Form (HTML)
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
A webform, web form or HTML form on a web page allows a user to enter data that is sent to a server for processing. Forms can resemble paper or database forms because web users fill out the forms using checkboxes, radio buttons, or text fields. For example, forms can be used to enter shipping or credit card data to order a product, or can be used to retrieve search results from a search engine.
Description
Forms are enclosed in the HTML <form> element. This element specifies the communication endpoint the data entered into the form should be submitted to, and the method of submitting the data, GET or POST.
Elements
Forms can be made up of standard graphical user interface elements:
<text>— a simple text box that allows input of a single line of text.<email>- a type of<text>that requires a partially validated email address<number>- a type of<text>that requires a number<password>— similar to<text>, it is used for security purposes, in which the characters typed in are invisible or replaced by symbols such as *<radio>— a radio button<file>— a file select control for uploading a file<reset>— a reset button that, when activated, tells the browser to restore the values to their initial values.<submit>— a button that tells the browser to take action on the form (typically to send it to a server)<textarea>— much like the<text>input field except a<textarea>allows for multiple rows of data to be shown and entered<select>— a drop-down list that displays a list of items a user can select from
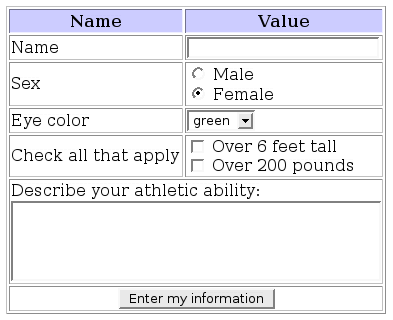
The sample image on the right shows most of these elements:
- a text box asking for your name
- a pair of radio buttons asking you to pick your sex
- a select box giving you a list of eye colors to choose from
- a pair of check boxes to click on if they apply to you
- a text area to describe your athletic ability
- a submit button to send it to the server
These basic elements provide most common graphical user interface (GUI) elements, but not all. For example, there are no equivalents to a tree view or grid view.
A grid view, however, can be mimicked by using a standard HTML table with each cell containing a text input element. A tree view could also be mimicked through nested tables or, more semantically appropriately, nested lists. In both cases, a server-side process is responsible for processing the information, while JavaScript handles the user-interaction. Implementations of these interface elements are available through JavaScript libraries such as jQuery.
HTML 4 introduced the <label> tag, which is intended to represent a caption in a user interface, and can be associated with a specific form control by specifying the id attribute of the control in the label tag's for attribute.[1] This allows labels to stay with their elements when a window is resized and to allow more desktop-like functionality (e.g. clicking a radio button or checkbox's label will activate the associated input element).
HTML 5 introduces a number of input tags that can be represented by other interface elements. Some are based upon text input fields and are intended to input and validate specific common data. These include <email> to enter email addresses, <tel> for telephone numbers, <number> for numeric values. There are additional attributes to specify required fields, fields that should have keyboard focus when the web page containing the form is loaded, and placeholder text that is displayed within the field but is not user input (such as the 'Search' text displayed in many search input fields before a search term is entered). These tasks used to be handled with JavaScript, but had become so common that support for them was added to the standard. The <date> input type displays a calendar from which the user can select a date or date range.[2][3] And the color input type can be represented as an input text simply checking the value entered is a correct hexadecimal representation of a color, according to the specification,[4] or a color picker widget (the latter being the solution used in most browsers which support this attribute).
Submission
When data that has been entered into HTML forms is submitted, the names and values in the form elements are encoded and sent to the server in an HTTP request message using GET or POST. Historically, an email transport was also used.[5] The default MIME type (internet media type), application/x-www-form-urlencoded, is based on a very early version of the general URI percent-encoding rules, with a number of modifications such as newline normalization and replacing spaces with "+" instead of "%20". Another possible encoding, Internet media type multipart/form-data, is also available and is common for POST-based file submissions.
Use with programming languages
Forms are usually combined with programs written in various programming language to allow developers to create dynamic web sites. The most popular languages include both client-side and/or server-side languages.
Although any programming language can be used on the server to process a form's data, the most commonly used languages are scripting languages, which tend to have stronger string handling functionality than programming languages such as C, and also have automatic memory management which helps to prevent buffer overrun attacks.
Client-side
The de facto client-side scripting language for web sites is JavaScript. Using JavaScript on the Document Object Model (DOM) leads to the method of Dynamic HTML that allows dynamic creation and modification of a web page within the browser.
While client-side languages used in conjunction with forms are limited, they often can serve to do pre-validation of the form data and/or to prepare the form data to send to a server-side program. This usage is being replaced, however, by HTML5's new input field types and required attribute.
Server-side execution
Server-side code can do a vast assortment of tasks to create dynamic web sites that, for technical or security reasons, client-side code cannot — from authenticating a login, to retrieving and storing data in a database, to spell checking, to sending e-mail. A significant advantage to server-side over client-side execution is the concentration of functionality onto the server rather than relying on different web browsers to implement various functions in consistent, standardized ways. In addition, processing forms on a server often results in increased security if server-side execution is designed not to trust the data supplied by the client and includes such techniques as HTML sanitization. One disadvantage to server side code is scalability—server side processing for all users occurs on the server, while client side processing occurs on individual client computers.
Interpreted languages
Some of the interpreted languages commonly used to design interactive forms in web development are PHP, Python, Ruby, Perl, JSP, Adobe ColdFusion and some of the compiled languages commonly used are Java and C# with ASP.NET.
PHP
PHP is one very common language used for server-side "programming" and is one of the few languages created specifically for web programming.[6][7]
To use PHP with an HTML form, the URL of the PHP script is specified in the action attribute of the form tag. The target PHP file then accesses the data passed by the form through PHP's $_POST or $_GET variables, depending on the value of the method attribute used in the form. Here is a basic form handler PHP script that will display the contents of the first-name input field on the page:
form.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="form_handler.php">
<p><label>Name: <input name="first-name" /></label></p>
<p><button type="submit">Submit</button></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
form_handler.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Output</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// This will print whatever the user entered into the form.html page.
$firstName = filter_input(INPUT_GET, "first-name", FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
echo "Hello, ${firstName}!";
?>
</body>
</html>
The sample code above uses PHP's filter_input() function to sanitize the user's input before inserting it onto the page. Simply printing (echoing) user input to the browser without checking it first is something that should be avoided in secure forms processors: if a user entered the JavaScript code <script>alert(1)</script> into the firstname field, the browser would execute the script on the form_handler.php page, just as if it had been coded by the developer; malicious code could be executed this way. filter_input() was introduced in PHP 5.2. Users of earlier PHP versions could use the htmlspecialchars() function, or regular expressions to sanitize the user input before doing anything with it.
Perl programming language
Perl is another language often used for web development. Perl scripts are traditionally used as Common Gateway Interface applications (CGIs). In fact, Perl is such a common way to write CGIs that the two are often confused. CGIs may be written in other languages than Perl (compatibility with multiple languages is a design goal of the CGI protocol) and there are other ways to make Perl scripts interoperate with a web server than using CGI (such as FastCGI, Plack or Apache's mod perl).
Perl CGIs were once a very common way to write web applications. However, many web hosts today effectively only support PHP, and developers of web applications often seek compatibility with them.
A modern Perl 5 CGI using the CGI module with a form similar to the one above might look like:
form_handler.pl
#!/usr/bin/env perl
use strict;
use CGI qw(:standard);
my $name = param("first-name");
print header;
print html(
body(
p("Hello, $name!"),
),
);
Form-to-email scripts
Among the simplest and most commonly needed types of server-side script is that which simply emails the contents of a submitted form. This kind of script is frequently exploited by spammers, however, and many of the most popular form-to-email scripts in use are vulnerable to hijacking for the purpose of sending spam emails. One of the most popular scripts of this type was "FormMail.pl" made by Matt's Script Archive. Today, this script is no longer widely used in new development due to lack of updates, security concerns, and difficulty of configuration.
Form builders
Some companies offer forms as a hosted service. Usually, these companies give some kind of visual editor, reporting tools and infrastructure to create and host the forms, that can be embedded into webpages.[8] Web hosting companies provide templates to their clients as an add-on service. Other form hosting services offer free contact forms that a user can install on their own website by pasting the service's code into the site's HTML.
History
HTML forms were first implemented by the Viola browser.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ "HTML/Elements/label". w3.org wiki. http://www.w3.org/wiki/HTML/Elements/label.
- ↑ Satrom, Brandon (November 2011). "Better Web Forms with HTML5 Forms". MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/hh547102.aspx.
- ↑ "Forms – HTML5". w3.org. W3C. http://www.w3.org/TR/html5/forms.html.
- ↑ "input type=color – color-well control". w3.org. W3C. http://www.w3.org/TR/html-markup/input.color.html.
- ↑ User-agent support for email based HTML form submission, using a 'mailto' URL as the form action, was proposed in RFC 1867 section 5.6, during the HTML 3.2 era. Various web browsers implemented it by invoking a separate email program, using their own rudimentary SMTP capabilities, or by becoming Internet suites by implementing entire Email clients. Although sometimes unreliable, it was briefly popular as a simple way to transmit form data without involving a web server or CGI scripts.
- ↑ "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor". http://www.php.net/.
- ↑ "Encyclopedia Web". http://www.lampfire.com/encyclopedia-web/php.php.
- ↑ Garofalo, Josh. "Intro to Online Forms and Form Builders". https://blitzen.com/blog/intro-online-forms-form-builders/.
- ↑ "ViolaWWW". Web Design Museum. https://www.webdesignmuseum.org/web-design-history/violawww-1992.
External links
- Forms in HTML documents, the W3C's spec page for forms in HTML 4.
- HTML5 forms specification
- Wikibooks: HyperText Markup Language/Forms
- Try out HTML properties.
 KSF
KSF