Gassmann triple
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
In mathematics, a Gassmann triple (or Gassmann-Sunada triple) is a group G together with two faithful actions on sets X and Y, such that X and Y are not isomorphic as G-sets but every element of G has the same number of fixed points on X and Y. They were introduced by Fritz Gassmann in 1926.
Applications
Gassmann triples have been used to construct examples of pairs of mathematical objects with the same invariants that are not isomorphic, including arithmetically equivalent number fields and isospectral graphs and isospectral Riemannian manifolds.
Examples
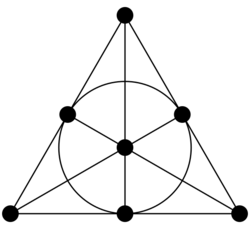
The simple group G = SL3(F2) of order 168 acts on the projective plane of order 2, and the actions on the 7 points and 7 lines give a Gassmann triple.
References
- Bosma, Wieb; de Smit, Bart (2002), "On arithmetically equivalent number fields of small degree", in Kohel, David R.; Fieker, Claus, Algorithmic number theory (Sydney, 2002), Lecture Notes in Comput. Sci., 2369, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 67–79, doi:10.1007/3-540-45455-1_6, ISBN 978-3-540-43863-2
- Gassmann, Fritz (1926), "Bemerkungen zur vorstehenden Arbeit von Hurwitz (Über Beziehungen zwischen den Primidealen eines algebraischen Körpers und den Substitutionen seiner Gruppe)", Mathematische Zeitschrift (Springer Berlin / Heidelberg) 25: 665–675, doi:10.1007/BF01283860, ISSN 0025-5874
- Sunada, T. (1985), "Riemannian coverings and isospectral manifolds", Annals of Mathematics 121 (1): 169–186, doi:10.2307/1971195
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Gassmann_triple18 views | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF