Economic Community of West African States
Topic: Organization
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 13 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 13 min
Economic Community of West African States
| |
|---|---|
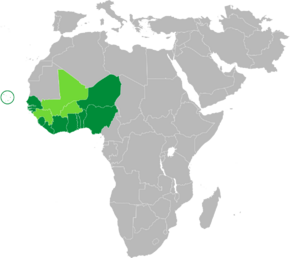 Member states Suspended states | |
| Headquarters | Abuja, Nigeria [ ⚑ ] 9°2′35″N 7°31′32″E / 9.04306°N 7.52556°E |
| Official languages |
|
| Member states | 15 members
|
| Leaders | |
• Chairman | Umaro Sissoco Embaló |
• President of the Commission | Omar Touray |
| Moustapha Cissé Lô | |
| Establishment | 28 May 1975 |
• Treaty of Lagos | 28 May 1975[1] |
• Treaty Revision | 24 July 1993 |
| Area | |
• Total | 5,114,162 km2 (1,974,589 sq mi) (7th) |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | 387 million ({{{population estimate rank}}}) |
• Density | 68.3/km2 (176.9/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate |
• Total | US$1.483 trillion[2] (18th) |
• Per capita | US$4,247[3] |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $816.4 billion[4] 2019 ({{{GDP nominal rank}}}) |
• Per capita | $2,089 |
| Currency |
|
| Time zone | UTC+0 to +1 |
Website www | |
| |
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese) is a regional political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an area of 5,114,162 km2 (1,974,589 sq mi), and in 2019 had an estimated population of over 387 million.
Considered one of the pillar regional blocs of the continent-wide African Economic Community (AEC), the stated goal of ECOWAS is to achieve "collective self-sufficiency" for its member states by creating a single large trade bloc by building a full economic and trading union. The union was established on 28 May 1975, with the signing of the Treaty of Lagos, with its stated mission to promote economic integration across the region. A revised version of the treaty was agreed and signed on 24 July 1993 in Cotonou.
The ECOWAS also serves as a peacekeeping force in the region, with member states occasionally sending joint military forces to intervene in the bloc's member countries at times of political instability and unrest.[5][6]
Member states
As of February 2017, ECOWAS has 15 member states; eight of these are French-speaking, five are English-speaking, and two Portuguese-speaking. All current members joined the community as founding members in May 1975, except Cape Verde which joined in 1977.[7][8]
The only former member of ECOWAS is Arabic-speaking Mauritania, which was also one of the founding members in 1975 and decided to withdraw in December 2000.[7] Mauritania recently signed a new associate-membership agreement in August 2017.[9]
Morocco officially requested to join ECOWAS in February 2017.[10] The application was endorsed in principle at the summit of heads of state in June 2017,[11][12] but Morocco's bid for membership was stalled.[13]
Mali was suspended from ECOWAS on 30 May 2021, following its second military coup within nine months.[14] Guinea was also suspended on 8 September 2021, shortly after a military coup took place in the country.[15][16] Sanctions were placed on both countries on 16 September.[17] On 10 January 2022, Mali announced its decision to close its borders and recalled several ambassadors with ECOWAS in response to sanctions imposed for deferring elections for four years.[18] On 28 January 2022, Burkina Faso was suspended from ECOWAS following a military coup.[19]
Statistics for population, nominal GDP and purchasing power parity GDP listed below are taken from World Bank estimates for 2015, published in December 2016.[20][21][22] Area data is taken from a 2012 report compiled by the United Nations Statistics Division.[23]
| Country | Area[23] (km2) |
Population[20] (thousands) |
GDP (nominal)[21] (millions USD) |
GDP (PPP)[22] (millions intl.$) |
Currency | Official language |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4,033 | 521 | 1,603 | 3,413 | escudo | Portuguese | |
| 11,295 | 1,991 | 939 | 3,344 | dalasi | English | |
| 245,857 | 12,609 | 6,699 | 15,244 | franc | French | |
| 36,125 | 1,844 | 1,057 | 2,685 | CFA franc | Portuguese | |
| 111,369 | 4,503 | 2,053 | 3,762 | dollar | English | |
| 1,240,192 | 17,600 | 12,747 | 35,695 | CFA franc | French | |
| 196,712 | 15,129 | 13,610 | 36,625 | CFA franc | French | |
| 72,300 | 6,453 | 4,215 | 10,127 | leone | English | |
| ECOWAS Zone A total | 1,917,883 | 60,550 | 42,923 | 110,895 | Template:Sortdash | |
| Country | Area[23] (km2) |
Population[20] (thousands) |
GDP (nominal)[21] (millions USD) |
GDP (PPP)[22] (millions intl.$) |
Currency | Official language |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 114,763 | 10,880 | 8,291 | 22,377 | CFA franc | French | |
| 272,967 | 18,106 | 10,678 | 30,708 | CFA franc | French | |
| 238,533 | 27,410 | 37,543 | 115,409 | cedi | English | |
| 322,463 | 22,702 | 31,759 | 79,766 | CFA franc | French | |
| 1,267,000 | 19,899 | 7,143 | 19,013 | CFA franc | French | |
| 923,768 | 211,400 | 481,066 | 1,093,921 | Naira | English | |
| 56,785 | 7,305 | 4,088 | 10,667 | CFA franc | French | |
| ECOWAS Zone B total | 3,196,279 | 277,502 | 580,568 | 1,371,861 | Template:Sortdash | |
History
The ECOWAS was formed initially from the region's former French, British and Portuguese colonies, and independent Liberia, following post-colonial independence throughout the region (particularly in the 1960s and 1970s). It was formed to provide regional economic cooperation, but has since evolved to include political and military cooperation, as well. [24]
The union was established on 28 May 1975, with the signing of the Treaty of Lagos, with its stated mission to promote economic integration across the region. A revised version of the treaty was agreed and signed on 24 July 1993 in Cotonou.[25] Considered one of the pillar regional blocs of the continent-wide African Economic Community (AEC), the stated goal of ECOWAS is to achieve "collective self-sufficiency" for its member states by creating a single large trade bloc by building a full economic and trading union.[26]
The ECOWAS also serves as a peacekeeping force in the region, with member states occasionally sending joint military forces to intervene in the bloc's member countries at times of political instability and unrest. In recent years these included interventions in Ivory Coast in 2003, Liberia in 2003, Guinea-Bissau in 2012, Mali in 2013, and The Gambia in 2017.[5][6]
Covering a region once known as a "coup belt," the ECOWAS, since the 1990s, has attempted to defend the region's shift towards democracy against authoritarian attacks. However, the group has been cited for weak and ineffective responses in the early 2020s, when three member countries suffered military coups d'état -- two in Burkina Faso, two in Mali, one attempt in Niger, and one in Guinea.[15][16]
In 2011, the ECOWAS adopted its development blueprint for the next decade, Vision 2020, and, to accompany it, a Policy on Science and Technology (ECOPOST).[citation needed]
Structure
Overall
The ECOWAS consists of two operating institutions to implement policies: the ECOWAS Commission and the ECOWAS Bank for Investment and Development (EBID) -- formerly known as the Fund for Cooperation, until it was renamed in 2001. [27]
In addition, ECOWAS includes the following institutions: ECOWAS Commission, Community Court of Justice,[28] Community Parliament,[29] ECOWAS Bank for Investment and Development (EBID),[29] West African Health Organisation (WAHO),[30] and the Inter-Governmental Action Group against Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing in West Africa (GIABA).[31]
ECOWAS includes two sub-regional blocks:
- The West African Economic and Monetary Union (also known by its French-language acronym UEMOA) is an organisation of eight, mainly French-speaking, states within the ECOWAS which share a customs union and currency union.[32] Established in 1994 and intended to counterbalance the dominance of English-speaking economies in the bloc (such as Nigeria and Ghana), members of UEMOA are mostly former territories of French West Africa. The currency they all use is the CFA franc, which is pegged to the euro.[32]
- The West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ), established in 2000, comprises six mainly English-speaking countries within ECOWAS which plan to work towards adopting their own common currency, the eco.[32]
The ECOWAS operates in three co-official languages—French, English, and Portuguese.[32]
Executive secretaries and presidents of the commission
| Executive Secretary | Country | In office |
|---|---|---|
| Inaugural holder Aboubakar Diaby Ouattara | January 1977 – 1985 | |
| Momodu Munu | 1985–1989 | |
| Abass Bundu | 1989–1993 | |
| Édouard Benjamin | 1993–1997 | |
| Lansana Kouyaté | September 1997 – 31 January 2002 | |
| Mohamed Ibn Chambas | 1 February 2002 – 31 December 2006 | |
| Mohamed Ibn Chambas | 1 January 2007 – 18 February 2010 | |
| James Victor Gbeho | 18 February 2010 – 1 March 2012 | |
| Kadré Désiré Ouedraogo | 1 March 2012 – 4 June 2016 | |
| Marcel Alain de Souza | 4 June 2016 – 1 March 2018 | |
| Jean-Claude Brou | 1 March 2018 – 3 July 2022 | |
| Omar Touray | 3 July 2022 – present |
Chairpersons
| Chairperson | Country | In office |
|---|---|---|
| Yakubu Gowon | 28 May 1975 – 29 July 1975 | |
| Gnassingbé Eyadéma | 29 July 1975 – 13 September 1977 | |
| Olusegun Obasanjo | 13 September 1977 – 30 September 1979 | |
| Léopold Sédar Senghor | 30 September 1979 – 31 December 1980 | |
| Gnassingbé Eyadéma | 1980–1981 | |
| Siaka Stevens | 1981–1982 | |
| Mathieu Kérékou | 1982–1983 | |
| Ahmed Sékou Touré | 1983–1984 | |
| Lansana Conté | 1984–1985 | |
| Muhammadu Buhari | 1985 – 27 August 1985 | |
| Ibrahim Babangida | 27 August 1985 – 1989 | |
| Dawda Jawara | 1989–1990 | |
| Blaise Compaoré | 1990–1991 | |
| Dawda Jawara | 1991–1992 | |
| Abdou Diouf | 1992–1993 | |
| Nicéphore Soglo | 1993–1994 | |
| Jerry Rawlings | 1994 – 27 July 1996 | |
| Sani Abacha | 27 July 1996 – 8 June 1998 | |
| Abdulsalami Abubakar | 9 June 1998 – 1999 | |
| Gnassingbé Eyadéma | 1999 – 1999 | |
| Alpha Oumar Konaré | 1999 – 21 December 2001 | |
| Abdoulaye Wade | 21 December 2001 – 31 January 2003 | |
| John Kufuor | 31 January 2003 – 19 January 2005 | |
| Mamadou Tandja | 19 January 2005 – 19 January 2007 | |
| Blaise Compaoré | 19 January 2007 – 19 December 2008 | |
| Umaru Musa Yar'Adua | 19 December 2008 – 18 February 2010 | |
| Goodluck Jonathan | 18 February 2010 – 17 February 2012 | |
| Alassane Ouattara | 17 February 2012 – 17 February 2013 | |
| John Mahama | 17 February 2013 – 19 May 2015 | |
| Macky Sall | 19 May 2015 – 4 June 2016 | |
| Ellen Johnson Sirleaf | 4 June 2016 – 4 June 2017 | |
| Faure Gnassingbé | 4 June 2017 – 31 July 2018 | |
| Muhammadu Buhari | 31 July 2018 – 29 June 2019 | |
| Mahamadou Issoufou | 29 June 2019 – 2 June 2020 | |
| Nana Akufo-Addo | 2 June 2020 – 3 July 2022 | |
| Umaro Sissoco Embaló | 3 July 2022 – Present |
Regional security co-operation
The ECOWAS nations assigned a non-aggression protocol in 1990 along with two earlier agreements in 1978 and 1981. They also signed a Protocol on Mutual Defence Assistance in Freetown, Sierra Leone, on 29 May 1981, that provided for the establishment of an Allied Armed Force of the Community.[33]
Community Parliament
The Community Parliament consists of 115 members, distributed based on the population of each member state.[34] This body is headed by the Speaker of the Parliament, who is above the Secretary General.
| Country | Parliament Seats |
|---|---|
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 8 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 7 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 35 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 |
Expanded ECOWAS Commission
For the third time since its inception in 1975, ECOWAS is undergoing institutional reforms. The first was when it revised its treaty on 24 July 1993; the second was in 2007 when the Secretariat was transformed into a Commission. As of July 2013, ECOWAS now has six new departments (Human Resources Management; Education, Science and Culture; Energy and Mines; Telecommunications and IT; Industry and Private Sector Promotion. Finance and Administration to Sierra Leone has been decoupled, to give the incoming Ghana Commissioner the new portfolio of Administration and Conferences).[35]
Community Court of Justice
The ECOWAS Community Court of Justice was created by a protocol signed in 1991 and was later included in Article 6 of the Revised Treaty of the Community in 1993.[36] However, the Court did not officially begin operations until the 1991 protocol came into effect on 5 November 1996. The jurisdiction of the court is outlined in Article 9 and Articles 76 of the Revised Treaty and allows rulings on disputes between states over interpretations of the Revised Treaty. It also provides the ECOWAS Council with advisory opinions on legal issues (Article 10). Like its companion courts, the European Court of Human Rights and East African Court of Justice, it has jurisdiction to rule on fundamental human rights breaches.[36]
Sporting and cultural exchange
ECOWAS nations organise a broad array of cultural and sports events under the auspices of the body, including the CEDEAO Cup in football, the 2012 ECOWAS Games and the Miss CEDEAO beauty pageant.[37] The Community Heads of State and Government adopted African Traditional Wrestling as the Community Sport, and through its Specialised Agency in charge of youth and sports development, the Ouagadougou-based ECOWAS Youth and Sports Development Centre (EYSDC), has consistently organised the yearly ECOWAS African Wrestling Tournament mainly in Dakar (Senegal) and Niamey ((Niger) based on a harmonized African wrestling code. The Community, through the EYSDC, also organized 2 editions of the ECOWAS International Cycling tour, taking close to 100 riders from all member States, from Lagos to Accra and then from Lagos o Abidjan. In addition to the sports and well-being objective of the tour, the race also served to demonstrate and put into practice the ECOWAS protocol on free movement of goods and persons. In 2019, the EYSDC instituted the ECOWAS Abuja International Marathon. The first edition brought together international marathoners from West Africa, Kenya, Ethiopia and Cameroon. Similarly, the Community, through its specialised agency, promotes regional sports development by offering sponsorship to regional sports federations and specialized disciplines such as the West African Deaf Sports Union ((WADSU), the West African Liaison Office of the International Council for Military Sports (WALO-CISM), the Region 2 of the African Athletics Federation, the West African University Games (WAUG), among others.
Economic integration
West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA)

The West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU,[38] also known as UEMOA from its name in French, Union économique et monétaire ouest-africaine) is an organisation of eight, mainly francophone West African states within the ECOWAS, previously colonies of French West Africa, that were dominated otherwise by Anglophone heavyweights like former British colonies Nigeria and Ghana.[39] It was established to promote economic integration among countries that share the CFA franc as a common currency. UEMOA was created by a Treaty signed at Dakar, Senegal, on 10 January 1994, by the heads of state and governments of Benin, Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast, Mali, Niger, Senegal, and Togo. On 2 May 1997, Guinea-Bissau, a former Portuguese colony, became the organisation's eighth (and only non-francophone) member state.
UEMOA is a customs union and currency union between the members of ECOWAS. Its objectives include:[40]
- Greater economic competitiveness, through open markets, in addition to the rationalisation and harmonisation of the legal environment
- The convergence of macro-economic policies and indicators
- The creation of a common market
- The co-ordination of sectoral policies
- The harmonisation of fiscal policies
Among its achievements, the UEMOA has successfully implemented macro-economic convergence criteria and an effective surveillance mechanism. It has adopted a customs union and common external tariff and has combined indirect taxation regulations, in addition to initiating regional structural and sectoral policies. A September 2002 IMF survey cited the UEMOA as "the furthest along the path toward integration" of all the regional groupings in Africa.[41]
ECOWAS and UEMOA have developed a common plan of action on trade liberalisation and macroeconomic policy convergence. The organizations have also agreed on common rules of origin to enhance trade, and ECOWAS has agreed to adopt UEMOA's customs declaration forms and compensation mechanisms.[42]
Membership
 Benin (Founding Member)
Benin (Founding Member) Burkina Faso (Founding Member)
Burkina Faso (Founding Member) Guinea-Bissau (Joined on 2 May 1997)
Guinea-Bissau (Joined on 2 May 1997) Ivory Coast (Founding Member)
Ivory Coast (Founding Member) Mali (Founding Member)
Mali (Founding Member) Niger (Founding Member)
Niger (Founding Member) Senegal (Founding Member)
Senegal (Founding Member) Togo (Founding Member)
Togo (Founding Member)
West African Monetary Zone
Formed in 2000, the West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ) is a group of six countries within ECOWAS that plan to introduce a common currency called the Eco.[43] The six member states of WAMZ are Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Nigeria and Sierra Leone who founded the organisation together in 2000 and Liberia who joined on 16 February 2010. Apart from Guinea, which is francophone, they are all English-speaking countries. Along with Mauritania, Guinea opted out of the CFA franc currency shared by all other former French colonies in West and Central Africa.
The WAMZ attempts to establish a strong stable currency to rival the CFA franc, whose exchange rate is tied to that of the euro and is guaranteed by the French Treasury. The eventual goal is for the CFA franc and eco to merge, giving all of West and Central Africa a single, stable currency. The launch of the new currency is being developed by the West African Monetary Institute based in Accra, Ghana.
Membership
 Gambia (Founding Member)
Gambia (Founding Member) Ghana (Founding Member)
Ghana (Founding Member) Guinea (Founding Member)
Guinea (Founding Member) Liberia (Joined on 16 February 2010)[44][45]
Liberia (Joined on 16 February 2010)[44][45] Nigeria (Founding Member)
Nigeria (Founding Member) Sierra Leone (Founding Member)
Sierra Leone (Founding Member)
Transport
A Trans-ECOWAS project, established in 2007, plans to upgrade railways in this zone.[46]
Tourism
In 2019, ECOWAS unveiled its Ecotour Action Plan 2019 – 2029. It focuses on tourism heritage protection and development, and on the development of standards, regulations and control systems. [47][48][49] The plan includes five programmes for implementation, and detailed mechanisms for monitoring and evaluation. Ecotourism is not specifically developed, yet it has been mentioned that the program has the opportunity to create linkages between institutions and stakeholder collaboration, to suit ecotourism projects that prioritize community, biodiversity, and socioeconomics.[50]
See also
- Brown card system – motor insurance scheme of ECOWAS
- East African Community
- Economy of Africa
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- ECOWAS Peace Pageant
References
- ↑ "African Union". http://www.african-union.org/root/au/RECs/ecowas.htm.
- ↑ Data. "GDP, PPP (current international $) | Table". World Bank. http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.PP.CD?order=wbapi_data_value_2013+wbapi_data_value+wbapi_data_value-last&sort=desc.
- ↑ Data. "GNI per capita, PPP (current international $) | Table". World Bank. http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GNP.PCAP.PP.CD/countries.
- ↑ Data. "Enoch Randy Aikins (2023) West Africa/ECOWAS. Updated 7 June 2023. (current US$) | Table". futures.issafrica.org.. https://futures.issafrica.org/geographic/regions/west-africa-ecowas/#economics.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Adeyemi, Segun (6 August 2003). "West African Leaders Agree on Deployment to Liberia". Jane's Defence Weekly.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "The 5 previous West African military interventions". Yahoo News. AFP. 20 January 2017. https://www.yahoo.com/news/5-previous-west-african-military-interventions-111050770.html.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Pazzanita, Anthony (2008). Historical Dictionary of Mauritania. Scarecrow Press. pp. 177–178. ISBN 978-0-8108-6265-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=-KU_9MfXKKYC&pg=PA177.
- ↑ Odeyemi, Temitayo Isaac (2020), Oloruntoba, Samuel Ojo, ed., "Regional Integration and the Political Economy of Morocco's Desire for Membership in the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)" (in en), Pan Africanism, Regional Integration and Development in Africa (Springer International Publishing): pp. 97–123, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-34296-8_6, ISBN 978-3-030-34295-1
- ↑ Okanla, Karim. "Like a magnet". https://www.dandc.eu/en/article/ecowas-has-made-considerable-progress-still-has-ample-room-improvement.
- ↑ "Afrique". Diplomatie.ma. 24 February 2017. https://www.diplomatie.ma/Politique%C3%A9trang%C3%A8re/Afrique/tabid/136/vw/1/ItemID/14476/language/en-US/Default.aspx?platform=hootsuite.
- ↑ "Togolese president Faure Gnassingbe takes the reins of the ECOWAS Authority of Heads of State and Government". 7 June 2017. http://www.ecowas.int/togolese-president-faure-gnassingbe-takes-the-reins-of-the-ecowas-authority-of-heads-of-state-and-government/.
- ↑ Odeyemi, Temitayo Isaac (2020), Oloruntoba, Samuel Ojo, ed., "Regional Integration and the Political Economy of Morocco's Desire for Membership in the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)" (in en), Pan Africanism, Regional Integration and Development in Africa (Springer International Publishing): pp. 97–123, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-34296-8_6, ISBN 978-3-030-34295-1
- ↑ Imru AL Qays Talha Jebril (13 February 2020). "Morocco-ECOWAS: Good intentions are not enough". Moroccan Institute for Policy Analysis. https://mipa.institute/7323.
- ↑ "ECOWAS suspends Mali over second coup in nine months". Al Jazeera. 31 May 2021. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2021/5/31/ecowas-suspends-mali-over-second-coup-in-nine-months.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Samb, Saliou; Eboh, Camillus; Inveen, Cooper (September 9, 2021). "West African leaders due in Guinea as post-coup calm pervades Conakry". Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/world/africa/west-african-leaders-due-guinea-post-coup-calm-pervades-conakry-2021-09-09/.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "West African leaders suspend Guinea from Ecowas following coup," September 9, 2021, BBC News, retrieved September 9, 2021
- ↑ Christian, Akorlie; Samb, Saliou; Felix, Bate; Inveen, Cooper; Prentice, Alessandra (September 17, 2021). "West African bloc resorts to sanctions over Guinea and Mali coups". Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/world/africa/west-african-leaders-meet-decide-guinea-after-coup-2021-09-16/.
- ↑ AHMED, BABA (2022-01-10). "Mali's junta deplores new sanctions imposed by regional bloc" (in en-US). https://www.sfgate.com/news/article/Mali-s-junta-deplores-new-sanctions-imposed-by-16763433.php.
- ↑ "West African regional bloc suspends Burkina Faso's membership over coup" (in en). France 24. 28 January 2022. https://www.france24.com/en/africa/20220128-west-african-regional-bloc-suspends-burkina-faso-s-membership-over-coup.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 "Population 2015". World Bank. 16 December 2016. http://databank.worldbank.org/data/download/POP.pdf.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 "Gross domestic product 2015". World Bank. 16 December 2016. http://databank.worldbank.org/data/download/GDP.pdf.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 "Gross domestic product 2015, PPP". World Bank. 16 December 2016. http://databank.worldbank.org/data/download/GDP_PPP.pdf.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 "Demographic Yearbook – Population by sex, annual rate of population increase, surface area and density". United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. pp. 1–2. http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/products/dyb/dyb2012/Table03.pdf.
- ↑ Yansane, Aguibou (September 1977). The State of Economic Integration in North West Africa South of the Sahara: The Emergence of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) 20 (2): 63–87. doi:10.2307/523653. https://www.jstor.org/stable/523653.
- ↑ Odeyemi, Temitayo Isaac (2020), Oloruntoba, Samuel Ojo, ed., "Regional Integration and the Political Economy of Morocco's Desire for Membership in the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)" (in en), Pan Africanism, Regional Integration and Development in Africa (Springer International Publishing): pp. 97–123, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-34296-8_6, ISBN 978-3-030-34295-1
- ↑ "Basic information | Economic Community of West African States(ECOWAS)". https://ecowas.int/about-ecowas/basic-information/.
- ↑ "Aboutus – EBID | ECOWAS Bank for Investment and Development". https://www.bidc-ebid.org/en/?page_id=42697.
- ↑ "CCJ Official Website". http://prod.courtecowas.org/.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Economic Community of West African States(ECOWAS) | .". https://www.ecowas.int/.
- ↑ "WAHO | West African Health Organization". https://www.wahooas.org/web-ooas/.
- ↑ "Welcome !". GIABA. https://www.giaba.org.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 "Basic information | Economic Community of West African States(ECOWAS)". https://ecowas.int/about-ecowas/basic-information/.
- ↑ "Profile: Economic Community of West African States". Africa Union. 18 November 2010. http://www.africa-union.org/Recs/ECOWASProfile.pdf.
- ↑ About Us - ECOWAS Parliament, accessed 6 March 2017
- ↑ Bensah, Emmanuel K. (24 July 2013). "Communicating the ECOWAS Message (4): A New Roadmap for the Ouedraogo Commission(1)". Modernghana.com. http://www.modernghana.com/news/477274/1/communicating-the-ecowas-message-4-a-new-roadmap-f.html.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "ECOWAS (2007) Information Manual: The Institutions of the Community ECOWAS". http://www.ecowascourt.org/French/texts/information.pdf.
- ↑ "Miss ECOWAS 2010". The Economist. 18 November 2010. https://www.economist.com/blogs/baobab/2010/11/west_african_beauty_pageant.
- ↑ "West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU)". 9 October 2020. https://ecfr.eu/special/african-cooperation/waemu/.
- ↑ "La concurrence des organisations régionales en Afrique". Paris: L'Harmattan. 2012.
- ↑ "Chapter 1. Introduction: Reflections on an Agenda for Regional Integration and Cooperation in West Africa: International Development Research Centre". http://www.idrc.ca/en/ev-68350-201-1-DO_TOPIC.html. REGIONAL INTEGRATION AND COOPERATION IN WEST AFRICA A Multidimensional Perspective, Chapter 1. Introduction: Reflections on an Agenda for Regional Integration and Cooperation in West Africa
- ↑ "Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)" fact sheet from the US Department of State's Bureau of African Affairs
- ↑ "Annual Report on Integration in Africa 2002" All Africa, 1 March 2002
- ↑ "Common West Africa currency: ECO in 2015". MC Modern Ghana. http://www.modernghana.com/news/219137/1/common-west-africa-currency-eco-in-2015.html.
- ↑ "The Supplementary Wamz Payment System Development Project the Gambia, Guinea, Sierra Leone, and Liberia". Africa Development Bank Group. 2011. http://www.afdb.org/en/projects-and-operations/project-portfolio/project/p-z1-hz0-002/.
- ↑ "WAMZ gets US$7.8 million grant". Accra Daily Mail. 2011. http://www.accra-mail.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=27733:wamz-gets-us-78-million-grant&catid=81:business&Itemid=211.
- ↑ Proposed Ecowas railway . railwaysafrica.com.
- ↑ ECOWAS Regional Tourism Action Plan
- ↑ ECOWAS ECOTOUR pdf
- ↑ ECOWAS to promote regional development through tourism
- ↑ West Africa's (eco)tourism initiative: Last chance to protect African biodiversity
External links
 KSF
KSF
