Kingdom
The most recent recession to affect the United Kingdom was the 2020 recession[147] attributed to the COVID-19 global pandemic, the first recession since the Great Recession.
United States


According to economists, since 1854, the U.S. has encountered 32 cycles of expansions and contractions, with an average of 17 months of contraction and 38 months of expansion.[16] From 1980 to 2018 there were only eight periods of negative economic growth over one fiscal quarter or more,[148] and four periods considered recessions:
- July 1981 – November 1982: 15 months
- July 1990 – March 1991: 8 months
- March 2001 – November 2001: 8 months
- December 2007 – June 2009: 18 months[149][150]
For the last three of these recessions, the NBER decision has approximately conformed with the definition involving two consecutive quarters of decline. While the 2001 recession did not involve two consecutive quarters of decline, it was preceded by two quarters of alternating decline and weak growth.[148]
Since then, the NBER has also declared a 2-month COVID-19 recession for February 2020 – April 2020.[151]
NBER has sometimes declared a recession before a second quarter of GDP shrinkage has been reported, but beginnings and endings can also be declared over a year after they are reckoned to have occurred. In 1947, NBER did not declare a recession despite two quarters of declining GDP, due to strong economic activity reported for employment, industrial production, and consumer spending.[152]
An administration generally gets credit or blame for the state of the economy during its time in office;[153] this state of affairs has caused disagreements about how particular recessions actually started.[154]
For example, the 1981 recession is thought to have been caused by the tight-money policy adopted by Paul Volcker, chairman of the Federal Reserve Board, before Ronald Reagan took office. Reagan supported that policy. Economist Walter Heller, chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers in the 1960s, said that "I call it a Reagan-Volcker-Carter recession."[155]
Late 2000s
Official economic data shows that a substantial number of nations were in recession as of early 2009. The US entered a recession at the end of 2007,[156] and 2008 saw many other nations follow suit. The US recession of 2007 ended in June 2009[157] as the nation entered the current economic recovery. The timeline of the Great Recession details the many elements of this period.
United States
The United States housing market correction (a consequence of the United States housing bubble) and subprime mortgage crisis significantly contributed to a recession.
The 2007–2009 recession saw private consumption fall for the first time in nearly 20 years. This indicated the depth and severity of the recession. With consumer confidence so low, economic recovery took a long time. Consumers in the U.S. were hit hard by the Great Recession, with the value of their houses dropping and their pension savings decimated on the stock market.[158]
U.S. employers shed 63,000 jobs in February 2008,[159] the most in five years. Former Federal Reserve chairman Alan Greenspan said on 6 April 2008 that "There is more than a 50 percent chance the United States could go into recession."[160] On 1 October, the Bureau of Economic Analysis reported that an additional 156,000 jobs had been lost in September. On 29 April 2008, Moody's declared that nine US states were in a recession. In November 2008, employers eliminated 533,000 jobs, the largest single-month loss in 34 years.[161] In 2008, an estimated 2.6 million U.S. jobs were eliminated.[162]
The unemployment rate in the U.S. grew to 8.5% in March 2009,[163] and there were 5.1 million job losses by March 2009 since the recession began in December 2007.[164] That was about five million more people unemployed compared to just a year prior,[165] which was the largest annual jump in the number of unemployed persons since the 1940s.[166]
Although the US economy grew in the first quarter by 1%,[167][168] by June 2008 some analysts stated that due to a protracted credit crisis and "rampant inflation in commodities such as oil, food, and steel", the country was nonetheless in a recession.[169] The third quarter of 2008 brought on a GDP retraction of 0.5%,[170] the biggest decline since 2001. The 6.4% decline in spending during Q3 on non-durable goods, like clothing and food, was the largest since 1950.[171]
A November 2008 report from the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia based on the survey of 51 forecasters, suggested that the recession started in April 2008 and would last 14 months.[172] They projected real GDP declining at an annual rate of 2.9% in the fourth quarter and 1.1% in the first quarter of 2009. These forecasts represented significant downward revisions from the forecasts of three months prior.
A December 2008 report from the National Bureau of Economic Research stated that the U.S. had been in a recession since December 2007, when economic activity peaked, based on several measures including job losses, declines in personal income, and declines in real GDP.[173] By July 2009, a growing number of economists believed that the recession may have ended.[174][175] The National Bureau of Economic Research announced on 20 September 2010 that the 2008/2009 recession ended in June 2009, making it the longest recession since World War II.[176] Prior to the start of the recession, it appears that no known formal theoretical or empirical model was able to accurately predict the advance of this recession, except for minor signals in the sudden rise of forecasted probabilities, which were still well under 50%.[110]
See also
- 1991 Indian economic crisis
- Credit crunch
- Deflation
- Depression
- Disinflation
- Economic collapse
- Economic stagnation
- Flooding the market
- Foreclosure
- Inventory bounce
- List of recessions in the United States
- Overproduction
- Stagflation
- Underconsumption
- COVID-19 recession
References
- ↑ "Recession". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/recession.
- ↑ "Encarta World English Dictionary [North American Edition"]. Encarta World English Dictionary [North American Edition]. Microsoft Corporation. 2007. http://encarta.msn.com/encnet/features/dictionary/DictionaryResults.aspx?refid=1861699686. Retrieved 19 November 2008.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Claessens, Stijn; Kose, M. Ayhan (2011). "Recession: When Bad Times Prevail - Back to Basics". https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/basics/recess.htm.
- ↑ "Business Cycle Dating Committee Announcement January 7, 2008". 2008-01-07. https://www.nber.org/cycles/jan08bcdc_memo.html.
- ↑ "FAQ | EABCN". https://eabcn.org/dc/faq.
- ↑ "The CEPR and NBER Approaches". https://eabcn.org/files/cepr-and-nber-approaches.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Q&A: What is a recession?". BBC News. 8 July 2008. https://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/7495340.stm.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Glossary of Treasury terms". HM Treasury. http://www.hm-treasury.gov.uk/junebudget_glossary.htm.
- ↑ Bonham, Mark S.; Poulin, Jessica (6 July 2023). "Recession in Canada". https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/recession.
- ↑ Deveau, Denise (3 August 2022). "An economist explains: What to know about a recession". https://www.cpacanada.ca/news/canada/recession-explainer.
- ↑ [7][8][9][10]
- ↑ Shiskin, Julius (1 December 1974). "Points of View" (in en-US). The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/1974/12/01/archives/the-changing-business-cycle-points-op-view.html.
- ↑ Dale, Edwin L. Jr (6 April 1974). "U.S. to Broaden the Base Of Consumer Price Index" (in en-US). The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/1974/04/06/archives/us-to-broaden-the-base-of-consumer-price-index-woodcock-criticism.html.
- ↑ Silk, Leonard (28 August 1974). "Recession: Some Criteria Missing, So Far" (in en-US). The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/1974/08/28/archives/recession-some-criteria-missing-so-far-there-will-be-no-recession.html.
- ↑ Lakshman, Achuthan; Banerji, Anirvan (May 7, 2008). "The risk of redefining recession". CNN Money. https://money.cnn.com/2008/05/05/news/economy/recession/.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Business Cycle Expansions and Contractions". National Bureau of Economic Research. https://www.nber.org/cycles/.
- ↑ Anstey, Chris (28 July 2022). "'Technical Recession' Sets Up Washington War of the Words". Bloomberg News. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-07-28/technical-recession-sets-up-washington-battle-of-words.
- ↑ Cox, Jeff (28 July 2022). "The economy may look like it's in recession, but we still don't know for sure". CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2022/07/28/the-economy-may-look-like-its-in-recession-but-we-still-dont-know-for-sure.html.
- ↑ Jacobsen, Louis (26 July 2022). "What exactly is a recession? Sorting out a confusing topic". PolitiFact. https://www.politifact.com/article/2022/jul/26/what-exactly-recession-sorting-out-confusing/.
- ↑ Loe, Megan; Lewis, Brandon (28 July 2022). "Yes, there is an official definition of a recession". KUSA.com. https://www.9news.com/article/news/verify/what-is-a-recession-official-definition/536-47a3cc51-3385-4f43-8fbd-1456c01536df.
- ↑ "Recession | U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA)". Bureau of Economic Analysis. 2022. https://www.bea.gov/help/glossary/recession.
- ↑ "OECD Economic Outlook, Volume 2008 Issue 2". oecd-ilibrary.org. OECD Economic Outlook. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. 2008. doi:10.1787/eco_outlook-v2008-2-en. ISBN 978-92-64-05469-1. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/oecd-economic-outlook-volume-2008-issue-2_eco_outlook-v2008-2-en.
- ↑ "Advance Warning Indicators of Past Severe GDP per Capita Recessions in Turkey". 11 October 2016. https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/advance-warning-indicators-of-past-severe-gdp-per-capita-recessions-in-turkey_5jlpq7swq4wf-en.html.
- ↑ Jiří, Mazurek (22 December 2012). "On some issues concerning definition of an economic recession". https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/43381/.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Koo, Richard (2009). The Holy Grail of Macroeconomics-Lessons from Japan's Great Recession. John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte. Ltd.. ISBN 978-0-470-82494-8.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Koo, Richard C. (12 December 2011). "The world in balance sheet recession: causes, cure, and politics". Real-World Economics Review (58): 19. http://www.paecon.net/PAEReview/issue58/Koo58.pdf. Retrieved 3 August 2022.
- ↑ Saul Eslake (Nov 2008). "What is the difference between a recession and a depression?". https://www.saul-eslake.com/difference-recession-depression/.
- ↑ Kaur, Rajwant; Sidhu, A.S. (Spring 2012). Sarkar, Siddhartha. ed. "Global Recession and Its Impact on Foreign Trade in India". International Journal of Afro-Asian Studies (Universal-Publishers) 3 (1): 62. ISBN 9781612336084. https://books.google.com/books?id=pGHTXAD9QnIC&pg=PA62.
- ↑ "Key Indicators 2001: Growth and Change in Asia and the Pacific". ADB.org. http://www.adb.org/Documents/Books/Key_Indicators/2001/default.asp.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Joseph Brusuelas (28 April 2025). "Introducing the RSM US Recession Monitor". https://realeconomy.rsmus.com/introducing-the-rsm-us-recession-monitor/.
- ↑ Joe Seydl (28 January 2025). "Five factors we use to track recession risk, and what they say now". https://privatebank.jpmorgan.com/nam/en/insights/markets-and-investing/five-factors-we-use-to-track-recession-risk-and-what-they-say-now.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 "The Conference Board Leading Economic Index® (LEI) for the U.S.". https://www.conference-board.org/topics/us-leading-indicators.
- ↑ Samuelson, Robert J. (14 June 2010). "Our economy's crisis of confidence". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/06/13/AR2010061303330.html.
- ↑ "The Conference Board – Consumer Confidence Survey Press Release – May 2010". Conference-board.org. 25 March 2010. http://www.conference-board.org/economics/consumerconfidence.cfm.
- ↑ Akerlof, George A.; Shiller, Robert J. (2010). Animal Spirits: How Human Psychology Drives the Economy, and Why It Matters for Global Capitalism. Princeton University Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-4008-3472-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=2Rz_cuu88DwC&pg=PR23.
- ↑ Shiller, Robert J. (27 January 2009). "Animal Spirits Depend on Trust". The Wall Street Journal. https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB123302080925418107.
- ↑ How to be an Adult (13 May 2020). "Psychological Biases and Errors that led to historic bubbles and crashes". https://medium.com/@how.to.be.an.adult.01/biases-and-errors-that-led-to-historic-bubbles-and-crashes-52df73cf44f.
- ↑ Jupe, Robert (2014). "Accounting, balance sheet". in Michie, Jonathan. Reader's Guide to the Social Sciences. Routledge. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-135-93226-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=ip_IAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA11.
- ↑ Krugman, Paul (10 July 2014). "Does He Pass the Test? 'Stress Test: Reflections on Financial Crises' by Timothy Geithner". New York Review of Books. http://www.nybooks.com/articles/archives/2014/jul/10/geithner-does-he-pass-test/. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- ↑ White, Gregory (14 April 2010). "Presentation by Richard Koo – The Age of Balance Sheet Recessions". Business Insider. http://www.businessinsider.com/richard-koo-recession-2010-4#-1.
- ↑ Krugman, Paul (17 August 2010). "Notes On Koo (Wonkish)". The New York Times. https://krugman.blogs.nytimes.com/2010/08/17/notes-on-koo-wonkish/.
- ↑ Krugman, Paul (18 November 2010). "Debt, deleveraging, and the liquidity trap". Voxeu.org). https://voxeu.org/article/debt-deleveraging-and-liquidity-trap-new-model.
- ↑ Eggertsson, Gauti B. (2018). "Liquidity Trap" (in en). The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 7929–7936. doi:10.1057/978-1-349-95189-5_2482. ISBN 978-1-349-95189-5. https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1057/978-1-349-95189-5_2482.
- ↑ Correia, Isabel; Farhi, Emmanuel; Nicolini, Juan Pablo; Teles, Pedro (August 2012). "Unconventional Fiscal Policy at the Zero Bound: Working Paper 698". Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. p. 1. https://www.minneapolisfed.org/research/wp/wp698.pdf.
- ↑ Krugman, Paul (2009). The Return of Depression Economics and the Crisis of 2008. W.W. Norton Company Limited. ISBN 978-0-393-07101-6. https://archive.org/details/returnofdepressi00krug.
- ↑ "How Much of the World is in a Liquidity Trap?". Krugman.blogs.nytimes.com. 17 March 2010. https://krugman.blogs.nytimes.com/2010/03/17/how-much-of-the-world-is-in-a-liquidity-trap/.
- ↑ Lipsey, Richard G.; Harbury, Colin (1992). First Principles of Economics. Oxford University Press. p. 294. ISBN 978-0-297-82120-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=cV0EZuJxod8C&pg=PA294.
- ↑ "A Minsky Meltdown: Lessons for Central Bankers". 16 April 2009. https://www.frbsf.org/our-district/press/presidents-speeches/yellen-speeches/2009/april/yellen-minsky-meltdown-central-bankers/.
- ↑ Cochrane, John (December 7, 2022). "Recessions are difficult, but stagnant growth could prove more challenging, Stanford economist warns". https://news.stanford.edu/stories/2022/12/why-recessions-are-misunderstood.
- ↑ Peck, Emily (December 22, 2023). "Why everyone was so wrong about the 2023 economy". Axios. https://www.axios.com/2023/12/22/2023-economy-predictions-wrong-recession.
- ↑ Barbuscia, Davide (July 29, 2024). "US yield curve nears flip with jury out on recession signal". Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/markets/rates-bonds/us-yield-curve-nears-flip-with-jury-out-recession-signal-2024-07-29/#:~:text=%22Right%20now%2C%20as%20the%20yield,previous%20inversion%20record%20from%201978..
- ↑ "10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity Minus 2-Year Treasury Constant Maturity". Federal Reserve Economic Data. https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/T10Y2Y.
- ↑ Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Consumer Confidence: A Useful Indicator of ... the Labor Market?
Jason Bram, Robert Rich, and Joshua Abel ... Conference Board's Present Situation Index
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Wall Street starts 2017 with tailwind | By Juergen Buettner | 4 January 2017 | Chart 1: Consumer Confidence Index and Historically Shocks". https://www.journal.ky/2017/01/04/wall-street-starts-2017-with-tailwind/.
- ↑ Consumer Confidence Drops – Why Does It Matter? Forbes. 27 June 2019. Brad McMillan.
- ↑ "Gundlach: We don't see a recession on the horizon. But there's bad news...". Yahoo! Finance. 14 February 2019. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/gundlach-recession-prediction-030834565.html.
- ↑ "Seeking Alpha | Take Me To Your Leader: Analyzing The Latest Leading Indicators | by −1.9% | 24 September 2019". https://seekingalpha.com/article/4293195-take-leader-analyzing-latest-leading-indicators.
- ↑ "Background on the Chicago Fed National Activity Index | Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago | 19 September 2019". https://www.chicagofed.org/~/media/publications/cfnai/background/cfnai-background-pdf.pdf.
- ↑ "Grim Stock Signals Piling Up as Wall Street Mulls Recession Odds". Bloomberg L.P.. 25 November 2018. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-11-25/grim-stock-signals-piling-up-as-wall-street-mulls-recession-odds.
- ↑ A Estrella, FS Mishkin (1995). "Predicting U.S. Recessions: Financial Variables as Leading Indicators". Review of Economics and Statistics (MIT Press) 80: 45–61. doi:10.1162/003465398557320. http://www.nber.org/papers/w5379.pdf. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- ↑ Ozyildirim, Ataman. "Leading Economic Indicators and the Oncoming Recession". https://www.conference-board.org/publications/pdf/index.cfm?brandingURL=Leading-Indicators-Recession.
- ↑ 62.00 62.01 62.02 62.03 62.04 62.05 62.06 62.07 62.08 62.09 62.10 62.11 62.12 Kelley, David (2019). "Which Leading Indicators Have Done Better at Signaling Past Recessions?". https://www.chicagofed.org/publications/chicago-fed-letter/2019/425.
- ↑ Stuart M. Glosser, Lonnie Golden (1997). "Average work hours as a leading economic variable in US manufacturing industries". International Journal of Forecasting (Elsevier) 13 (2): 175–195. doi:10.1016/S0169-2070(96)00725-X. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S016920709600725X. Retrieved 5 August 2024.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Backus, David (2024). "Business-Cycle Indicators". https://pages.stern.nyu.edu/~dbackus/2303/notes_indicators.pdf.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 Edwards, William (31 August 2024). "Stock Market Crash: Expert Warns of 70% Potential Downside for S&P 500". Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/stock-market-crash-recession-indicators-labor-market-rate-cuts-hussman-2024-8.
- ↑ Premack, Rachel. "The "bloodbath" in America's trucking industry has officially spilled over to the rest of the economy". https://www.businessinsider.com/trucking-truckers-bloodbath-signals-recession-inverted-yield-2019-8.
- ↑ "Cass Freight Index Report". August 2019. https://www.cassinfo.com/hubfs/Freight%20Payment%20/Transportation%20Indexes/Cass%20Freight%20Index/Reports/Cass%20Freight%20Index%20Report%20-%20August%202019.pdf?hsCtaTracking=5fde9be4-1dd0-462f-8c5f-b100aca52fc1%7C0990f099-885d-442a-972a-aeb259c5a188.
- ↑ "Research Confirms Transportation Index as Leading Indicator". December 15, 2017. https://www.bts.gov/newsroom/research-confirms-transportation-index-leading-indicator.
- ↑ Smith, Stacey Vanek (12 September 2024). "Why the inverted yield curve is typically a recession predictor". Marketplace. https://www.marketplace.org/2024/09/12/inverted-yield-curve-recession-predictor-indicator/.
- ↑ Conerly, Bill (15 August 2019). "How Bad Is The U.S. Economy In 2019?". Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/billconerly/2019/08/15/how-bad-is-the-us-economy-in-2019/.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 Fisher, Ken (2024). "Bear Market Indicators". https://www.fisherinvestments.com/en-us/resource-library/market-cycles/bear-markets/indicators.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 72.3 "Recessionary Indicators". https://www.gurufocus.com/news/2508303/recessionary-indicators.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 Wisenberg Brin, Dinah (11 September 2024). "Jeffrey Gundlach: 6 Signs Recession Is Near, or Here". ThinkAdvisor. https://www.thinkadvisor.com/2024/09/11/jeffrey-gundlach-6-signs-recession-is-near-or-here/.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 Cloonan, Kelly (25 September 2024). "2 under-the-radar recession signals are flashing red this month, research firm says". Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/labor-market-indicators-recession-warning-signs-bca-research-berezin-2024-9.
- ↑ Fox, Matthew (26 August 2024). "The Sahm Rule has flashed, but there's a simpler recession indicator investors should be watching". Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/recession-indicator-perkins-rule-negative-payroll-report-sahm-unemployment-rate-2024-8.
- ↑ Adinolfi, Joseph (7 May 2024). "A reliable labor-market recession indicator has triggered — but this time it could be bullish for stocks". Marketwatch. https://www.marketwatch.com/livecoverage/stock-market-today-dow-futures-flat-after-1000-point-rally-in-four-days/card/a-reliable-labor-market-recession-indicator-has-triggered-but-this-time-it-could-be-bullish-for-stocks-sXgJRUlCo2TNywR6XgDc.
- ↑ Edwards, William (3 August 2024). "2 recession indicators with perfect track records show the US just entered a downturn — opening the door for stocks to plummet as the Fed gets set to cut rates". Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/stock-market-crash-recession-indicators-jobs-report-unemploymnet-rate-sp500-2024-8.
- ↑ Payne, Charles (7 August 2024). "Sahm Rule is picking up on something that's 'very worrisome' - New Century Advisors chief economist Claudia Sahm weighs in on the Fed's next rate move". FOX Business. https://www.foxbusiness.com/video/6360053882112.
- ↑ Goldstein, Steve (18 September 2024). "The unemployment measure you've never heard is flashing a recession warning". Marketwatch. https://www.marketwatch.com/story/the-unemployment-measure-youve-never-heard-is-flashing-a-recession-warning-1ccfd4ad.
- ↑ "Income and wealth inequality make recessions worse, research reveals". 2016. https://phys.org/news/2016-08-income-wealth-inequality-recessions-worse.html.
- ↑ Neves, Pedro Cunha; Afonso, Óscar; Silva, Sandra Tavares (February 2016). "A Meta-Analytic Reassessment of the Effects of Inequality on Growth". World Development 78: 386–400. doi:10.1016/j.worlddev.2015.10.038.
- ↑ Sor, Jennifer (25 September 2024). "A key US consumer indicator has dipped to 'crisis levels,' SocGen says". Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/recession-outlook-savings-household-spending-economy-2008-financial-crisis-2024-9.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 83.2 83.3 83.4 Wade, Jacob (16 July 2024). "5 Buying Habits That Experts Believe Are Key Signs of a Looming Recession". yahoo! finance. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/5-buying-habits-experts-believe-110110863.html.
- ↑ Raice, Shayndi (19 August 2019). "An Economic Warning Sign: RV Shipments Are Slipping". The Wall Street Journal. https://www.wsj.com/articles/one-countys-rv-industry-points-to-recession-around-the-bend-11566207001.
- ↑ Nash, Jennifer. "Conference Board Leading Economic Index: Continued to Trend Down in June". https://www.advisorperspectives.com/dshort/updates/2024/07/18/cb-leading-economic-index-continued-to-trend-down-in-june.
- ↑ Are Aastveit, Knut; Anundsen, André K.; Herstad, Eyo I. (October–December 2019). "Residential investment and recession predictability". International Journal of Forecasting 35 (4): 1790–1799. doi:10.1016/j.ijforecast.2018.09.008.
- ↑ Mackie, Kevin (7 December 2018). "Forecasting The Next Recession Using The Architectural Billings Index". https://seekingalpha.com/article/4227045-forecasting-next-recession-using-architectural-billings-index.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 Schmidt, Dan (April 17, 2024). "Predicting a Bear Market: 7 Signs and Why it's Tough to Do". https://www.marketbeat.com/learn/predicting-a-bear-market-7-signs-and-why-its-tough-to-do/.
- ↑ Engstrom, Eric C.; Sharpe, Steven A. (February 2019). "The near-term forward yield spread as a leading indicator: A less distorted mirror". Finance and Economics Discussion Series. 2018-055 (Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System) 2018.0 (55r1). doi:10.17016/FEDS.2018.055r1. https://www.federalreserve.gov/econres/feds/the-near-term-forward-yield-spread-as-a-leading-indicator-a-less-distorted-mirror.htm.
- ↑ McGeever, Jamie (5 June 2024). "Yield curve disinversion is the recession signal to watch". Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/markets/us/yield-curve-disinversion-is-recession-signal-watch-2024-06-04/.
- ↑ [1] JPMorgan | The US Economic Outlook | Feb. 2020 | Page 22]
- ↑ Webb, Niklas (19 December 2024). "BofA: Fund manager survey (12/19/2024)". https://sellside.substack.com/p/bofa-fund-manager-survey-12192024.
- ↑ Dwyer, Gerald P.; Devereux, John; Baier, Scott; Tamura, Robert (2013). "Recessions, growth and banking crises". Journal of International Money and Finance 38: 18–40. doi:10.1016/j.jimonfin.2013.05.009. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/SSRN_ID2269676_code16268.pdf?abstractid=2269676&mirid=2.
- ↑ "GDPNow - Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta". 10 August 2024. https://www.atlantafed.org/cqer/research/gdpnow.
- ↑ "Texas Manufacturing Outlook Survey - Comments from survey respondents". 26 August 2024. https://www.dallasfed.org/research/surveys/tmos/2024/2408#tab-comments.
- ↑ Harring, Alex (26 August 2024). "Increased sausage demand could be worrying signal on the economy". CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2024/08/26/increased-sausage-demand-could-be-worrying-signal-on-the-economy.html.
- ↑ Ashworth, Louis (27 August 2024). "The latest US recession indicator just dropped — and it's a banger (Prepare for the wurst)". Financial Times. https://www.ft.com/content/325487cd-d771-451e-9e8e-93a6176d93d9.
- ↑ Goodkind, Nicole (26 March 2022). "Is a recession coming? Alan Greenspan says the answer is in men's underwear". CNN. https://edition.cnn.com/2022/03/26/economy/recession-underwear-alan-greenspan/index.html.
- ↑ Leading Economic Indicators Suggest U.S. In Recession 21 January 2008
- ↑ [0=Topic%2C1%7CEconomy%23ECO%23%7CLeading%20indicators%20and%20tendency%20surveys%23ECO_LEA%23&pg=0&fc=Topic&bp=true&snb=4&df[ds]=dsDisseminateFinalDMZ&df[id]=DSD_STES%40DF_CLI&df[ag]=OECD.SDD.STES&df[vs]=4.1&dq=.M.LI...AA...H&lom=LASTNPERIODS&lo=10&to[TIME_PERIOD]=false "OECD Data Explorer: Composite Leading Indicators"]. https://data-explorer.oecd.org/vis?fs[0]=Topic%2C1%7CEconomy%23ECO%23%7CLeading%20indicators%20and%20tendency%20surveys%23ECO_LEA%23&pg=0&fc=Topic&bp=true&snb=4&df[ds]=dsDisseminateFinalDMZ&df[id]=DSD_STES%40DF_CLI&df[ag]=OECD.SDD.STES&df[vs]=4.1&dq=.M.LI...AA...H&lom=LASTNPERIODS&lo=10&to[TIME_PERIOD]=false.
- ↑ "Texas Leading Index". 22 August 2024. https://www.dallasfed.org/research/econdata/tli.
- ↑ "A 'Big Data' View of the U.S. Economy: Introducing the Brave-Butters-Kelley Indexes – Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago". https://www.chicagofed.org/publications/chicago-fed-letter/2019/422.
- ↑ "Weekly Economic Index (Lewis-Mertens-Stock)". 5 January 2008. https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/WEI.
- ↑ "Smoothed U.S. Recession Probabilities". 1 February 1967. https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/RECPROUSM156N.
- ↑ "Chicago Fed National Financial Conditions Index (NFCI)". 7 August 2024. https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/NFCI.
- ↑ Ulatan, Jeffrey (3 July 2020). "2020 Recession Signals, After US-Iran Airstrike. Vanguard ETF Best Performing Funds for 2020". Harvard Dataverse. doi:10.7910/DVN/AWWQPN.
- ↑ Grading Bonds on Inverted Curve By Michael Hudson
- ↑ Wright, Jonathan H., The Yield Curve and Predicting Recessions (March 2006). FEDs Working Paper No. 2006-7.
- ↑ "The Yield Curve as a Leading Indicator". Federal Reserve Bank of New York. 2020. https://www.newyorkfed.org/research/capital_markets/ycfaq.html#/interactive.
- ↑ 110.0 110.1 Park, Byeong U.; Simar, Léopold; Zelenyuk, Valentin (2019-05-15). "Forecasting of recessions via dynamic probit for time series: replication and extension of Kauppi and Saikkonen (2008)". Empirical Economics (Springer Science and Business Media LLC) 58 (1): 379–392. doi:10.1007/s00181-019-01708-2. ISSN 0377-7332. https://dial.uclouvain.be/pr/boreal/fr/object/boreal%3A196164/datastream/PDF_01/view.
- ↑ [2] Using the U.S. Treasury Yield Curve to predict S&P 500 returns and U.S. recessions | Theodore Gregory Hanks | Pennsylvania State University, Schreyer Honors College Department of Finance | Spring 2012
- ↑ Estrella, Arturo; Mishkin, Frederic S. (June 1996). "The Yield Curve as a Predictor of U.S. Recessions" (in en). The Federal Reserve Bank of New York. https://www.newyorkfed.org/research/current_issues/ci2-7.html.
- ↑ "Labor Model Predicts Lower Recession Odds". The Wall Street Journal. 28 January 2008. https://blogs.wsj.com/economics/2008/01/28/labor-model-predicts-lower-recession-odds/.
- ↑ Sahm, Claudia (6 May 2019). "Direct Stimulus Payments to Individuals". https://www.hamiltonproject.org/assets/files/Sahm_web_20190506.pdf.
- ↑ Lihn, Stephen H. T. (10 August 2019). "Real-time Recession Probability with Hidden Markov Model and Unemployment Momentum". SSRN 3435667.
- ↑ "Sahm Rule Recession Indicator". Federal Reserve Economic Data. https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/SAHMCURRENT. "Sahm Recession Indicator signals the start of a recession when the three-month moving average of the national unemployment rate (U3) rises by 0.50 percentage points or more relative to the minimum of the three-month averages from the previous 12 months"
- ↑ Stiglitz, Joseph E.; Ocampo, José Antonio, eds (2008). Capital Market Liberalization and Development. OUP Oxford. p. 360. ISBN 978-0-19-923058-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=u8OTK5cIOSoC&pg=PA360.
- ↑ Ahuja, H.L. (2019). "Monetarism and Friedman's Restatement of Quantity Theory of Money". Macroeconomics, 20e. S. Chand Publishing. p. 527. ISBN 978-93-5283-732-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=7psGEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA527.
- ↑ Thornton, Saranna (2018). Bucking The Deficit: Economic Policymaking In America. Routledge. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-429-97052-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=jwHFDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA30.
- ↑ Mason, J.W (2020). "Chapter 1: Macroeconomic lessons from the past decade". in MacLean, Brian K.; Bougrine, Hassan; Rochon, Louis-Philippe. Aggregate Demand and Employment: International Perspectives. Edward Elgar Publishing. p. 29. ISBN 978-1-78643-205-6. https://www.elgaronline.com/downloadpdf/edcoll/9781786432049/9781786432049.00009.xml.
- ↑ Gale, William G.; Haldeman, Claire (6 July 2021). "Searching for supply-side effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act". pp. 3–4. https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/20210628_TPC_GaleHaldeman_TCJASupplySideEffectsReport_FINAL.pdf.
- ↑ Jahan, Sarwat; Mahmud, Ahmed Saber; Papageorgiou, Chris (September 2014). "What Is Keynesian Economics? – Back to Basics". Finance & Development 51 (1): 54. https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2014/09/pdf/basics.pdf.
- ↑ Jahan, Sarwat; Papageorgiou, Chris (March 2014). "What Is Monetarism? – Back to Basics". Finance and Development 51 (1): 38. https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2014/03/pdf/basics.pdf.
- ↑ Skaperdas, Arsenios (7 July 2017). "How Effective is Monetary Policy at the Zero Lower Bound? Identification Through Industry Heterogeneity". pp. 2–3. https://www.federalreserve.gov/econres/feds/files/2017073pap.pdf.
- ↑ Eggertsson, Gauti B. (1 January 2011). "What Fiscal Policy Is Effective at Zero Interest Rates?". NBER Macroeconomics Annual 25: 59–60. doi:10.1086/657529. ISSN 0889-3365. https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/full/10.1086/657529.
- ↑ Krugman, Paul (13 December 2010). "Opinion – Block Those Economic Metaphors". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2010/12/13/opinion/13krugman.html.
- ↑ Nayak, Pulin B. (2009). "Anatomy of the Financial Crisis: Between Keynes and Schumpeter". Economic and Political Weekly 44 (13): 160. ISSN 0012-9976. https://www.jstor.org/stable/40278675.
- ↑ Siegel, Jeremy J. (2002). Stocks for the Long Run: The Definitive Guide to Financial Market Returns and Long-Term Investment Strategies, 3rd, New York: McGraw-Hill, 388. ISBN 978-0-07-137048-6
- ↑ "From the subprime to the terrigenous: Recession begins at home". Land Values Research Group. 2 June 2009. http://lvrg.org.au/blog/2009/06/from-subprime-to-terrigenous-recession.html. "A downturn in the property market, especially in turnover (sales) of properties, is a leading indicator of recession, with a lead time of up to 9 quarters..."
- ↑ Shiller, Robert J. (6 June 2009). "Why Home Prices May Keep Falling". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2009/06/07/business/economy/07view.html.
- ↑ Sloan, Allan (11 December 2007). "Recession Predictions and Investment Decisions". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/12/10/AR2007121001589.html.
- ↑ Unemployment Rate p. 1. The Saylor Foundation. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ↑ 133.0 133.1 133.2 Vaitilingam, Romesh (17 September 2009). "Recession Britain: New ESRC report on the impact of recession on people's jobs, businesses and daily lives". Economic and Social Research Council. http://www.esrc.ac.uk/ESRCInfoCentre/PO/releases/2009/september/recessionbritain.aspx.
- ↑ Rampell, Catherine (11 January 2011). "More Workers Complain of Bias on the Job, a Trend Linked to Widespread Layoffs". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2011/01/12/business/12bias.html?ref=business.
- ↑ 135.0 135.1 The Recession that Almost Was. Kenneth Rogoff, International Monetary Fund, Financial Times, 5 April 2002
- ↑ "The world economy Bad, or worse". The Economist. 9 October 2008. https://www.economist.com/finance/displaystory.cfm?story_id=12381879.
- ↑ Lall, Subir. International Monetary Fund, 9 April 2008. "IMF Predicts Slower World Growth Amid Serious Market Crisis"
- ↑ 138.0 138.1 138.2 138.3 138.4 Global Economic Slump Challenges Policies IMF. January 2009.
- ↑ 139.0 139.1 139.2 "Global Recession Risk Grows as U.S. "Damage" Spreads. Jan 2008". Bloomberg L.P.. 28 January 2008. https://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=20601087&sid=arlKrFbn3pfY&refer=home.
- ↑ "World Economic Outlook (WEO) April 2013: Statistical appendix – Table A1 – Summary of World Output". IMF. 16 April 2013. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/01/pdf/tables.pdf.
- ↑ 141.0 141.1 Davis, Bob (22 April 2009). "What's a Global Recession?". The Wall Street Journal. https://blogs.wsj.com/economics/2009/04/22/whats-a-global-recession/.
- ↑ 142.0 142.1 "World Economic Outlook – April 2009: Crisis and Recovery". Box 1.1 (pp. 11–14). IMF. 24 April 2009. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2009/01/pdf/text.pdf.
- ↑ Australian Economic Indicators, Australian Bureau of Statistics, 27 February 1998, http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/90a12181d877a6a6ca2568b5007b861c/d4a22ad91e0348bfca256fd3007baf93!OpenDocument, retrieved 11 August 2015
- ↑ "Reasons for 1990s Recession", The Age (Melbourne), 2 December 2006, http://www.theage.com.au/news/business/the-real-reasons-why-it-was-the-1990s-recession-we-had-to-have/2006/12/01/1164777791623.html?page=3, retrieved 11 August 2015
- ↑ Janda, Michael (3 June 2020), Australian Recession, Australian Broadcasting Corporation, https://www.abc.net.au/news/2020-06-03/australian-economy-gdp-recession-march-quarter-2020/12315140, retrieved 3 June 2020
- ↑ "Eurozone recession deepened at end of 2012". 2013-02-14. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-21455423.
- ↑ "UK officially in recession for first time in 11 years". The BBC. 12 August 2020. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-53748278.
- ↑ 148.0 148.1 "Percent change from preceding period". U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). https://www.bea.gov/national/xls/gdpchg.xls.
- ↑ Isidore, Chris (1 December 2008). "It's official: Recession since Dec. '07". CNN. https://money.cnn.com/2008/12/01/news/economy/recession/index.htm?postversion=2008120112.
- ↑ "US economy out of recession". BBC News – Business. 29 October 2009. https://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/8332773.stm.
- ↑ "Business Cycle Dating Committee Announcement July 19, 2021". 19 July 2021. https://www.nber.org/news/business-cycle-dating-committee-announcement-july-19-2021.
- ↑ Blake, Aaron (July 28, 2022). "What two negative GDP quarters means for 'recession' – and our politics". The Washington Post.
- ↑ "Economy puts Republicans at risk". BBC. 29 January 2008. https://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/7215351.stm.
- ↑ The Bush Recession Prepared by: Democratic staff, Senate Budget Committee, 31 July 2003
- ↑ Church, George J. (23 November 1981). "Ready for a Real Downer". Time. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,922689-2,00.html.
- ↑ "Determination of the December 2007 Peak in Economic Activity.". NBER Business Cycle Dating Committee. 11 December 2008. https://www.nber.org/cycles/dec2008.pdf.
- ↑ Izzo, Phil (20 September 2010). "Recession Over in June 2009". The Wall Street Journal. https://blogs.wsj.com/economics/2010/09/20/nber-recession-ended-in-june-2009/.
- ↑ Economic Crisis: When will it End? IBISWorld Recession Briefing " Dr. Richard J. Buczynski and Michael Bright, IBISWorld, January 2009
- ↑ Andrews, Edmund L. (7 March 2008). "Employment Falls for Second Month". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2008/03/07/business/07cnd-econ.html.
- ↑ Recession unlikely if US economy gets through next two crucial months
- ↑ Uchitelle, Louis; Andrews, Edmund L.; Labaton, Stephen (6 December 2008). "U.S. Loses 533,000 Jobs in Biggest Drop Since 1974". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2008/12/06/business/economy/06jobs.html.
- ↑ Uchitelle, Louis (9 January 2009). "U.S. lost 2.6 million jobs in 2008". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2009/01/09/business/worldbusiness/09iht-jobs.4.19232394.html.
- ↑ Unemployment rate in March 2009 6 April 2009. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ 2 million jobs lost so far in '09 CNN/Money. 3 April 2009. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ "Employment Situation Summary". Bls.gov. 2 July 2010. http://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.nr0.htm.
- ↑ Goldman, David (9 January 2009). "Worst year for jobs since '45". CNN. https://money.cnn.com/2009/01/09/news/economy/jobs_december/index.htm.
- ↑ Meyer, Brent (16 October 2008). "Real GDP First-Quarter 2008 Preliminary Estimate :: Brent Meyer :: Economic Trends :: 06.03.08 :: Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland". Clevelandfed.org. http://www.clevelandfed.org/research//trends/2008/0608/01ecoact.cfm.
- ↑ "Fragile economy improves but not out of woods yet". Yahoo! Finance. https://finance.yahoo.com/.
- ↑ Why it's worse than you think , 16 June 2008, Newsweek.
- ↑ "Gross Domestic Product: Third quarter 2008". Bea.gov. https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/gdpnewsrelease.htm.
- ↑ Chandra, Shobhana (30 October 2008). "U.S. Economy Contracts Most Since the 2001 Recession". Bloomberg. https://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=20601087&sid=aB3KBZXgh.Rk&refer=home.
- ↑ "Fourth quarter 2008 Survey of Professional Forecasters". Philadelphiafed.org. 17 November 2008. http://www.philadelphiafed.org/research-and-data/real-time-center/survey-of-professional-forecasters/2008/survq408.cfm?loc=interstitialskip.
- ↑ "Text of the NBER's statement on the recession". USA Today. 1 December 2008. https://www.usatoday.com/money/economy/2008-12-01-recession-nber-statement_N.htm.
- ↑ Gross, Daniel (2009-07-13). "Daniel Gross: The Recession is Over?". https://www.newsweek.com/daniel-gross-recession-over-82097.
- ↑ Keilis-Borok, V. I.; Soloviev, A. A.; Intriligator, M. D.; Winberg, F. E. (2008). "Pattern of Macroeconomic Indicators Preceding the End of an American Economic Recession". Journal of Pattern Recognition Research 3 (1): 40–53. doi:10.13176/11.106. ISSN 1558-884X. http://jprr.org/index.php/jprr/article/viewFile/106/23. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ↑ "Business Cycle Dating Committee, National Bureau of Economic Research". 20 September 2010. https://www.nber.org/cycles/sept2010.html.
External links
| Library resources about Recession |
- Moore, Geoffrey H. (2002). "Recessions". in Henderson, David R.. Concise Encyclopedia of Economics (1st ed.). Library of Economics and Liberty. http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc1/Recessions.html. OCLC 317650570, 50016270, 163149563
- Business Cycle Expansions and Contractions The National Bureau Of Economic Research
Template:United States – Commonwealth of Nations recessions
de:Konjunktur#Rezession
 |
 KSF
KSF