Hilbert basis (linear programming)
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
The Hilbert basis of a convex cone C is a minimal set of integer vectors such that every integer vector in C is a conical combination of the vectors in the Hilbert basis with integer coefficients.
Definition
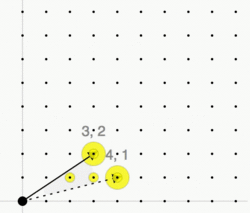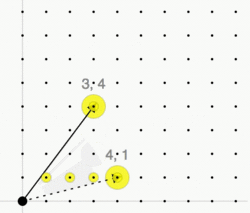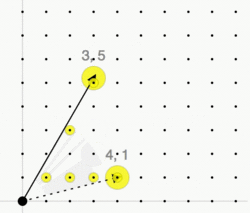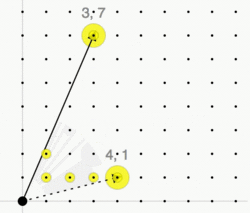
Given a lattice and a convex polyhedral cone with generators
we consider the monoid . By Gordan's lemma, this monoid is finitely generated, i.e., there exists a finite set of lattice points such that every lattice point is an integer conical combination of these points:
The cone C is called pointed if implies . In this case there exists a unique minimal generating set of the monoid —the Hilbert basis of C. It is given by the set of irreducible lattice points: An element is called irreducible if it can not be written as the sum of two non-zero elements, i.e., implies or .
References
- Bruns, Winfried; Gubeladze, Joseph; Henk, Martin; Martin, Alexander; Weismantel, Robert (1999), "A counterexample to an integer analogue of Carathéodory's theorem", Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik 1999 (510): 179–185, doi:10.1515/crll.1999.045
- Cook, William John; Fonlupt, Jean; Schrijver, Alexander (1986), "An integer analogue of Carathéodory's theorem", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 40 (1): 63–70, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(86)90064-X
- Eisenbrand, Friedrich; Shmonin, Gennady (2006), "Carathéodory bounds for integer cones", Operations Research Letters 34 (5): 564–568, doi:10.1016/j.orl.2005.09.008, http://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/121640
- D. V. Pasechnik (2001). "On computing the Hilbert bases via the Elliott—MacMahon algorithm". Theoretical Computer Science 263 (1–2): 37–46. doi:10.1016/S0304-3975(00)00229-2.
 |
 KSF
KSF