Perinatal mortality
Topic: Medicine
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 9 min
| Perinatal mortality | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Perinatal death |
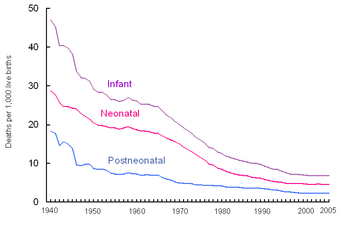 | |
| Infant, neonatal, and postneonatal mortality rates: United States, 1940–2005 | |
| Specialty | Public health |
Perinatal mortality (PNM) is the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate.[1] Perinatal means "relating to the period starting a few weeks before birth and including the birth and a few weeks after birth."[2]
Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion or exclusion of early fetal and late neonatal fatalities. The World Health Organization defines perinatal mortality as the "number of stillbirths and deaths in the first week of life per 1,000 total births, the perinatal period commences at 22 completed weeks (154 days) of gestation,[3] and ends seven completed days after birth",[4] but other definitions have been used.[5]
The UK figure is about 8 per 1,000 and varies markedly by social class with the highest rates seen in Asian women. Globally, an estimated 2.6 million neonates died in 2013 before the first month of age down from 4.5 million in 1990.[6]
Causes
Preterm birth is the most common cause of perinatal mortality, causing almost 30 percent of neonatal deaths.[7] Infant respiratory distress syndrome, in turn, is the leading cause of death in preterm infants, affecting about 1% of newborn infants.[8] Birth defects cause about 21 percent of neonatal death.[7]
Some major causes of perinatal mortality rate is:
- Maternal diseases
- Pelvic diseases; endometriosis, ovarian tumor
- Anatomical defects; Uterine, Cervical anomalies
- Endocrine imbalance
- Blood incompatibilities
- Malnutrition
- Toxemias of pregnancy
- APH
- Congenital defects
- Advanced maternal age
Fetal mortality
Fetal mortality refers to stillbirths or fetal death.[9] It encompasses any death of a fetus after 20 weeks of gestation or 500 gm. In some definitions of the PNM early fetal mortality (week 20–27 gestation) is not included, and the PNM may only include late fetal death and neonatal death. Fetal death can also be divided into death prior to labor, antenatal (antepartum) death, and death during labor, intranatal (intrapartum) death.
Neonatal mortality
Neonatal mortality refers to death of a live-born baby within the first 28 days of life. Early neonatal mortality refers to the death of a live-born baby within the first seven days of life, while late neonatal mortality refers to death after 7 days until before 28 days. Some definitions of the PNM include only the early neonatal mortality. Neonatal mortality is affected by the quality of in-hospital care for the neonate. Neonatal mortality and postneonatal mortality (covering the remaining 11 months of the first year of life) are reflected in the infant mortality rate.
Perinatal mortality rate
| Top ten countries with the highest perinatal mortality rates – 2012[10][11][12] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Country | PNMR | Rank | Country | PNMR |
| 1 | 40.7 | 6 | 29.0 | ||
| 2 | 32.7 | 7 | 28.9 | ||
| 3 | 30.8 | 8 | 28.3 | ||
| 4 | 29.7 | 9 | 27.5 | ||
| 5 | 29.4 | 10 | 27.4 | ||
| As per 2014 "Save the Children" report for intrapartum stillbirths and neonatal deaths on first day of birth (per 1,000 total births) | |||||
The PNMR refers to the number of perinatal deaths per 1,000 total births. It is usually reported on an annual basis.[13] It is a major marker to assess the quality of health care delivery. Comparisons between different rates may be hampered by varying definitions, registration bias, and differences in the underlying risks of the populations.
PNMRs vary widely and may be below 10 for certain developed countries and more than 10 times higher in developing countries.[14] The WHO has not published contemporary data.
Effects of neonatal nutrition on neonatal mortality
Probiotic supplementation of preterm and low birthweight babies during their first month of life can reduce the risk of blood infections, bowel sickness and death in low- and middle-income settings. However, supplementing with Vitamin A does not reduce the risk of death and increases the risk of bulging fontanelle, which may cause brain damage.[15]
See also
References
- ↑ "Perinatal mortality rate (PMR) — MEASURE Evaluation". 9 September 2020. http://www.cpc.unc.edu/measure/prh/rh_indicators/specific/nb/perinatal-mortality-rate-pmr.
- ↑ Concise medical dictionary. Jonathan Law, E. A. Martin (10th ed.). Oxford. 2020. ISBN 978-0-19-187376-8. OCLC 1142355883.
- ↑ "UpToDate". https://www.uptodate.com/contents/perinatal-mortality/print.
- ↑ "WHO – Maternal and perinatal health". https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/topics/maternal/maternal_perinatal/en/.
- ↑ "The perinatal mortality rate as an indicator of quality of care in international comparisons". Medical Care 36 (1): 54–66. January 1998. doi:10.1097/00005650-199801000-00007. PMID 9431331.
- ↑ "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet 385 (9963): 117–71. 17 December 2014. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMID 25530442.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 March of Dimes / Neonatal Death Retrieved on November 10, 2014
- ↑ Rodriguez RJ, Martin RJ, and Fanaroff, AA. Respiratory distress syndrome and its management. Fanaroff and Martin (eds.) Neonatal-perinatal medicine: Diseases of the fetus and infant; 7th ed. (2002):1001–1011. St. Louis: Mosby.
- ↑ "NVSS – Fetal Deaths". 8 November 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/fetal_death.htm.
- ↑ "Ending Newborn Deaths". https://www.savethechildren.net/sites/default/files/libraries/ENDING-NEWBORN-DEATHS.pdf.
- ↑ "Million babies die a year – charity – IOL". http://www.iol.co.za/lifestyle/family/birth/million-babies-die-a-year-charity-1.1653041#.Uw791uNUCKU.
- ↑ "Nigeria, Pakistan, India lead the world in infant deaths – PM NEWS Nigeria". 25 February 2014. http://www.pmnewsnigeria.com/2014/02/25/nigeria-pakistan-india-lead-the-world-in-infant-deaths/.
- ↑ "Miscarriage Risk by Week and What Affects Your Risks of Miscarriage". 23 August 2015. http://www.checkpregnancy.com/miscarriage-statistics/.
- ↑ "Centre for International Health". http://www.cih.uib.no/journals/EJHD/ejhdv14-n3/ejhd-14-3-page-335.htm.
- ↑ Imdad, Aamer; Rehman, Faseeha; Davis, Evans; Ranjit, Deepika; Surin, Gamael S. S.; Attia, Suzanna L.; Lawler, Sarah; Smith, Abigail A. et al. (2021). "Effects of neonatal nutrition interventions on neonatal mortality and child health and development outcomes: A systematic review" (in en). Campbell Systematic Reviews 17 (1). doi:10.1002/cl2.1141. ISSN 1891-1803. PMID 37133295.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
fi:Kohtukuolema
 |
 KSF
KSF