Navigation bar
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
A navigation bar (or navigation system) is a section of a graphical user interface intended to aid visitors in accessing information. Navigation bars are implemented in operating systems, file browsers,[1] web browsers, apps, web sites and other similar user interfaces.
File browsers
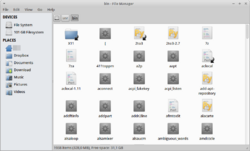
File browsers use a navigation bar to assist the user in traversing the filesystem. Navigation bars may include the current path, breadcrumbs, or a list of favorites.[2]
Web browsers
A web browser navigation bar includes the back and forward buttons, as well as the Location bar where URLs are entered.[3] Formerly, the functionality of the navigation bar was split between the browser's toolbar and the address bar, but Google Chrome introduced the practice of merging the two.
Web design
Typically, websites will have a primary navigation bar[4] and sometimes secondary navigation bar on all pages. These webpage sections will include links to the most important sections of the site. The implementation and design of navigation bars is a crucial aspect of web design and web usability.
In general, navigation bars are found in a page's header but may also be found in the form of a sidebar.
-
A typical webpage header with a navigation bar
-
A minimally styled header bar
-
Page navigation
With different purposes, there are different kinds of the navigation bars to be chosen, such as horizontal navigation bars and vertical navigation bars. And with a dynamic website project including JavaScript, navigation bars can be designed to be responsive.
HTML5 nav tag
Some early versions of Netscape used the HTML link tag to construct a navigation bar to navigate websites.[5] Today, the nav tag can be used for the same purpose.[6] In HTML5, navigation elements are enclosed in a <nav> tag, often, containing a list of links.
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="/blog">Blog</a></li>
<li><a href="/contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="/about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
See also
- Web template
References
- ↑ "Personalize the Windows Explorer Navigation Bar" (in en). https://www.pcworld.com/article/436135/personalize-the-windows-explorer-navigation-bar.html.
- ↑ "Dolphin". https://userbase.kde.org/Dolphin.
- ↑ "Avant Browser Help - Navigation Bar". http://www.avantbrowser.com/help/pgNavigationBar.htm.
- ↑ "Navigation Bar: Explanations and Samples". https://www.dropdownmenugenerator.com/create/navigation-bar.aspx.
- ↑ "Link". http://www.blooberry.com/indexdot/html/tagpages/l/link.htm. "The LINK element can be used to define a toolbar of navigation buttons or an equivalent mechanism such as menu items. Many of the values for the REL attribute could be reserved for this purpose (such as Home, Next, Previous, etc.)"
- ↑ "HTML <nav> Tag". https://www.w3schools.com/tags/tag_nav.asp.
 |
 KSF
KSF
