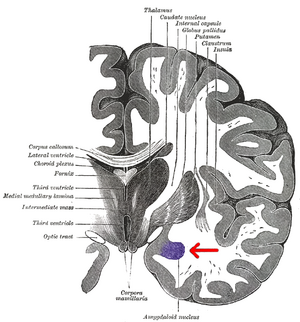
Central nucleus of the amygdala
Topic: Medicine
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
| Central nucleus of the amygdala | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy |
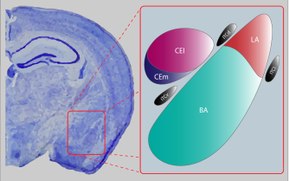
The central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA or aCeN) is a nucleus within the amygdala.[1][2] It "serves as the major output nucleus of the amygdala and participates in receiving and processing pain information."[3][4][5][6]
CeA "connects with brainstem areas that control the expression of innate behaviors and associated physiological responses."[7]
CeA is responsible for "autonomic components of emotions (e.g., changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration) primarily through output pathways to the lateral hypothalamus and brain stem." The CeA is also responsible for "conscious perception of emotion primarily through the ventral amygdalofugal output pathway to the anterior cingulate cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, and prefrontal cortex."[8]
Amygdala subdividisions and outputs
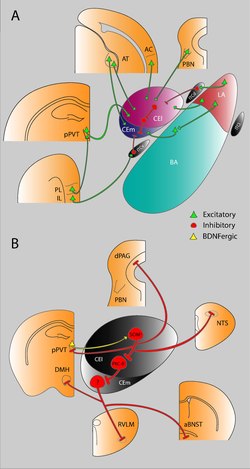
The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals.[9] Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, and the central nucleus. The basolateral complex can be further subdivided into the lateral, the basal, and the accessory basal nuclei.[10][self-published source?][11]
The amygdalofugal pathway (Latin for "fleeing from the amygdala" and commonly distinguished as the ventral amygdalofugal pathway) is one of the three principal pathways by which fibers leave the amygdala. The other main efferent pathways from the amygdala are the stria terminalis and anterior commissure. The anterior commissure also serves to connect the two amygdala.[12]
The ventral amygdalofugal pathway carries output from the central and basolateral nuclei and delivers it to a number of targets; namely, the medial dorsal nucleus of the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the basal forebrain, the brain stem, septal nuclei and nucleus accumbens.[13]
Research
- "psychological stressor induced an increase in both CRH mRNA levels and CRH content in the CEA. Exposure to the psychological stressor also caused a significant increase in CRH mRNA levels with a trend for an increase in CRH content in the dorsolateral subdivision of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) which is anatomically associated with the CEA."[14]
- "oxytocin in the CeA exerts a facilitatory role in the maintenance of hydroelectrolyte balance"[15]
- "the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) and its connections with the nigral dopamine system have been reported to modulate cognitive processes dependent substantially on attentional allocation. CeA dopamine function is involved in modulation of disengagement behavior."[16]
- "Opioid mechanisms are involved in the control of water and NaCl intake and opioid receptors (ORs) are present in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA)" μ-opioid receptors "in the CeA increases hypertonic sodium intake, whereas antagonizing these sites inhibits hypertonic sodium intake. …μ-ORs in the CeA in a positive regulation of sodium intake."[17]
- CeA "is essential for acquiring and expressing conditional fear after overtraining"[18]
- "glucocorticoids can facilitate CRH mRNA expression in the CEA, a site implicated in anxiety and fear"[19]
- Neuronal activity in the central nucleus of the amygdala was found to be a critical brain substrate for incubation of methamphetamine craving as well as neurobiological responses to ethanol.[3][20][21][22]
- Neurons in the central nucleus of the amygdala were found to respond to, and control, predatory hunting.[23]
See also
- Fear conditioning
- Intercalated cells of the amygdala
References
- ↑ "The Physiology of Fear: Reconceptualizing the Role of the Central Amygdala in Fear Learning". Physiology 30 (5): 389–401. September 2015. doi:10.1152/physiol.00058.2014. PMID 26328883.
- ↑ "The role of the central nucleus of the amygdala in mediating fear and anxiety in the primate". The Journal of Neuroscience 24 (24): 5506–5515. June 2004. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0292-04.2004. PMID 15201323.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Lateral habenula-projecting central amygdala circuits expressing GABA and NPY Y1 receptor modulate binge-like ethanol intake in mice" (in en). Addiction Neuroscience 3: 100019. 2022-09-01. doi:10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100019. ISSN 2772-3925. PMID 36059430.
- ↑ "The central amygdala and alcohol: role of γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and neuropeptides". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 2 (12): a012195. December 2012. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a012195. PMID 23085848.
- ↑ "What is the amygdala?" (in English). Trends in Neurosciences 21 (8): 323–331. August 1998. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(98)01265-X. PMID 9720596.
- ↑ "GABAA receptors in the central nucleus of amygdala (CeA) affect on pain modulation". Brain Research 1241: 36–41. November 2008. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.09.041. PMID 18838064.
- ↑ "Amygdala". Scholarpedia 3 (4): 2698. 2008. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.2698. Bibcode: 2008SchpJ...3.2698L.
- ↑ "Limbic System: Amygdala". Homeostasis and Higher Brain Function. Neuroscience Online. University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s4/chapter06.html. Retrieved 2013-02-14.
- ↑ "An investigation of the structural, connectional, and functional subspecialization in the human amygdala". Human Brain Mapping 34 (12): 3247–3266. December 2013. doi:10.1002/hbm.22138. PMID 22806915.
- ↑ "The Amygdala and the Emotions". The Anatomical Basis of Mind. August 28, 2012. http://www.benbest.com/science/anatmind/anatmd9.html.
- ↑ "Diffusion tensor imaging segments the human amygdala in vivo". NeuroImage 49 (4): 2958–2965. February 2010. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.027. PMID 19931398.
- ↑ "Connection Pathways of the Cerebral Amygdala". The Amygdaloid Nuclear Complex: Anatomic Study of the Human Amygdala: 49–58. 2016. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-23243-0_6. ISBN 978-3-319-23242-3.
- ↑ "Revealing the ventral amygdalofugal pathway of the human limbic system using high spatial resolution diffusion tensor tractography". Brain Structure & Function 221 (7): 3561–3569. September 2016. doi:10.1007/s00429-015-1119-3. PMID 26454651.
- ↑ "Psychological stress increased corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA and content in the central nucleus of the amygdala but not in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in the rat". Brain Research 850 (1–2): 136–143. December 1999. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(99)02114-9. PMID 10629757.
- ↑ "Oxytocin in the central amygdaloid nucleus modulates the neuroendocrine responses induced by hypertonic volume expansion in the rat". Journal of Neuroendocrinology 25 (5): 466–477. May 2013. doi:10.1111/jne.12021. PMID 23331859.
- ↑ "The role of central amygdala dopamine in disengagement behavior". Behavioral Neuroscience 127 (2): 164–174. April 2013. doi:10.1037/a0031043. PMID 23316710.
- ↑ "Activation of μ-opioid receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala induces hypertonic sodium intake". Neuroscience 233: 28–43. March 2013. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.026. PMID 23270855.
- ↑ "The central nucleus of the amygdala is essential for acquiring and expressing conditional fear after overtraining". Learning & Memory 14 (9): 634–644. September 2007. doi:10.1101/lm.607207. PMID 17848503.
- ↑ "Corticosterone effects on corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA in the central nucleus of the amygdala and the parvocellular region of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus". Brain Research 640 (1–2): 105–112. March 1994. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(94)91862-7. PMID 8004437. https://zenodo.org/record/1253840.
- ↑ "GABAA receptor antagonism in the extended amygdala decreases ethanol self-administration in rats". European Journal of Pharmacology 283 (1–3): 151–159. September 1995. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(95)00314-B. PMID 7498304.
- ↑ "Neuropeptide Y opposes alcohol effects on gamma-aminobutyric acid release in amygdala and blocks the transition to alcohol dependence" (in English). Biological Psychiatry 69 (11): 1091–1099. June 2011. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.02.004. PMID 21459365.
- ↑ "The central amygdala nucleus is critical for incubation of methamphetamine craving". Neuropsychopharmacology 40 (5): 1297–1306. March 2015. doi:10.1038/npp.2014.320. PMID 25475163.
- ↑ "Integrated Control of Predatory Hunting by the Central Nucleus of the Amygdala". Cell 168 (1-2): 311–324.e18. January 2017. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.027. PMID 28086095.
 |
 KSF
KSF