Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
Topic: Organization
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 26 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 26 min
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation | |
|---|---|
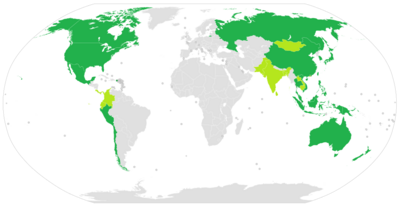
| Member economies of APEC Member economies of APEC | |
| Headquarters | |
| Type | Economic meeting |
| Membership | 21 economies
|
| Leaders | |
• Chairperson | |
• Executive Director | Eduardo Pedrosa |
| Establishment | 1989 |
Website www | |
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC /ˈeɪpɛk/ AY-pek[1]) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region.[2] Following the success of ASEAN's series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s,[3] APEC started in 1989,[4] in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; it aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe.[5] Headquartered in Singapore,[6] APEC is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific / Americas region,[7] and exerts significant global influence.[8][9][10][11]
The heads of government of all APEC members except Taiwan (which is represented by a ministerial-level official as economic leader)[12] attend an annual APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting. The location of the meeting rotates annually among the member economies, and a famous tradition, followed for most (but not all) summits, involves the attending leaders dressing in a national costume of the host country. APEC has three official observers: the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat, the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council and the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat.[13] APEC's Host Economy of the Year is considered to be invited in the first place for geographical representation to attend G20 meetings following G20 guidelines.[14][15]
History
File:APEC ABC.ogv The initial inspiration for APEC came when the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)'s series of post-ministerial conferences, launched in the mid-1980s, had demonstrated the feasibility and value of regular conferences among ministerial-level representatives of both developed and developing economies. By 1986, the post-ministerial conferences had expanded to embrace 12 members (the then six members of ASEAN and its six dialogue partners). The developments led Australian Prime Minister Bob Hawke to believe in the necessity of region-wide co-operation on economic matters. In January 1989, Bob Hawke called for more effective economic co-operation across the Pacific Rim region. This led to the first meeting of APEC in the Australian capital of Canberra in November, chaired by Australian Foreign Affairs Minister Gareth Evans. Attended by ministers from twelve countries, the meeting concluded with commitments to hold future annual meetings in Singapore and South Korea. Ten months later, representatives of 12 Asia-Pacific economies met in Canberra, Australia, to establish APEC. The APEC Secretariat, based in Singapore, was established to co-ordinate the activities of the organisation.[4][5] The organization was initially an Australian initiative intended to secure greater Japanese engagement in the region, but it quickly evolved into a forum for broader economic cooperation. Its early years were characterized by a dynamic tension between members favoring a structured trade agreement and those, like the United States, who preferred a looser, more consultative approach.[16]
During the 1994 meeting in Bogor, Indonesia, APEC leaders adopted the Bogor Goals, which aimed for free and open trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific by 2010 for industrialised economies and by 2020 for developing economies. During the November 1995 Ministerial Meeting in Osaka, Japan, a business advisory body named the APEC Business Advisory Council (ABAC) composed of three business executives from each member-country was agreed to be established in 1996.[17][18]
In April 2001, APEC, in collaboration with five other international organisations (Eurostat, International Energy Agency, Organización Latinoamericana de Energía (es), Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and the United Nations Statistics Division) launched the Joint Oil Data Exercise, which in 2005 became the Joint Organisations Data Initiative (JODI).
Meeting locations
The location of the annual meeting rotates among the members.[citation needed]
| Year | # | Dates | Country | City | Host Leader |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | 1st | 6–7 November | Canberra | Prime Minister Bob Hawke | |
| 1990 | 2nd | 29–31 July | Singapore | Prime Minister Lee Kuan Yew | |
| 1991 | 3rd | 12–14 November | Seoul | President Roh Tae-woo | |
| 1992 | 4th | 10–11 September | Bangkok | Prime Minister Anand Panyarachun |
| Year | # | Dates | Country | City | Host Leader |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993 | 1st | 19–20 November | Blake Island | President Bill Clinton | |
| 1994 | 2nd | 15–16 November | Bogor | President Suharto | |
| 1995 | 3rd | 18–19 November | Osaka | Prime Minister Tomiichi Murayama | |
| 1996 | 4th | 24–25 November | Subic | President Fidel Ramos | |
| 1997 | 5th | 24–25 November | Vancouver | Prime Minister Jean Chrétien | |
| 1998 | 6th | 17–18 November | Kuala Lumpur | Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad | |
| 1999 | 7th | 12–13 September | Auckland | Prime Minister Jenny Shipley | |
| 2000 | 8th | 15–16 November | Bandar Seri Begawan | Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah | |
| 2001 | 9th | 20–21 October | Shanghai | General Secretary and President Jiang Zemin[lower-alpha 2] | |
| 2002 | 10th | 26–27 October | Los Cabos | President Vicente Fox | |
| 2003 | 11th | 20–21 October | Bangkok | Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra | |
| 2004 | 12th | 20–21 November | Santiago | President Ricardo Lagos | |
| 2005 | 13th | 18–19 November | Busan | President Roh Moo-hyun | |
| 2006 | 14th | 18–19 November | Hanoi | President Nguyễn Minh Triết[lower-alpha 3] | |
| 2007 | 15th | 8–9 September | Sydney | Prime Minister John Howard | |
| 2008 | 16th | 22–23 November | Lima | President Alan Garcia Perez | |
| 2009 | 17th | 14–15 November | Singapore | Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong | |
| 2010 | 18th | 13–14 November | Yokohama | Prime Minister Naoto Kan | |
| 2011 | 19th | 12–13 November | Honolulu | President Barack Obama | |
| 2012 | 20th | 9–10 September | Vladivostok | President Vladimir Putin | |
| 2013 | 21st | 5–7 October | Bali | President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono | |
| 2014 | 22nd | 10–11 November | Beijing | General Secretary and President Xi Jinping[lower-alpha 2] | |
| 2015 | 23rd | 18–19 November | Pasay | President Benigno Aquino III | |
| 2016 | 24th | 19–20 November | Lima | President Pedro Pablo Kuczynski | |
| 2017 | 25th | 10–11 November | Da Nang | President Trần Đại Quang[lower-alpha 3] | |
| 2018 | 26th | 17–18 November | Port Moresby | Prime Minister Peter O'Neill | |
| 2019 | 16–17 November (cancelled) |
Santiago | President Sebastián Piñera | ||
| 2020 | 28th | 20 November | Kuala Lumpur (hosted virtually)[19] | Prime Minister Muhyiddin Yassin | |
| 2021 | – | 16 July | Auckland (hosted virtually) | Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern | |
| 29th | 12 November[20] | ||||
| 2022 | 30th | 18–19 November | Bangkok | Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha[21] | |
| 2023 | 31st | 15–17 November[22] | San Francisco | President Joe Biden[23] | |
| 2024 | 32nd | 15–16 November | Lima | President Dina Boluarte[24] | |
| 2025 | 33rd | 31 October – 1 November[25] | Gyeongju | President Lee Jae Myung | |
| 2026 | 34th | TBA | Shenzhen[27] | General Secretary and President Xi Jinping[lower-alpha 2] | |
| 2027 | 35th | TBA | Phú Quốc[29] | TBA[lower-alpha 3] | |
| 2028 | 36th | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA |
| 2029 | 37th | TBA | TBA | TBA | TBA |
| 2030 | 38th | TBA | Singapore | TBA |
Member economies

Currently, APEC has 21 members. The criterion for membership, however, is that each member must be an independent economic entity, rather than a sovereign state. As a result, APEC uses the term member economies rather than member countries to refer to its members. One result of this criterion is that membership of the forum includes Taiwan (officially the Republic of China, participating under the name "Chinese Taipei") alongside People's Republic of China (see Cross-Strait relations), as well as Hong Kong, which entered APEC as a British colony but it is now a Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China. APEC also includes three official observers: ASEAN, the Pacific Islands Forum and the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council.[2]
| Member economy | Name as used in APEC | Date of accession | GDP (Nominal) in 2024 (Millions of US$)[31] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | November 1989 | 1,802,006 | |
| Brunei Darussalam | November 1989 | 15,510 | |
| Canada | November 1989 | 2,214,796 | |
| Chile | November 1994 | 328,720 | |
| People's Republic of China | November 1991 | 18,273,357 | |
| Hong Kong, China[lower-alpha 4] | November 1991 | 401,751 | |
| Indonesia | November 1989 | 1,402,590 | |
| Japan | November 1989 | 4,070,094 | |
| Malaysia | November 1989 | 439,748 | |
| Mexico | November 1993 | 1,848,125 | |
| New Zealand | November 1989 | 252,236 | |
| Papua New Guinea | November 1993 | 31,716 | |
| Peru | November 1998 | 283,309 | |
| The Philippines | November 1989 | 470,062 | |
| Russia | November 1998 | 2,184,316 | |
| Singapore | November 1989 | 530,708 | |
| Republic of Korea | November 1989 | 1,869,916 | |
| Chinese Taipei[lower-alpha 1] | November 1991 | 775,017 | |
| Thailand | November 1989 | 528,919 | |
| The United States | November 1989 | 29,167,779 | |
| Viet Nam | November 1998 | 468,485 |
Leaders
| Member | Leader position | Leader (mostly Head of government) | Finance portfolio | Portfolio Minister |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prime Minister | Anthony Albanese | Treasurer | Jim Chalmers | |
| Sultan Prime Minister |
Hassanal Bolkiah | Minister of Finance and Economy Second Minister of Finance and Economy |
Hassanal Bolkiah Amin Liew Abdullah | |
| Prime Minister | Mark Carney | Minister of Finance | François-Philippe Champagne | |
| President | Gabriel Boric | Minister of Finance | Mario Marcel | |
| CCP General Secretary President[lower-alpha 2] |
Xi Jinping | Minister of Finance | Lan Fo'an | |
| Chief Executive | John Lee | Financial Secretary | Paul Chan | |
| President | Prabowo Subianto | Minister of Finance | Purbaya Yudhi Sadewa | |
| Prime Minister | Sanae Takaichi | Minister of Finance | Satsuki Katayama | |
| President | Lee Jae Myung | Minister of Economy and Finance | Koo Yun-cheol | |
| Prime Minister | Anwar Ibrahim | Minister of Finance | Anwar Ibrahim Amir Hamzah Azizan | |
| President | Claudia Sheinbaum | Secretary of Finance and Public Credit | Edgar Amador Zamora | |
| Prime Minister | Christopher Luxon | Minister of Finance | Nicola Willis | |
| Prime Minister | James Marape | Minister for Finance and Rural Development | Yangakun Miki Kaeok | |
| President | José Jerí[32] | Minister of Economy and Finance | Denisse Miralles | |
| President | Bongbong Marcos | Secretary of Finance | Ralph Recto | |
| President | Vladimir Putin | Minister of Finance | Anton Siluanov | |
| Prime Minister | Lawrence Wong | Minister of Finance | Lawrence Wong | |
| President / Leader Envoy | Lai Ching-te (represented by Lin Hsin-i)[lower-alpha 1] | Minister of Finance | Chuang Tsui-yun | |
| Prime Minister | Anutin Charnvirakul[33][34] | Minister of Finance | Ekniti Nitithanprapas | |
| President | Donald Trump | Secretary of the Treasury | Scott Bessent | |
| President[lower-alpha 3] | Lương Cường | Minister of Finance | Nguyễn Văn Thắng |
Current leaders
-
 Australia
Australia
Anthony Albanese,
Prime Minister -
 Brunei
Brunei
Hassanal Bolkiah,
Sultan -
 Canada
Canada
Mark Carney,
Prime Minister -
 Chile
Chile
Gabriel Boric,
President -
 Hong Kong
Hong Kong
John Lee,
Chief Executive -
 Indonesia
Indonesia
Prabowo Subianto,
President -
 Japan
Japan
Sanae Takaichi,
Prime Minister -
 South Korea
South Korea
Lee Jae Myung,
President -
 Malaysia
Malaysia
Anwar Ibrahim,
Prime Minister -
 Mexico
Mexico
Claudia Sheinbaum,
President -
 New Zealand
New Zealand
Christopher Luxon,
Prime Minister -
 Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
James Marape,
Prime Minister -
 Philippines
Philippines
Bongbong Marcos,
President -
 Singapore
Singapore
Lawrence Wong,
Prime Minister -
 United States
United States
Donald Trump,
President
Possible enlargement
India has requested membership in APEC, and received initial support from the United States, South Korea, Australia,[35] and Papua New Guinea.[36] Officials have decided not to allow India to join for various reasons, including the fact that India does not border the Pacific Ocean, which all current members do.[37] However, India was invited to be an observer for the first time in November 2011.[38]
Bangladesh,[39] Pakistan,[39] Sri Lanka,[39] Macau,[39] Mongolia,[39] Laos,[39] Cambodia,[40] Costa Rica,[41] Colombia,[41][42] Panama,[41] and Ecuador,[43] are among a dozen other economies that have applied for membership in APEC. Colombia applied for APEC's membership as early as in 1995, but its bid was halted as the organisation stopped accepting new members from 1993 to 1996,[44] and the moratorium was further prolonged to 2007 due to the 1997 Asian financial crisis.[citation needed]
Business facilitation
As a regional organization, APEC has always played a leading role in the area of reform initiatives in the area of business facilitation. The APEC Trade Facilitation Action Plan (TFAPI) has contributed to a reduction of 6% in the cost of business transactions across the region between 2002 and 2006. According to APEC's projections, the cost of conducting business transactions will be reduced by another 5% between 2007 and 2010. To this end, a new Trade Facilitation Action Plan has been endorsed. According to a 2008 research brief published by the World Bank as part of its Trade Costs and Facilitation Project, increasing transparency in the region's trading system is critical if APEC is to meet its Bogor Goal targets.[45] The APEC Business Travel Card, a travel document for visa-free business travel within the region is one of the concrete measures to facilitate business. In May 2010 Russia joined the scheme, thus completing the circle.[46]
Proposed FTAAP
APEC first formally started discussing the concept of a Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP) at its summit in 2006 in Hanoi. However, the proposal for such an area has been around since at least 1966 and Japanese economist Kiyoshi Kojima's proposal for a Pacific Free Trade agreement. While it gained little traction, the idea led to the formation of Pacific Trade and Development Conference and then the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council in 1980 and then APEC in 1989.[citation needed]
In the wake of the 2006 summit, economist C. Fred Bergsten advocated a Free Trade Agreement of Asia-Pacific, including the United States amongst the proposed parties to any agreement at that time.[47] His ideas convinced the APEC Business Advisory Council to support this concept. Relatedly, ASEAN and existing free trade agreement (FTA) partners negotiated the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), not officially including Russia.[48] The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) without China or Russia involved became the US-promoted trade negotiation in the region. At the APEC summit in Beijing in 2014, the three plans were all in discussion.[49] President Obama hosted a TPP meeting at the US Embassy in Beijing in advance of the APEC gathering.[50]
The proposal for a FTAAP arose due to the lack of progress in the Doha round of World Trade Organization negotiations, and as a way to overcome the "noodle bowl" effect created by overlapping and conflicting elements of the copious free trade agreements – there were approximately 60 free trade agreements in 2007, with an additional 117 in the process of negotiation in Southeast Asia and the Asia-Pacific region.[51] In 2012, ASEAN+6 countries alone had 339 free trade agreements – many of which were bilateral.[lower-alpha 5]
The FTAAP is more ambitious in scope than the Doha round, which limits itself to reducing trade restrictions. The FTAAP would create a free trade zone that would considerably expand commerce and economic growth in the region.[51][53] The economic expansion and growth in trade could exceed the expectations of other regional free trade areas such as the ASEAN Plus Three (ASEAN + China, South Korea and Japan).[54] Some criticisms include that the diversion of trade within APEC members would create trade imbalances, market conflicts and complications with nations of other regions.[53] The development of the FTAAP is expected to take many years, involving essential studies, evaluations and negotiations between member economies.[51] It is also affected by the absence of political will and popular agitations and lobbying against free trade in domestic politics.[51][55]
At the 2014 APEC summit in Beijing, APEC leaders agreed to launch "a collective strategic study" on the FTAAP and instruct officials to undertake the study, consult stakeholders and report the result by the end of 2016.[56] APEC Executive Director Alan Bollard revealed in the Elite Talk show that FTAAP will be APEC's big goal out into the future.[57]
The Trans-Pacific Partnership included 12 of the 21 APEC members and had provisions for the accession of other APEC members, five of which expressed interest in membership.[citation needed]
APEC Study Centre Consortium
In 1993, APEC Leaders decided to establish a network of APEC Study Centres (APCs) among universities and research institutions in member economies. The purpose is to foster cooperation among tertiary and research institutes of member economies, thus having better academic collaboration on key regional economic challenges. To encourage independence from the APEC conference, the APCs are funded independently and choose their own research topics.[58]
As of December 2018, there are 70 APCs among the member economies. An annual conference is usually held in the host economy for that year.[58]
APEC Business Advisory Council
The APEC Business Advisory Council (ABAC) was created by the APEC Economic Leaders in November 1995 with the aim of providing advice to the APEC Economic Leaders on ways to achieve the Bogor Goals and other specific business sector priorities, and to provide the business perspective on specific areas of co-operation.[59][60]
Each economy nominates up to three members from the private sector to ABAC. These business leaders represent a wide range of industry sectors. ABAC provides an annual report to APEC Economic Leaders containing recommendations to improve the business and investment environment in the Asia-Pacific region, and outlining business views about priority regional issues. ABAC is also the only non-governmental organisation that is on the official agenda of the APEC Economic Leader's Meeting.[61]
Annual APEC economic leaders' meetings
File:1996 Asia Pacific Economic Leaders Meeting (APEC) Philippines - Subic Bay Freeport Zone.webm Since its formation in 1989, APEC has held annual meetings with representatives from all member economies. The first four annual meetings were attended by ministerial-level officials. Beginning in 1993, the annual meetings are named APEC Economic Leaders' Meetings and are attended by the heads of government from all member economies except Taiwan, which is represented by a ministerial-level official.[22]
Meeting developments
In 1997, the APEC meeting was held in Vancouver. Controversy arose after officers of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police used pepper spray against protesters. The protesters objected to the presence of autocratic leaders such as Indonesian president Suharto.[62][63][64][65][66][67]
At the 2001 Leaders' Meeting in Shanghai, APEC leaders pushed for a new round of trade negotiations and support for a program of trade capacity-building assistance, leading to the launch of the Doha Development Agenda a few weeks later. The meeting also endorsed the Shanghai Accord proposed by the United States, emphasising the implementation of open markets, structural reform, and capacity building. As part of the accord, the meeting committed to develop and implement APEC transparency standards, reduce trade transaction costs in the Asia-Pacific region by five percent over five years, and pursue trade liberalisation policies relating to information technology goods and services.[citation needed]
In 2003, Jemaah Islamiah leader Riduan Isamuddin had planned to attack the APEC Leaders Meeting to be held in Bangkok in October. He was captured in the city of Ayutthaya, Thailand by Thai police on 11 August 2003, before he could finish planning the attack.[68]
Chile became the first South American nation to host the Leaders' Meeting in 2004. The agenda of that year was focused on terrorism and commerce, small and medium enterprise development, and contemplation of free agreements and regional trade agreements.[citation needed]
The 2005 Leaders' Meeting was held in Busan, South Korea. The meeting focused on the Doha round of World Trade Organization (WTO) negotiations, leading up to the WTO Ministerial Conference of 2005 held in Hong Kong in December. Weeks earlier, trade negotiations in Paris were held between several WTO members, including the United States and the European Union, centred on reducing agricultural trade barriers. APEC leaders at the summit urged the European Union to agree to reduce farm subsidies. In a continuation of the climate information sharing initiative established by the APEC Climate Network working group, it was decided by the leaders to install the APEC Climate Center in Busan. Peaceful protests against APEC were staged in Busan, but the meeting schedule was not affected.[citation needed]
At the Leaders' Meeting held on 19 November 2006 in Hanoi, APEC leaders called for a new start to global free-trade negotiations while condemning terrorism and other threats to security. APEC also criticised North Korea for conducting a nuclear test and a missile test launch that year, urging the country to take "concrete and effective" steps toward nuclear disarmament. Concerns about nuclear proliferation in the region was discussed in addition to economic topics. The United States and Russia signed an agreement as part of Russia's bid to join the World Trade Organization.[citation needed]
The APEC Australia 2007 Leaders' Meeting was held in Sydney from 2–9 September 2007. The political leaders agreed to an "aspirational goal" of a 25% reduction of energy intensity correlative with economic development.[69] Extreme security measures including airborne sharpshooters and extensive steel-and-concrete barricades were deployed against anticipated protesters and potential terrorists. However, protest activities were peaceful and the security envelope was penetrated with ease by a spoof diplomatic motorcade manned by members of the Australian television program The Chaser, one of whom was dressed to resemble the Al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden.[citation needed]
The APEC Chile 2019, originally to be held 16–17 November 2019 in Chile, was cancelled due to ongoing protests by sections of its population over inequality, the cost of living and police repression.[70]
The 2023 APEC meeting was notable for a lack of consensuses of group members on their stance over the Russia–Ukraine and Gaza conflicts as well as consensus for WTO reforms. The meeting between Biden and Xi was also seen as significant in terms of reducing tensions between the US and China.[71]
APEC leaders' group photo
At the end of the APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting, the leaders gather for the official APEC Leaders' Family Photo. A tradition has the leaders dressing to reflect the culture of the host member. The tradition dates to the first such meeting in 1993 when then-U.S. President Bill Clinton insisted on informal attire and gave the leaders leather bomber jackets. At the 2010 meeting, Japan had the leaders dress in smart casual rather than the traditional kimono.[72] Similarly, when Honolulu was selected in 2009 as the site for the 2011 APEC meeting, U.S. President Barack Obama joked that he looked forward to seeing the leaders dressed in "flowered shirts and grass skirts". After viewing previous photos, and concerned that having the leaders dress in aloha shirts might give the wrong impression during a period of economic austerity, Obama instead decided it might be time to end the tradition. Leaders were given a specially designed aloha shirt as a gift but were not expected to wear it for the photo.[73] Leaders in Bali, Indonesia at the 2013 conference wore a batik outfit; in China 2014 Tang suit jackets; in the Philippines 2015 barong tagalogs; in Peru 2016 vicuña wool shawls; in 2017 Vietnamese silk shirts.[74]
-
APEC United States 1993
-
APEC Brunei 2000
-
APEC China 2001
-
APEC Thailand 2003
-
APEC Chile 2004
-
APEC South Korea 2005
-
APEC Vietnam 2006
-
APEC Australia 2007
-
APEC Peru 2008
-
APEC Singapore 2009
-
APEC Japan 2010
-
APEC United States 2011
-
APEC Russia 2012
-
APEC Indonesia 2013
-
APEC China 2014
-
APEC Philippines 2015
-
APEC Peru 2016
-
APEC Vietnam 2017
-
APEC Papua New Guinea 2018
-
APEC United States 2023
-
APEC Peru 2024
APEC Summits
 APEC Australia 1989
APEC Australia 1989 APEC Singapore 1990
APEC Singapore 1990 APEC South Korea 1991
APEC South Korea 1991 APEC Thailand 1992
APEC Thailand 1992 APEC United States 1993
APEC United States 1993 APEC Indonesia 1994
APEC Indonesia 1994 APEC Japan 1995
APEC Japan 1995 APEC Philippines 1996
APEC Philippines 1996 APEC Canada 1997
APEC Canada 1997 APEC Malaysia 1998
APEC Malaysia 1998 APEC New Zealand 1999
APEC New Zealand 1999 APEC Brunei 2000
APEC Brunei 2000 APEC China 2001
APEC China 2001 APEC Mexico 2002
APEC Mexico 2002 APEC Thailand 2003
APEC Thailand 2003 APEC Chile 2004
APEC Chile 2004 APEC South Korea 2005
APEC South Korea 2005 APEC Vietnam 2006
APEC Vietnam 2006 APEC Australia 2007
APEC Australia 2007 APEC Peru 2008
APEC Peru 2008 APEC Singapore 2009
APEC Singapore 2009 APEC Japan 2010
APEC Japan 2010 APEC United States 2011
APEC United States 2011 APEC Russia 2012
APEC Russia 2012 APEC Indonesia 2013
APEC Indonesia 2013 APEC China 2014
APEC China 2014 APEC Philippines 2015
APEC Philippines 2015 APEC Peru 2016
APEC Peru 2016 APEC Vietnam 2017
APEC Vietnam 2017 APEC Papua New Guinea 2018
APEC Papua New Guinea 2018 APEC Chile 2019
APEC Chile 2019 APEC Malaysia 2020
APEC Malaysia 2020 APEC New Zealand 2021
APEC New Zealand 2021 APEC Thailand 2022
APEC Thailand 2022 APEC United States 2023
APEC United States 2023 APEC Peru 2024
APEC Peru 2024 APEC South Korea 2025
APEC South Korea 2025 APEC China 2026
APEC China 2026 APEC Vietnam 2027
APEC Vietnam 2027 APEC Japan 2028
APEC Japan 2028
Criticism
APEC has been criticised for promoting free trade agreements that would impose restrictions on national and local laws, which regulate and ensure labour rights, environmental protection and safe and affordable access to medicine.[75] According to the organisation, it is "the premier forum for facilitating economic growth, cooperation, trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific region" established to "further enhance economic growth and prosperity for the region and to strengthen the Asia-Pacific community".[76] The effectiveness and fairness of its role has been questioned, especially from the viewpoints of European countries that cannot take part in APEC[77] and Pacific Island nations that cannot participate but stand to be affected by its decisions.
See also
- Anti-corruption
- ASEAN Free Trade Area
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- Asia-Pacific Trade Agreements Database
- East Asia Economic Caucus
- East Asia Summit
- List of country groupings
- List of multilateral free-trade agreements
- Pacific Alliance
- Pacific Economic Cooperation Council
- University Mobility in Asia and the Pacific
Other organisations of coastal states
- Bay of Bengal Initiative
- Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation
- Union for the Mediterranean
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Due to the complexities of the relations between it and Communist China (officially the People's Republic of China), the Republic of China (ROC or "Taiwan"; retroactively known as Nationalist China) is not represented under its official various names such as the "Republic of China", "Nationalist China" or "Taiwan". Instead, it participates in APEC under the name "Chinese Taipei". The President of the Republic of China cannot attend the annual APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting in person. Instead, it is generally represented by a ministerial-level official responsible for economic affairs or someone designated by the president. See List of Chinese Taipei Representatives to APEC.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 The de jure head of government of China is the Premier, whose current holder is Li Qiang. The President of China is legally a ceremonial office, but the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (de facto leader in one-party communist state) has always held this office since 1993 except for the months of transition, and the current general secretary is Xi Jinping.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 The actual head of the executive government of Vietnam is the Prime Minister, whose current holder is Phạm Minh Chính. The President of Vietnam is legally the head of state, but the General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam (practical highest political leader in a one-party communist state) is being Tô Lâm.
- ↑ Hong Kong joined APEC in 1991 during British administration with the name "Hong Kong." In 1997, Hong Kong became a Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China and took the name "Hong Kong, China."
- ↑ "As of January 2012 ASEAN countries have 186 FTAs implemented, signed, under negotiation or under proposal/study, which is substantial progress since… 1992. The ASEAN+6 countries have a total of 339 FTAs, including between ASEAN countries and the '+6' countries."[52]
References
- ↑ "What is APEC?". November 2018. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ABWwQg-CwY.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Member Economies". https://www.apec.org/about-us/about-apec/member-economies.
- ↑ Elek, Andrew (30 September 2005). "Back to Canberra: Founding APEC". http://www.pecc.org/resources/doc_view/601-back-to-canberra-founding-apec. "ASEAN's series of post-ministerial consultations,launched in the mid-1980s, had demonstrated the feasibility and value of regular consultations among ministerial-level representatives of both developed and developing economies."
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "History". https://www.apec.org/About-Us/About-APEC/History. "The idea of APEC was firstly publicly broached by former prime minister of Australia Bob Hawke during a speech in Seoul, Korea, on 31 January 1989. Ten months later, 12 Asia-Pacific economies met in Canberra to establish APEC."
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Elek, Andrew. "Back to Canberra: Founding APEC". https://www.pecc.org/resources/regional-cooperation/601-back-to-canberra-founding-apec/file.
- ↑ "What is APEC and what can it do for business?". http://www.ncapec.org/docs/what_is_apec.pdf. "The APEC Secretariat is based in Singapore. The Secretariat is staffed by 20 diplomats seconded from APEC member economies and by 20 local staff."
- ↑ Chu, Shulong (1 February 2017). "The East Asia Summit: Looking for an Identity". https://www.brookings.edu/opinions/the-east-asia-summit-looking-for-an-identity/. "APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation) is the oldest such forum and is generally recognized as the highest-level multilateral process in Asia-Pacific."
- ↑ "Achievements and Benefits". https://www.apec.org/About-Us/About-APEC/Achievements-and-Benefits.
- ↑ "How Could The 2016 APEC Forum Affect The World Economy?". 9 January 2017. https://www.fxcm.com/insights/2016-apec-forum-affect-world-economy/. "The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum represents a potentially large-scale trade area that, when functioning in a concerted manner, could in the future work to shift the axis of global manufacturing and trade away from the North Atlantic–European region toward the Pacific. [...] But the future of the bloc, which represents more than 50% of the world's GDP, may be in suspense."
- ↑ Parreñas, Julius Caesar (January 1998). "ASEAN and Asia-Pacific economic cooperation". The Pacific Review 11 (2): 233–248. doi:10.1080/09512749808719255.
- ↑ What Context does the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Forum (APEC)Provide for Employment Relations? (Report). https://www.anzam.org/wp-content/uploads/pdf-manager/2336_BAMBER_GREG_AMI-13.PDF. "APEC represents the most dynamic economic region in the world, having generated nearly 70 per cent of global economic growth in its first 10 years [...]."
- ↑ Conditions not right for APEC attendance: Ma . The China Post (27 August 2013). Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- ↑ "Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation -". http://www.apec.org/About-Us/How-APEC-Operates/APEC-Observers.
- ↑ "Invitees and International Organizations | G20 Foundation". https://www.g20foundation.org/g20/invitees-and-international-organizations.
- ↑ "Deputy PM meets US State Secretary on G20 meeting sidelines – Embassy of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam in the United States". http://vietnamembassy-usa.org/news/2017/02/deputy-pm-meets-us-state-secretary-g20-meeting-sidelines.
- ↑ Drysdale, Peter (December 1994). "APEC and the Political Economy of the Asia-Pacific". Foreign Affairs 73 (6): 20-25. https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/asia/1994-11-01/apec-and-political-economy-asia-pacific. Retrieved 24 October 2025.
- ↑ "1995 APEC Ministerial Meeting" (in en). https://www.apec.org/meeting-papers/annual-ministerial-meetings/1995/1995_amm.
- ↑ "1995 APEC Ministerial Meeting | 1995 APEC Ministerial Meeting" (in en). https://www.apec.org/meeting-papers/annual-ministerial-meetings/1995/1995_amm/att_decl.
- ↑ "Apec leaders' summit to be virtual". Bangkok Post. Kyodo News. 4 September 2020. https://www.bangkokpost.com/world/1980031/apec-leaders-summit-to-be-virtual.
- ↑ "New Zealand to host virtual APEC in 2021" (in en). 30 June 2020. https://www.beehive.govt.nz/release/new-zealand-host-virtual-apec-2021.
- ↑ "Statement by Prime Minister of Thailand on APEC" (in en). 10 February 2022. https://www.apec.org/press/news-releases/2022/statement-by-prime-minister-of-thailand-on-apec-hosting-year.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "Calendar – Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation 2023". https://www.state.gov/events-asia-pacific-economic-cooperation/.
- ↑ "Remarks by Vice President Harris on the Indo-Pacific Region" (in en). 24 August 2021. https://bidenwhitehouse.archives.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/08/24/remarks-by-vice-president-harris-on-the-indo-pacific-region/.
- ↑ PERÚ, Empresa Peruana de Servicios Editoriales S. A. EDITORA (13 September 2023). "Presidenta: Trujillo, Arequipa, Cusco, Ucayali y Lima serán sedes de APEC 2024". https://andina.pe/agencia/noticia-presidenta-trujillo-arequipa-cusco-ucayali-y-lima-seran-sedes-apec-2024-955177.aspx.
- ↑ 경주시홈페이지, 경주시. "경주시, 경주시홈페이지". https://www.gyeongju.go.kr/open_content/ko/page.do?mnu_uid=3757.
- ↑ "Xinhua News | China to host APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting in 2026". https://english.news.cn/20241117/e00914cecba64210b6886fb4064e8f72/c.html.
- ↑ "Xi says China's city of Shenzhen to host APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting in 2026" (in en). https://english.news.cn/20251101/e0e9fbf27f1945c49d9b29ec0e11b723/c.html.
- ↑ "2023 APEC Leaders' Golden Gate Declaration" (in en-US). 2023-11-18. Statement 16.. https://bidenwhitehouse.archives.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/11/17/2023-apec-leaders-golden-gate-declaration/.
- ↑ Thanh Van (2025-01-16). "Phu Quoc selected as host city for APEC Summit 2027" (in en). https://vir.com.vn/phu-quoc-selected-as-host-city-for-apec-summit-2027-121423.html.
- ↑ "Singapore set to host APEC Summit in 2030". https://www.channelnewsasia.com/singapore/singapore-apec-summit-2030-lawrence-wong-4752481.
- ↑ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects: October 2024". International Monetary Fund. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/October/weo-report?c=111,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2027&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Aquino, Marco; Morland, Sarah (10 October 2025). "Peru's president removed by Congress, legislature chief sworn in". Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/peru-lawmakers-make-fresh-push-remove-unpopular-president-office-2025-10-09/.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "Thailand's new prime minister takes office". Deutsche Welle. 7 September 2025. https://www.dw.com/en/thailands-new-prime-minister-takes-office/a-73908316.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 "Thai tycoon Anutin Charnvirakul takes office as PM after royal endorsement". CNA. 7 September 2025. https://www.channelnewsasia.com/asia/thailand-pm-paetongtarn-court-ruling-decision-hun-sen-cambodia-5321511.
- ↑ "APEC 'too busy' for free trade deal, says Canberra". The Australian. 12 January 2007. http://www.theaustralian.news.com.au/story/0,20867,21046591-2702,00.html.
- ↑ "Media Statement by the President of India upon the conclusion of his state visit to Papua New Guinea and New Zealand en route from Auckland to New Delhi". http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=144616.
- ↑ "AFP: West worried India would tip APEC power balance: official". 6 September 2007. http://afp.google.com/article/ALeqM5hZoirSNiHlYD3ZRa5JhKVsPbnKrA.
- ↑ Lee, Matthew (20 July 2011). "Clinton urges India to expand influence". https://www.yahoo.com/news/clinton-urges-india-expand-influence-093840435.html.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 39.3 39.4 39.5 "MACAU DAILY TIMES – No negotiations on APEC membership". 21 February 2013. http://www.macaudailytimes.com.mo/macau/23904-negotiations-APEC-membership.html.
- ↑ Bhandari, Neena. "India Voice – India will have to wait for APEC membership". http://www.india-voice.com/joomla/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=24&Itemid=50.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 Leff, Alex (22 June 2011). "Costa Rica Inches Toward Coveted APEC Membership". Americas Quarterly. http://www.americasquarterly.org/node/2600.
- ↑ "Peru, Colombia seek closer Central America, APEC trade ties –". Dominicantoday.com. 29 August 2006. http://www.dominicantoday.com/app/article.aspx?id=16917.
- ↑ "People's Daily Online – Ecuador seeks APEC accession in 2007". People's Daily. 8 October 2004. http://english.people.com.cn/200410/08/eng20041008_159319.html.
- ↑ "People's Daily Online – Colombia seeks APEC membership in 2007: FM". People's Daily. 6 September 2006. http://english.people.com.cn/200609/06/eng20060906_300141.html.
- ↑ "Transparency Reform Could Raise Trade by $148 Billion in APEC" John S. Wilson & Benjamin Taylor; Trade Facilitation Reform Research Brief, The World Bank. 2008.
- ↑ "Russia joins the APEC Business Travel Card Scheme". Sapporo. 29 May 2010. http://apec.org/Press/News-Releases/2010/0529_russia_abtc.aspx.
- ↑ Bergsten, C. Fred, "Toward a Free Trade Area of the Asia Pacific", Peterson Institute for International Economics Number Pb07-2. Pdf can be found via Google. Retrieved 9 November 2014.
- ↑ "China-led RCEP trade talks to begin in May". 25 April 2013. http://thebricspost.com/china-led-rcep-trade-talks-to-begin-in-may/.
- ↑ "Chinese President touts 'Asia-Pacific dream'". Deutsche Welle. 11 September 2014. https://www.dw.com/en/chinas-president-xi-touts-asia-pacific-dream-ahead-of-apec-summit/a-18050065.
- ↑ Goodman, Lee-Anne (10 November 2014). "Harper, Obama attend Asia-Pacific trade deal meeting in Beijing". The Canadian Press. https://globalnews.ca/news/1662792/harper-obama-attend-trade-meeting-in-beijing-as-deadline-for-deal-nears/.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 51.3 "FTAAP". Brookings.edu. September 2007. http://www.brookings.edu/opinions/2007/09northeastasia_brilliant.aspx.
- ↑ Chia Siow Yue. "The Emerging Regional Economic Integration Architecture in East Asia". Asian Economic Papers (MIT Press). Vol. 12, No. 1 (2013): p. 1–37
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 "Plan B for World Trade". Petersoninstitute.org. http://www.petersoninstitute.org/publications/opeds/oped.cfm?ResearchID=655. No reference to numbers of FTAs.
- ↑ Policy Briefs in International Economics (PDF)
- ↑ "Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific". https://www.pecc.org/research/ftaap.
- ↑ "APEC roadmap on FTAAP a historic decision: Xi". 11 November 2014. http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2014-11/11/c_133782162.htm.
- ↑ "Elite Talk: A talk with APEC chief Alan Bollard on China's APEC championship, the FTAAP and New Silk Road". 10 November 2014. http://en.people.cn/102775/310666/index.html.
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 "APEC Study Center Contortium". Archived from the original on 1 December 2010. https://web.archive.org/web/20101201162758/http://www.apec.org/en/Groups/Other-Groups/APEC-Study-Centers-Consortium.aspx.
- ↑ "Home – APEC Business Advisory Council". https://www2.abaconline.org/.
- ↑ "National Center for APEC – About ABAC". http://www.ncapec.org/abac/index.html.
- ↑ "APEC Business Advisory Council (ABAC) – China APEC Development Council". http://www.chinaapec.org/en/about_apec/content_2.shtml.
- ↑ Pue, W. Wesley (2000). Pepper in our Eyes: the APEC Affair. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada: UBC Press. ISBN 978-0-7748-0779-1. https://archive.org/details/pepperinoureyesa0000unse.
- ↑ Wallace, Bruce (21 September 1998). "APEC Protest Controversy". Maclean's via The Canadian Encyclopedia (Historica Foundation of Canada). http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/index.cfm?PgNm=TCE&Params=M1ARTM0011768.
- ↑ Nuttall-Smith, Chris (27 November 1997). "APEC summit gets nasty at UBC". Varsity News (Varsity Publications, Inc.). http://www.varsity.utoronto.ca/archives/118/nov27/news/APEC.html.
- ↑ Schmidt, Sarah (6 January 1998). "Student protesters fight back for civil rights". Varsity News (Varsity Publications, Inc.). http://www.varsity.utoronto.ca/archives/118/jan06/news/APEC.html.
- ↑ "Civil rights group denounces attack on UBC students' APEC protests" (Press release). British Columbia Civil Liberties Association (BCCLA). 23 November 1997. Archived from the original on 5 October 2006. Retrieved 6 September 2006.
- ↑ "Student member of BCCLA executive arrested!" (Press release). British Columbia Civil Liberties Association (BCCLA). 25 November 1997. Archived from the original on 5 October 2006. Retrieved 6 September 2006.
- ↑ Bonner, David Johnston With Raymond (2003-08-15). "Suspect in Indonesia Bombings Is Captured in Asia" (in en-US). The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/2003/08/15/world/suspect-in-indonesia-bombings-is-captured-in-asia.html.
- ↑ "Apec supports nuclear, agrees climate targets". World Nuclear News. 10 September 2007. http://www.world-nuclear-news.org/energyEnvironment/APEC_supports_nuclear_agrees_climate_targets.shtml.
- ↑ Phillips, Tom; Watts, Jonathan; Franklin, Jonathan (30 October 2019). "Chilean president cancels Apec and climate summits amid wave of unrest" (in en-GB). The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/oct/30/chile-protests-president-sebastian-pinera-protest-unrest.
- ↑ "Apec summit ends with unity on WTO reform but not Gaza or Ukraine" (in en-GB). The Guardian. 2023-11-18. ISSN 0261-3077. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/nov/18/apec-summit-ends-with-unity-on-wto-reform-but-not-gaza-or-ukraine.
- ↑ "No kimonos for APEC leaders in Japan". Reuters. 11 November 2010. https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE6AA4H220101111.
- ↑ "No aloha for Hawaiian shirts at APEC family photo". Honolulu Star-Advertiser. 13 November 2011. http://www.staradvertiser.com/news/breaking/133780488.html?id=133780488.
- ↑ "Awkward Apec Fashion: what the world leaders wore". 8 November 2018. https://www.theguardian.com/world/gallery/2015/nov/17/awkward-apec-fashion-what-the-world-leaders-wore-in-pictures.
- ↑ Gerhardt, Tina (11 November 2011). "America's Pacific Century?: APEC Summit in Hawaii Seeks to Implement Free Trade Agreement of the Asia Pacific Region". Commondreams. http://www.commondreams.org/view/2011/11/11-0.
- ↑ "About APEC – Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation". http://www.apec.org/apec/about_apec.html.
- ↑ "APEC—a pretty empty chatter". The Economist. 12 September 2007. http://www.economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=9788478.
Further reading
- Alkan, Abdulkadir (2014). "APEC 2014: Better diplomatic ties for better economic relations". Daily Sabah. http://www.dailysabah.com/asia/2014/11/15/apec-2014-better-diplomatic-ties-for-better-economic-relations.
- Fazzone, Patrick B. (2012). "The Trans-Pacific Partnership—Towards a Free Trade Agreement of Asia Pacific?". Georgetown Journal of International Law 43 (3): 695–743. ISSN 1550-5200.
External links
Template:APEC Template:APEC leaders Template:APEC foreign ministers Template:APEC finance ministers Template:Eastern world
 |
 KSF
KSF










































