Fournier gangrene
Topic: Medicine
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
| Fournier gangrene | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Frequency | 1 per 62,500 males a year[1] |
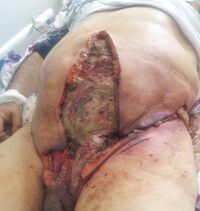
Fournier gangrene is a type of necrotizing fasciitis or gangrene affecting the external genitalia or perineum. It commonly occurs in older men, but it can also occur in women and children. It is more likely to occur in people with diabetes or alcoholism or those who are immunocompromised.
About one per 62,500 males are affected per year.[1] Males are affected about 40 times more often than females.[1] It was first described by Baurienne in 1764 and is named after a French venereologist, Jean Alfred Fournier, following five cases he presented in clinical lectures in 1883.[2]
Signs and symptoms
Initial symptoms of Fournier gangrene include swelling or sudden pain in the scrotum, fever, pallor, and generalized weakness. It is characterized by pain that extends beyond the border of the demarcated erythema.[2] Most cases present mildly, but can progress in hours. Subcutaneous air is often one of the specific clinical signs, but is not seen in >50% of presenting clinical cases. More marked cases are characterized by a foul odor and necrotic infected tissue. Crepitus has been reported.[2] It begins as a subcutaneous infection. However, necrotic patches soon appear in the overlying skin, which later develop into necrosis.[2]
Cause
Most cases of Fournier gangrene are infected with both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens. It can also result from infections caused by group A streptococcus (GAS), as well as other pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio vulnificus.[3] Lack of access to sanitation, medical care, and psychosocial resources has been linked to increased mortality.[4]
A 2006 Turkish study reported that blood sugar levels were elevated in 46 percent of patients diagnosed with Fourniers.[5] Another study reported that about one third of patients were alcoholic, diabetic, and malnourished, while another ten percent had been immunosuppressed through chemotherapy, steroids, or malignancy.[6]
Fournier gangrene is a rare side effect of SGLT2 inhibitors (canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin),[7] which increase the excretion of glucose in the urine.[8]
Diagnosis
Fournier gangrene is usually diagnosed clinically, but laboratory tests and imaging studies are used to confirm diagnosis, determine severity, and predict outcomes.[2] X-rays and ultrasounds may show the presence of gas below the surface of the skin.[2] A CT scan can be useful in determining the site of origin and extent of spread.[2]
Treatment
Fournier gangrene is a urological emergency requiring intravenous antibiotics and debridement (surgical removal) of dead tissue.[2] Formation of a colostomy may be required to divert bowel motions away from the area.[9] In addition to surgery and antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be useful and acts to inhibit the growth of and kill the anaerobic bacteria.[10] Multiple wound debridement may be required in cases with extensive tissue involvement. Simple reconstructive procedures following wound debridement yield satisfactory outcomes in majority of the cases.[citation needed]
Prognosis
While recent case series (n=980) studies have found a mortality rate of 20–40%, a large (n=1641) 2009 study reported a mortality rate of 7.5%.[11]
Epidemiology
A 2009 epidemiological study found the incidence of Fournier gangrene to be 1.6 cases per 100,000 males, in the United States.[11] Males 50 to 79 years old had the highest rate at 3.3 per 100,000.[11] Of 1,680 cases identified in the study, 39 were women.[11]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Hamdy, Freddie C.; Eardley, Ian (2017) (in en). Oxford Textbook of Urological Surgery. Oxford University Press. p. 76. ISBN 9780191022524. https://books.google.com/books?id=qpc4DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA76.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Mallikarjuna, MN; Vijayakumar, A et al. (2012). "Fournier's gangrene: Current practices". ISRN Surgery 2012: 942437. doi:10.5402/2012/942437. PMID 23251819.
- ↑ Thwaini, A; Khan, A et al. (2006). "Fournier's gangrene and its emergency management". Postgrad Med J 82 (970): 516–9. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2005.042069. PMID 16891442.
- ↑ Kessler, CS; Bauml, J (November 2009). "Non-Traumatic Urologic Emergencies in Men: A Clinical Review". West J Emerg Med 10 (4): 281–7. PMID 20046251.
- ↑ Yanar, H; Taviloglu, K et al. (2006). "Fournier's gangrene: Risk factors and strategies for management". World J Surg 30 (9): 1750–4. doi:10.1007/s00268-005-0777-3. PMID 16927060.
- ↑ Tahmaz, L; Erdemir, F et al. (2006). "Fournier's gangrene: Report of thirty-three cases and a review of the literature". International Journal of Urology 13 (7): 960–7. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2006.01448.x. PMID 16882063.
- ↑ Bersoff-Matcha, Susan J.; Chamberlain, Christine; Cao, Christian; Kortepeter, Cindy; Chong, William H. (June 4, 2019). "Fournier Gangrene Associated With Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: A Review of Spontaneous Postmarketing Cases". Ann Intern Med 170 (11): 764–769. doi:10.7326/M19-0085. PMID 31060053.
- ↑ "FDA warns about rare occurrences of a serious infection of the genital area with SGLT2 inhibitors for diabetes" (in en). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 7 September 2018. p. Drug Safety and Availability. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm617360.htm.
- ↑ Sarofim, Mina; Di Re, Angelina; Descallar, Joseph; Toh, James Wei Tatt (December 2021). "Relationship between diversional stoma and mortality rate in Fournier's gangrene: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery 406 (8): 2581–2590. doi:10.1007/s00423-021-02175-z. ISSN 1435-2451. PMID 33864128. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33864128/.
- ↑ Zamboni, WA; Riseman, JA; Kucan, JO (1990). "Management of Fournier's gangrene and the role of hyperbaric oxygen". J. Hyperbaric Med 5 (3): 177–86. http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/4431. Retrieved 2008-05-16.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Sorensen, MD; Krieger, JN et al. (2009). "Fournier's gangrene: Population based epidemiology and outcomes". The Journal of Urology 181 (5): 2120–6. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.01.034. PMID 19286224.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |
 KSF
KSF