Federal University of ABC
Topic: Organization
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 26 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 26 min
Universidade Federal do ABC | |
 Seal | |
Other names | UFABC |
|---|---|
| Motto | Uma trajetória coletiva de transformação social (Portuguese) |
Motto in English | A collective trajectory of social transformation |
| Type | Public |
| Established | 26 July 2005; |
| Endowment | R$ 223,134,706.00 (2012)[1] |
| Rector | Dácio Roberto Matheus[2] |
Academic staff | 490 (100% PhD)[3] |
| Students | 16,415(2018)[3] |
| Undergraduates | 14,898[3] |
| Postgraduates | 1,517 (master's & doctorate)[3] |
| Location | Santo André (headquarters), São Bernardo do Campo , São Paulo , Brazil [ ⚑ ] : 23°38′42″S 46°31′41″W / 23.6450°S 46.5280°W |
| Campus | Urban |
| Green and yellow |u}}rs | Green and yellow |
| Affiliations | ANDIFES,[4] CRUB,[5] RENEX,[6] AULP.[7] |
| Website | www |
Federal University of ABC (Portuguese: Universidade Federal do ABC, UFABC) is a Brazilian federal public institution of higher learning based in Santo André and São Bernardo do Campo, municipalities belonging to the ABC region, both in the state of São Paulo.
UFABC is the only federal university in Brazil with 100% of its professors holding PhDs[8] and, for the second consecutive year in 2011, emerged as the only university in Brazil with impact factor in scientific publications above the world average according to SCImago Institutions Rankings.[9][10] The institution was evaluated by the General Course Index (IGC) of the Ministry of Education (MEC) as the best university in the State of São Paulo, being rated as the 1st in the ranking of undergraduate courses among all universities in Brazil. The IGC takes into account in its assessment factors such as infrastructure, faculty and graduates' scores in the National Student Performance Exam (ENADE).[11] It occupies the 1st place among Brazilian universities in the "Internationalization" item in the University Ranking of the Folha de São Paulo newspaper.[12][13]
The chairman of the committee that formulated the proposal of the university was Luiz Bevilacqua, who became its second rector.[14]
History and expansion

In 2004, the Ministry of Education sent Bill 3.962 / 2004 to the National Congress, which provided for the creation of the Federal University of ABC Foundation. This law was sanctioned by the President of the Republic Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and published in the Federal Official Gazette (D.O.U.) of 27 July 2005, under No. 11,145 and dated 26 July 2005.
UFABC aims to integrate several campuses in the Greater ABC region. The current campuses are based in the municipalities of Santo André (headquarters) and São Bernardo do Campo.[15]
Deans
The first rector of UFABC was the ex-rector of the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), professor Hermano Tavares (PhD in Automation at the Université de Toulouse), whose term lasted from 2005 to 2007.[16]
Tavares was succeeded by the former president of the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB), professor Luiz Bevilacqua (PhD in Applied Mechanics at Stanford University and Grand Cross of the National Order of Scientific Merit), who had been his vice-chancellor and presided over the university implantation committee.[17]
For health reasons, Bevilacqua left office in mid-2008, being succeeded, pro tempore, by the former president of the Brazilian Society of Physics, Professor Adalberto Fazzio (PhD in Renewable Energies by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and Great Cross of the National Order of Scientific Merit).[18][19]
In January 2010, President Lula appointed the former Dean of Research at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) and Full Professor at the University of São Paulo (USP), Professor Helio Waldman (PhD in Electrical Engineering from Stanford University and Commander of the National Order of Scientific Merit) to exercise the position of rector of UFABC for the next four years. Professor Waldman had obtained the unanimous preference of the Electoral College in the composition of the triple list and won the Consultation to the Community, obtaining the majority of votes in all categories of voters (students, teachers and administrative technicians).[20][21]
Recognition
- The French newspaper Le Monde published an article that highlights the fact that it is the first Brazilian university to rely on 100% of professors with doctorates.[22]
- Writing in the Mexican Gnoseogénesis, the doctor José Luis Morán López of the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México highlights the pleasant surprise of the creation of UFABC and its interdisciplinary project created by 25 Brazilian scientists.[23]
- The portal of the Methodist University of São Paulo published an article on the inauguration of one of the blocks UFABC made by the then-president of the Republic, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva where it talks about the goal of leaving the UFABC among the 100 best universities in the world, for example, ahead of the Brazilian university USP that was in 138th position among the best universities in the world.[24]
- Writing in the Portal Luis Nassif, Adalberto Fazzio (professor, USP) and Armando Z. Milioni (associate professor, ITA), highlight the six interdisciplinary axes at AFABC and the fact that less than 50% of the subjects that make up student grades are compulsory.[25]
- During the presentation of the seminar "Interdisciplinarity", held in April 2009, a professor of Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG), doctor Alaor Clark commented that he considers the UFABC the most advanced interdisciplinary project in Brazil and in the world.[26]
- In a presentation to the Center of Physics of Porto (Portugal), the professor doctor Daniel Zanetti de Florio cites the fact that UFABC have an innovative educational project based on Bologna Process.[27]
- In an article in the newspaper Diário do Grande ABC by the then-dean of research in UFABC, Helio Waldman comments that the newly created UFABC was born in an advanced stage for the 20th century and achieved in a few years the development in research that universities such as USP and Unicamp, for example, took decades to build. The article is constructed from the result of a notice that shows the UFABC in the first time of Brazilian universities in nanotechnology.[28]
- Another article published in the Diário do Grande ABC by professor Armando Zeferino Milioni (ITA) said the creation of the Masters and Doctorate of UFABC and highlights its qualified staff.[29]
Undergraduate teaching

Unlike many universities in Brazil, where the curriculum has a fixed order, at UFABC, the student can decide the order in which the subjects will be taken, without prerequisites, only recommendations. That means that anyone can take any subject, given that the class isn't full. Also the year is divided in three four-months periods, instead of two semesters.
At the end of each period, the student chooses the classes they want to take. On each class, the students are listed by their CR (which is UFABC's version of the GPA) and the first ones will attend that class on the next period. However, if the class is from a specific course, the criteria becomes the CP (a number ranging from 0 to 1 that indicates how much of that specific course was completed by that student). All disciplines have an associated "credit", which represents the number of classes per two weeks.
After their basic university education, the student has several options: they can enter the job market with a bachelor's degree in Science and Technology or may continue at the university and attend one or two years in a bachelor's program specifically or eight forms of engineering. There is also the possibility of holding a master's degree and moving to master's degree programs in other national and international programs.
The graduate of an interdisciplinary bachelor's program of a university may enroll in up to two of 21 options for undergraduate courses as their basic training, divided into bachelor's degrees and.[30]
The UFABC was the first institution of higher education in Brazil to adopt the interdisciplinary bachelor's degree.[31]
Disciplines
There are three types of disciplines at UFABC, mandatory, limited option and free. The type of any given discipline is different for each course, meaning that the same discipline might be of one type on a course, but of other type on another. Mandatory disciplines are the ones required by a course in order to finish it. For computer science students, Databases discipline required, so for the computer science course, it is mandatory. Limited option disciplines are meant to enhance the student's knowledge on a certain field of study. Molecular evolution, for example, is a limited option discipline for Biology students. Free disciplines are all disciplines that don't fit in either one of the previous categories. LIBRAS is a free discipline on all non-licentiate courses.
Evaluation
The fact that the curriculum has no fixed order introduces some disadvantages, for example, one professor may apply harder exams than the others, creating a disparity between grades on the same discipline. Some, however, are "unified", meaning that the same exams and evaluations will be applied to all students, preventing that disparity. Excluding Quantum Physics and Structure of Matter, all Physics related disciplines are unified.
Different disciplines have different evaluation systems. One may have three, two, one or no exams at all (in this case, the evaluation is made via a project developed by the student). There may also be a student project and one or two exams.
Students who get a lower than C grade have the option to do one last exam, which is sometimes referred to as "recovery exam", that can increase their grade up to a C. If one gets an F and doesn't do well on the recovery exam, they will have to redo the discipline.
Coefficients[32]
At UFABC, all undergrad students have four coefficients. They are the , the , the and the .
CR ("Coeficiente de Rendimento", orYield Coefficient)
It represents how well the student is doing at the disciplines. As mentioned, it is the equivalent of the GPA. It can be calculated by the following formula:
Where is the number of completed disciplines, is the grade on that discipline, is the discipline's credits and is:
and .
CA ("Coeficiente Acadêmico", or Academic Coefficient)
It is similar to the CR, however, if a student takes the same discipline multiple times, only the one with the higher grade will be accounted. It is calculated using the following formula:
Where is the number of different disciplines taken by the student, is the number of credits on that discipline is the greatest grade on that discipline. is:
and .
CPk ("Coeficiente de Progressão", or Progression Coefficient)
Represents the ratio between the approved disciplines' credits on a course and the total of credits on that course. It grows as the student finishes disciplines according to their category (mandatory, limited option and free). When it reaches 1, it means that student has finished all the required credits on that course . Its formula is:
Where:
- is the number of approved credits on the mandatory disciplines;
- is the number of approved credits on the limited option disciplines;
- is the number of approved credits on the free disciplines;
- is the total number of required credits on mandatory disciplines for the course ;
- is the total number of required credits on limited option disciplines for the course ;
- is the suggested number of credits on free disciplines for the course .
Ik ("Coeficiente de Afinidade", or Affinity Coefficient)
It combines the , the and the number of periods a student has studied on the university. The calculation is as follows:
Bachelor of Science and Technology (BC&T)
Bachelor of Science and Technology is a general course that teaches the foundation on mathematics, physics, biology, chemistry and computer science, while giving a slight introduction on human sciences. The idea behind that is to have students working with interdisciplinary subjects via a methodology that encourages an investigative approach to situations and stimulates scientific research and production.[33]
Examples of subjects studied are:
- Classical mechanics
- Thermodinamics
- Electromagnetism
- Quantum mechanics
- Epistemology
- Interactions between science and society
- Calculus
- Basic programming
- Origins and evolution of life
- Basic chemistry
The course takes a total of 2,400 hours of study to be completed.

Bachelor of Science and Humanities (BC&H)
The Bachelor of Science and Humanities is a course of general science. The initiation in Natural Science, Formal, Social, and Philosophy is through lectures with participation in research groups, under the supervision of a senior researcher.[34]
The course also takes 2,400 hours to finish.
Post-BC&T and post-BC&H degrees
After completing either the BC&T or the BC&H, the student can choose up to two specific degrees to pursue. Students that graduate on BC&T have the following options:
- Santo André's campus:
- São Bernardo's campus:
Students that graduate on BC&H, can choose between (all of them at São Bernardo's campus):
- Economics
- Philosophy (Graduation or Licentiate)
- Spatial planning
- Public policies
- International relations

Research
The UFABC is the only federal university in the Brazil that has 100% of professors with a doctoral degree. UFABC research in Nanotechnology has been recognised by CNPq.[28] Researchers in Nanotechnology in UFABC were able to publish articles in the scientific journal Nano Letters.[35]
The university employs professors who received the Capes awards for Best Thesis, researchers with the Commendation and the Grand Cross of the Brazilian Order of Scientific Merit, members of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences, and representatives of national scientific organizations.[36]

In March 2007 the CAPES approved 10 of 11 applications for the opening of post-graduate studies (Master and Doctorate). The CAPES on average approves only one third of the applications referred to it.[29]
UFABC participates in major research projects worldwide, among them the presence of the university in the largest scientific project of all time, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) of the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) that is operating the largest particle accelerator ever built[37] and also in the DZero Experiment of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab) of the United States Department of Energy that conducts research on the basic structure of matter in the second-largest particle accelerator in the world.[38] The university has a presence in the first Brazilian space mission to deep space, the Mission Aster (Missão Aster), of the Brazilian Space Agency, which provides for the launching of a space probe in 2015.[39]
UFABC has research completed or in progress with research institutions such as the COPPE-UFRJ,[40] the National Institute for Space Research,[40] the Brazilian Space Agency,[40] the Angra Nuclear Power Plant,[41] the National Education and Research Network (RNP),[40] UNICAMP,[40] Unifesp,[42] USP,[43] UFSCar,[43] the Brazilian National Synchrotron Light Laboratory (LNLS),[44] the Institute for Advanced Studies of the Brazilian General Command for Aerospace Technology (CTA-IEAv),[45] the Eletronuclear,[46] the Institute for Research on Stem Cells (IPCTRON),[47] the Brazilian National Laboratory for Scientific Computing (LNCC),[48] the Braziliam Navy Technology Center (CTMSP),[49] the National Institute of Science and Technology for Optical Communications (FOTONICOM),[40] the ICMC-USP,[40] the Brazilian Society of Biophysics,[50] UFRGS,[40] UNIFEI[40] and UNIFENAS.[40]
The university collaborates with research institutes as the Max Planck Institute[51] (Germany), the Paris-Sud 11 University[52] (France), the National Acoustic Laboratories[40] (Australia) and the Pierre Auger Observatory[44] (Argentina ), the National Institute for Materials Science (Japan),[53] the University of Texas System (USA),[54] the Universidade do Algarve (Portugal)[55] and the Universidade de Coimbra (Portugal).[56]
Undergraduate research

For science projects the institution created the PDPD program ("Researching Since The First Day" or "Pesquisando Desde o Primeiro Dia" in Portuguese), where first-year students participate in research projects funded by the institution and supervised by doctors.[57]
Besides this program, students from other university years participate in undergraduate research programs with funding from organs such as the Institutional Program of Scientific Initiation, PIC-UFABC and PIBIC-UFABC, financed with resources from the UFABC. There is also the PIBIC-CNPq, financed by CNPq and PIBIC-Affirmative Action a pilot program launched and funded in UFABC by CNPq that provides scholarships for research by undergraduate students who entered the university system by affirmative actions (social quota). Students can also obtain research grants from organs such as Fapesp.[58]
The university has instituted a Scholarship Assistance - Events, which finances the participation of its students in extracurricular activities such as presentation of scientific work (e.g. work of graduate students approved at international conferences[59]) and going to technological events such as the Campus Party.
Infrastructure for research
The campus of Santo André has equipment such as[60][61] Atomic force microscopy and Tunneling, Circular dichroism, Elemental Analysis, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance, Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy of High Resolution, Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, Gas chromatograph, Atomic Emission Spectroscopy, Infrared spectroscopy, Potentiostat / Galvanostat, Centrifuge Refrigerated Superspeed, Absorption Spectroscopy and Atomic Emission For Multicomponent Analysis, Gas Chromatography-Mass Detector, Liquid Chromatography System, Modular Electrochemical Microscope, Spectroscopy of Fluorescence, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Dynamic Mechanical Analyzer, Differential scanning calorimetry, Thermogravimetric Analysis, Optical microscope, High performance liquid chromatography Coupled With Mass spectrometry With Mass Detector, Scanning electron microscope, X-ray crystallography, wind tunnel and supersonic wind tunnel.
In addition, UFABC has two networks of high-performance computers. The Chromo UFABC went into operation in June 2007 and is a project financed by FAPESP and CNPq, and the Bull Novascale UFABC is a project funded by CAPES.[44]
Library
The library website provides services such as queries to the collection, and renewal of loans of books. Also available are a list of acquisitions in recent months and the articles published on scientific journals by researchers of the UFABC. In addition, the library website is integrated to Twitter via Twitter @AnyWhere allowing interaction among the users of the system.[62]
Postgraduate education
The UFABC has courses of postgraduate education (Master or PhD) approved by the Capes.[63] They are:[64]
- Biological systems engineering (Master and PhD)
- Biotechnology (Master and PhD)
- Computer science (Master and PhD)
- Materials science (Master)
- Environmental technology (Master)
- Chemistry (Master and PhD)
- Social sciences (Master and PhD)
- Economics (Master)
- World Economy (Master and PhD)
- Energy engineering (Master and PhD)
- Biomedical engineering (Master)
- Information engineering (Master and PhD)
- Engineering management (Master)
- Electrical engineering (Master)
- Mechanical engineering (Master)
- Teaching and History of Sciences and Math (Master)
- Evolution (Master and PhD)
- Philosophy (Master)
- Physics (Master and PhD)
- Mathematics (Master and PhD)
- Nanotechnology (Master and PhD)
- Neuroscience (Master and PhD)
- Spatial planning (Master and PhD)
- Public Policies (Master)

High school
Since 2010 UFABC has offered a preparatory course for the ENEM, free for public school students in the ABC Region, as part of an extension project of the university. In this course, classes are held Monday through Friday by students from the undergraduate institution; these are complemented with cultural activities and lectures by professors from UFABC on Saturdays. Some of the students who teach classes are scholarship of the Pro-rectory of University Extension while the majority are student volunteers.[65]
Selection of students
The first three classes of UFABC were formed through the selection processes via Vestibular. The students enrolled in the years 2007 to 2009.
From 2010 the selection of new students is done with the ENEM. classes. The Bachelor of Science and Technology of UFABC was the most sought-after course in the country in the "Unified Selecting System" (SISU) of Ministry of Education in 2010.[66]
According to statistics collected by the institution,[67] the Bachelor of Science and Technology (BC&T) had a demand of 13,758 applicants competing for 1,500 places (candidate/vacancy ratio of 9.2, with a 10,9% acceptance rate), while the Bachelor of Science and Humanities (BC&H) has 2320 registered for 200 places (candidate/vacancy ratio of 11.6, with an 8,6% acceptance rate).
There is a reservation of 50% of seats of all its courses in both periods (morning and evening) for candidates who attended high school in public schools, as well as those self-declared indigenous and African descent.[68]

Infrastructure

The Federal University of ABC has modern facilities in the city of Santo André (SP) and facilities under construction in São Bernardo do Campo (SP).
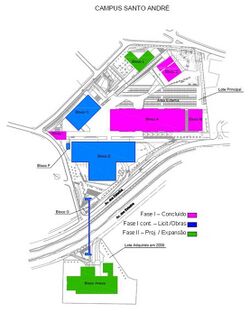
Centers and cores
The university has abolished the system of "departments" and "schools" that exist in other universities. In UFABC, all professors are bound to one of three major Centres Interdisciplinary:[69]
- CMCC - Center of Mathematics, Computing and Cognition
- CECS - Center of Engineering, Modelling and Applied Social Sciences
- CCNH - Centre for Natural Sciences and Humanities
Besides these, professors may be associated with the Interdisciplinary Centers linked to the rectory of UFABC:[69]
- NCSC - Center for Cognition and Complex Systems
- NCTS - Center for Science, Technology and Society
There are organs like the President's Office, Office of International Affairs, Center for Information Technology and Center for Technological Innovation, in addition to several secretaries and numerous research groups.[69]
Campus of Santo André
Santo André's Campus of the UFABC has six blocks, a total of 96409.03 square meters of built area in the headquarters campus of the university. The design of the campus of Santo André was by Libeskindllovet Architects S/S Ltda. and the construction work was in charge of the Constructor Augusto Velloso SA.[70]
Besides these main blocks located between the Avenida dos Estados and Avenida Santa Adelia, in Santo André city, the UFABC has a building with teaching laboratory, computer rooms and classrooms on Avenida Altântica, in Valparaíso neighborhood, and an administrative headquarters at Rua Catequese, in Jardim neighborhood, both in Santo André.[71] The university has acquired a large piece of land to the other side of the Avenida dos Estados (across from the current headquarters) to build new research laboratories and support to engineering.[72]
Campus of São Bernardo do Campo
On 25 August 2009 President Lula, accompanied by first lady Marisa Leticia, the Minister of Education, Fernando Haddad, the mayor of Sao Bernardo do Campo, Luiz Marinho, the deputy mayor, Frank Aguiar, and the Senator of the state of São Paulo, Aloisio Mercadante, laid the foundation stone of the campus of UFABC the city of São Bernardo do Campo. The campus of São Bernardo do Campo UFABC has six blocks.
The project is designed by Benno Perelmutter Architecture and Planning S/C Ltda.
Besides these six blocks, UFABC has a building with teaching laboratory, computer rooms and classrooms located in downtown São Bernardo do Campo, in the former headquarters of the College Salete named Block Sigma.[73]
University-enterprise integration
The Board of Education and Research (Consep) of UFABC published in 2010 a resolution asking for corporations and industries interested in signing agreements of internship to enable the students to form placements in these firms.[74] More than 100 companies signed the agreement with UFABC in 2010. Among such companies are names like[75] IBM, Itaú, Nestlé, Globo Organizations, General Motors (GM), Ford, Siemens, Honda, Sun Microsystems, Pirelli, BASF, and Accenture.
Sport
Students can play basketball, chess, handball, futsal, volleyball, swimming, table tennis, soccer, rugby and martial arts.[76]
Students take part in competitions with universities throughout Brazil. In the Tournament "Semana da Asa" that occurs in the CTA, annually organized by the ITA, the athletes of UFABC won 3rd place overall in the first year of participation in 2008, and 1st place overall in the second year of participation in 2009;[77]
In 2010, the Engenharíadas tournament brought together engineering colleges),[78] the University Games Paulistanos (organized by the city of São Paulo), the Liga Deportiva Universitaria Paulista (major league sports university in the country)[79] and the Cup of the University of São Carlos, the TUSCA, (organized by UFSCar and USP-São Carlos).[80]
Academic Athletic Association September XI
On 11 September 2006, the first class entered the Federal University of ABC. In 2007 a group of students began the Athletic UFABC, starting the Academic Athletic Association XI September (Portuguese: Associação Atlética Acadêmica XI de Setembro), AXIS, whose name was chosen in homage to the days of the first class.[81]
|
AXIS is now a student representation recognized by UFABC formed by an elected board and that represents all athletes of the university. The Athletics (AXIS) of UFABC supports sports at the university, and conducts the selection of athletes for the leagues in which they participate.
The campuses of UFABC have sports fields, swimming pools, gyms and sports courts.[83][84] Furthermore, AXIS has agreements with SESI (Social Service of Industry) of Santo André and with Santo André's Club Bochófilo for the use of sport facilities of these sites by the students of the institution.
AXIS works closely with the DCE (Central Directory of Students) of UFABC organizing parties, sponsoring the travel of athletes, performing the manufacture and sale of customized sports equipment (such as shirts, kimono, swimming caps,[85] etc.), and providing training and transportation for the athletes to participate in tournaments and doing extra activities such as mountaineering, abseiling[86] and internal tournaments.
Groups linked to Athletic's UFABC are Cheerleaders, the Infantry (responsible for the UFABC's fanfare in sports tournaments) and the Martial Arts Group, who train practitioners of Karate, Kung Fu, Tae Kwon Do and other martial arts.
Student representation
The DCE (Central Directory of Students) represents the graduate students. Its members are chosen in an annual election in which all undergraduates can vote. The Directory of UFABC was established in 2008, from the former Academic Center, and helps students' stay, by helping with their problems, monitoring projects that relate to academic life, as discussions in ConsEP, ConsUni and CEU.
The UFABC has student organizations representing groups of students. Some of these are officially recognized by the university while others rely on the coordination of support from professors and education cores,[87] including:
- Athletics: the Athletic Association Academic Eleventh of September, or AXIS, deals with student representation on matters involving student athletes from UFABC, always working with the DCE.[81]
- Branch of the IEEE: The student branch of IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, the professional organization that brings together professionals from all engineering and computing) of UFABC promotes the dissemination of scientific and technical knowledge of the exact sciences in UFABC. UFABC's IEEE branch has run the Robot Competition of UFABC.[88] the course of Formal Conversation in English, acquiring a driver for an airplane, installing a center of excellence in engineering at the university, the project of recycling of electronic material, and the project TISP on engineering education in high schools.[89]
- Association of Republics: The association of student republics is for residents in the republics of UFABC.
- Fubeca: The Fubeca is a social networking site for students. With internal systems of blog, wiki and integration with Twitter, the site is a meeting point for students, faculty and staff of the university.
- Theatre Group brings together students, faculty, staff and the community passionate about the art of acting.
- Choir: The choir of UFABC is composed of students and staff. It is governed by Daniel Moura, who has experience in lyrical singing and choir.
- Community Prism is a community created to promote the integration of the LGBT academic community of UFABC and their friends.
- Film Club brings together students and professors interested in watching and discussing cinema classics.
- Group Bible Study: In the style of groups such as IFES and ABU (Biblical Alliance University of Brazil) is a brief discussion and reflection on biblical texts.
- UFABC Anime Club: UFABC Anime Club is a cultural and social space for fans of Japanese animation and manga.
- GPDA: The Aerospace Research and Development Group consists of graduate and undergraduate students who seek to put into practice the concepts learned in the classroom through research, design and construction of aircraft. Currently the group is divided into subgroups related to airplanes, rockets and aerospace materials, as well as compete in competitions such as SAE Brazil Aerodesign and Baja.

See also
- Universities and Higher Education in Brazil
- ABC Region
- Interdisciplinarity
References
- ↑ "Propladi - CPE - Orçamento". http://propladi.ufabc.edu.br/images/leis/loa_2012.pdf.
- ↑ "Ministro da Educação assina posse de novo Reitor da UFABC, Dácio Roberto Matheus". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/noticias/ministro-da-educacao-assina-posse-de-novo-reitor-da-ufabc.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Portal UFABC - UFABC in Numbers (in Portuguese)". http://propladi.ufabc.edu.br/informacoes/ufabc-em-numeros.
- ↑ "ANDIFES - Associação Nacional dos Dirigentes das IFES". http://www.andifes.org.br/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=297&Itemid=118.
- ↑ "CRUB - Conselho de Reitores das Universidades Brasileiras". http://www.crub.org.br/interna.php?id=119.
- ↑ "PROEX - Fórum de Pró-Reitores de Extensão das Universidades Públicas Brasileiras". http://www.renex.org.br/proreitores.php.
- ↑ "AULP - Associação das Universidades de Lingua Portuguesa". http://www.aulp.org/memb.php?tipo=1&id=90.
- ↑ "UFABC a espera de seus alunos". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=623:ufabc-a-espera-de-seus-alunos&catid=187:artigos&Itemid=184.
- ↑ "UFABC aparece em ranking internacional". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=4189:ufabc-aparece-em-ranking-internacional&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Ranking Ibero-Americano SIR 2011". http://www.scimagoir.com/pdf/ranking_iberoamericano_2011_pt.pdf.
- ↑ "As melhores instituições de ensino superior no Brasil" (in pt-BR). 2012-12-07. https://exame.com/carreira/as-faculdades-excelentes-segundo-a-avaliacao-do-mec/.
- ↑ Folha de S. Paulo, Newspaper. "University Ranking of the Folha de S. Paulo newspaper". https://ruf.folha.uol.com.br/2019/lista-universidades-instituicoes/fundacao-universidade-federal-do-abc-4925.shtml.
- ↑ Folha de S. Paulo, Jornal. "Internalization - University Ranking of the Folha de S. Paulo newspaper". University Ranking of the Folha de S. Paulo newspaper. https://ruf.folha.uol.com.br/2013/rankinguniversitariofolha/rankingporinternacionalizacao/.
- ↑ "MEC - Assessoria de Comunicação Social". http://mecsrv04.mec.gov.br/acs/asp/noticias/noticiasId.asp?Id=8153.
- ↑ Brasil, Diário Oficial da União (2004). "Criação da Fundação Universidade Federal do ABC". Brazilian Congress. https://www.camara.leg.br/proposicoesWeb/prop_mostrarintegra;jsessionid=0CB7D902D381919DD7EAD3328A381333.node1?codteor=299997&filename=Avulso+-PL+3962/2004.
- ↑ "Lattes CNPq- Currículo de Hermano de Medeiros Ferreira Tavares". http://buscatextual.cnpq.br/buscatextual/visualizacv.jsp?id=K4787028A9.
- ↑ "Lattes CNPq - Currículo de Luiz Bevilacqua". http://buscatextual.cnpq.br/buscatextual/visualizacv.jsp?id=K4787137U2.
- ↑ "INCT - Ordem Nacional do Mérito Científico". http://www.inct-inofar.ccs.ufrj.br/gra_cruz.html.
- ↑ "Lattes CNPq - Currículo de Adalberto Fazzio". http://buscatextual.cnpq.br/buscatextual/visualizacv.jsp?id=K4787782H0.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Presidente Lula Nomeia Novo Reitor". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2843:presidente-lula-nomeia-novo-reitor&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Lattes CNPq - Currículo de Helio Waldman". http://buscatextual.cnpq.br/buscatextual/visualizacv.jsp?id=K4787028Z3.
- ↑ "MEC - Jornal Francês Destaca Investimento do Brasil". http://portal.mec.gov.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=14487.
- ↑ "Gnoseogénesis - La Importancia de la Multidisciplina". http://gnoseogenesis.emuseo.org/?p=171.
- ↑ "Metodista - Presidente Lula Inaugura Novo Prédio da UFABC". http://www.metodista.br/rronline/cidades/presidente-lula-inaugura-novo-predio-da-ufabc.
- ↑ "Luis Nassif - UFABC: Quebrando Paradigmas no Ensino de Engenharia no Brasil". http://luisnassif.com/profiles/blogs/ufabc-quebrando-paradigmas-no.
- ↑ "Portal da UFABC - Professor da UFMG Aponta UFABC Como Projeto Avançado de Interdisciplinaridade". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1624:professorda-ufmg-aponta-ufabc-como-projeto-avancado-de-interdisciplinaridade&catid=440:2009&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Centro de Física do Porto - UFABC: A New Brazilian University and Its Fuel Cell Program". http://faraday.fc.up.pt/cfp/events/seminars/2008/models-of-human-dynamics/.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Portal UFABC - UFABC: Conquistas e Desafios". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=617:ufabc-conquistas-e-desafios&catid=187:artigos&Itemid=184.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Portal UFABC - A Pós-graduação na UFABC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=618:a-pos-graduacao-na-ufabc-&catid=187:artigos&Itemid=184.
- ↑ "Prograd UFABC - Cursos". http://prograd.ufabc.edu.br/cursos.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - UFABC recebe Ministério da Educação e universidades federais para discutir Bacharelados Interdisciplinares". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3111:ufabc-recebe-ministerio-da-educacao-e-universidades-federais-e-discute-bacharelados-interdisciplinares&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Resolução ConsEPE nº 147 - Define os coeficientes de desempenho utilizados nos cursos de graduação da UFABC. - Universidade Federal do ABC" (in pt-br). http://www.ufabc.edu.br/administracao/conselhos/consepe/resolucoes/resolucao-consepe-no-147-define-os-coeficientes-de-desempenho-utilizados-nos-cursos-de-graduacao-da-ufabc.
- ↑ "Pró-Reitoria de Graduação - BC&T" (in pt-br). http://prograd.ufabc.edu.br/bct.
- ↑ "Prograd UFABC - Bacharelado em Ciências e Humanidades". http://prograd.ufabc.edu.br/bch.
- ↑ "UFABC - Importante Revista da Área de Nanociências Publica Trabalho Feito na UFABC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3003:importante-revista-da-area-de-nanociencias-publica-trabalho-feito-na-ufabc&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Discurso do Reitor da UFABC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=916:discurso-do-reitor-da-ufabc&catid=187:artigos&Itemid=184.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Recriando o Big-Bang no LHC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=970:recriando-o-big-bang-no-lhc&catid=187:artigos&Itemid=184.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Universidade Integra Pesquisa Mundial Sobre Estrutura da Matéria". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=301:universidade-integra-pesquisa-mundial-sobre-estrutura-da-materia&catid=221:2007&Itemid=8.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Professores da UFABC colaboram em projeto de 1ª missão espacial brasileira para o espaço profundo". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3410:professores-da-ufabc-colaboram-em-projeto-de-1o-missao-espacial-brasileira-para-o-espaco-profundo&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ 40.00 40.01 40.02 40.03 40.04 40.05 40.06 40.07 40.08 40.09 40.10 "Engenharia da Informação UFABC - Projetos de Pesquisa". http://posinfo.ufabc.edu.br/index_arquivos/projetos.htm.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Professores e Aluno da UFABC Participam de Projeto em Angra". http://ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1182:professores-e-aluno-da-ufabc-participam-de-projeto-em-angra-ii&catid=222:2008&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e a Unifesp". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3032:ato-decisorio-no-02-de-28-de-agosto-de-2009-aprovacao-de-convenio-entre-a-ufabc-e-a-unifespepm&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 "Nanociências UFABC - Docentes Colaboradores". http://nano.ufabc.edu.br/colaboradores.htm.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 44.2 "Física UFABC - Infra-Estrutura Para Pesquisa". http://www.fisica-ufabc.net/2007/01/infra-estrutura-para-pesquisa.html.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e IEAv". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=4127:ato-decisorio-no-25-de-05-de-outubro-de-2010-convenio-entre-a-ufabc-e-o-ieav&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e a Eletronuclear". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3995:ato-decisorio-no-24-de-10-de-setembro-de-2010-aprovar-cooperacao-e-intercambio-cientifico-e-tecnologico-entre-a-ufabc-e-a-eletronuclear&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e IPCTRON". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3036:ato-decisorio-no-06-de-27-de-outubro-de-2009-aprovacao-do-convenio-entre-a-ufabc-e-o-instituto-de-pesquisas-em-celulas-tronco-ipctron&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "LNCC - Projetos de Pesquisa". http://www.lncc.br/departamentos/producao_projetos.php?vprint=on&Idt_Projeto=207&tipProd=3&vTipo=todos&vCabecalho=&vTitulo=&vAno=2010.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e Centro Tecnológico da Marinha em São Paulo". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3045:ato-decisorio-no-14-de-25-de-fevereiro-de-2010-aprovacao-do-convenio-entre-a-ufabc-e-o-centro-tecnologico-da-marinha-em-sao-paulo-ctmsp&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e a Sociedade Brasileira de Biofísica". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3547:ato-decisorio-no-21-de-1o-de-junho-de-2010-aprovar-quanto-ao-merito-o-protocolo-de-intencoes-que-entre-si-celebram-a-ufabc-e-a-sociedade-brasileira-de-biofisica&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Grupo de pesquisa do CMCC estabelece parceria com o Max Planck Institute". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3534:grupo-de-pesquisa-do-cmcc-estabelece-parceria-com-o-max-planck-institute&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Ciência da Computação UFABC - Projetos de Pesquisa". http://bcc.ufabc.edu.br/pages/projpesqand.php.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e o National Institute for Materials Science". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=4129:ato-decisorio-no-26-de-05-de-outubro-de-2010-convenio-entre-a-ufabc-e-o-national-institute-for-material-science--tsukuba-japao&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e a Universidade do Texas". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3033:ato-decisorio-no-03-de-28-de-agosto-de-2009-aprovacao-de-convenio-entre-a-ufabc-e-a-universidade-do-texas&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e a Universidade do Algarve". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3043:ato-decisorio-no-12-de-28-de-dezembro-de-2009-assinatura-do-protocolo-geral-de-cooperacao-entre-a-universidade-de-algarve-em-portugal-e-a-universidade-federal-do-abc&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Convênio entre a UFABC e a Universidade de Comimbra". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3901:ato-decisorio-no-23-de-17-de-agosto-de-2010-aprovar-acordo-geral-de-colaboracao-entre-a-ufabc-e-a-universidade-de-coimbra&catid=604:consep-atos-decisorios&Itemid=2.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - PDPD: Pesquisando Desde o Primeiro Dia". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1307&Itemid=145.
- ↑ "Proex UFABC - Pró-Reitoria de Extensão". http://extensao.ufabc.edu.br/.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Sistema Computacional Elaborado na UFABC Aponta Características da Epidemia de Dengue no Rio". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2900:novo-sistema-computacional-elaborado-na-ufabc-aponta-caracteristicas-da-epidemia-de-dengue-no-rio&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Infra-Estrutura para Pesquisa". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=665&Itemid=229.
- ↑ "MEC - Jornal francês destaca investimento do Brasil". http://portal.mec.gov.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=14487:jornal-frances-destaca-investimento-do-brasil&catid=212.
- ↑ "Biblioteca da UFABC". http://200.133.215.45/cgi-bin/wxis.exe?IsisScript=phl.xis&cipar=phl81.cip&lang=por.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - CAPES Aprova Cursos de Mestrado e Doutorado da UFABC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?p=adm/noticias/n200708061114Capes%20aprova%20cursos%20de%20mestrado%20e%20doutorado%20da%20UFABC.php.
- ↑ "Cursos | Pós-Graduação UFABC" (in pt-BR). http://propg.ufabc.edu.br/cursos/.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Aulas de Cursinho Para o Enem Começam dia 22". https://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3012:aulas-de-cursinho-para-o-enem-comecam-dia-22&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - BC&T Aparece Como Curso Mais Procurado no SiSU". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2853:bcat-aparece-como-curso-mais-procurado-no-sisu&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Primeira Etapa do SiSU Deve Terminar Com BC&T Como Mais Procurado". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2855:primeira-etapa-do-sisu-deve-terminar-com-bcat-como-mais-procurado&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Ingresso aos Cursos de Graduação em 2010". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2348&Itemid=9.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 69.2 "Setores da UFABC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=259&Itemid=218.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Descrição do Campus Santo André". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3117&Itemid=53.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Contatos e Endereços da UFABC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=612&Itemid=10.
- ↑ "ACIAM - UFABC Planeja Oferecer Ensino Médio". http://www.aciam.org.br/noticias.asp?id=15760.
- ↑ "DCE - Fotos do Bloco Sigma em 19/03". http://dce.ufabc.net/fotos-colegio-salete-em-1903/.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Resolução ConsEP nº 60". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3378:resolucao-consep-no-60-100510-regulamenta-o-procedimento-para-a-realizacao-de-convenio-de-cooperacao-de-estagio-para-alunos-de-graduacao-da-ufabc&catid=427:consep-resolucoes&Itemid=28.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Resolução ConsEP nº 61". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3379:resolucao-consep-no-61-100510-regulamenta-a-validade-dos-convenios-de-cooperacao-de-estagio-firmados-pela-ufabc&catid=427:consep-resolucoes&Itemid=28.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 "AXIS - Associação Atlética Acadêmica XI de Setembro". http://axis.ufabc.net/.
- ↑ "AXIS - Torneio Semana da Asa". http://axis.ufabc.net/campeonatos/torneio-semana-da-asa/.
- ↑ "AXIS - Torneio Engenharíadas". http://axis.ufabc.net/campeonatos/engenhariadas/.
- ↑ "AXIS - Torneio Liga Universitária Paulistana". http://axis.ufabc.net/campeonatos/liga-paulista-universitaria/.
- ↑ "AXIS - Torneio Tusca". http://axis.ufabc.net/campeonatos/tusca/.
- ↑ 81.0 81.1 "AXIS - História". http://axis.ufabc.net/historico/historia/.
- ↑ "AXIS - Mascote". http://axis.ufabc.net/historico/mascote/.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Descrição do Campus São Bernardo". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/images/stories/administracao/campussaobernardo/0906_campus_sbo.pdf.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Descrição do Campus". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3117&Itemid=13.
- ↑ "AXIS - Toucas de Natação". http://axis.ufabc.net/2010/04/14/toucas-de-natacao/.
- ↑ "AXIS - Fotos do Rapel". http://axis.ufabc.net/2010/04/14/fotos-do-rapel/.
- ↑ "DCE - Grupos de Alunos". http://dceufabc.com.br/academico/grupos-de-alunos/.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - IEEE Promove Competição de Robôs na UFABC". http://ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1730:ieee-promove-competicao-de-robos-da-lego-na-ufabc&catid=440:2009&Itemid=183.
- ↑ "Portal UFABC - Ramo do IEEE Completa Primeiro ano na UFABC". http://www.ufabc.edu.br/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3261:ramo-do-ieee-completa-primeiro-ano-na-ufabc-com-novos-projetos&catid=587:2010&Itemid=183.
External links
- Official website
- Officers Information of UFABC on Twitter
- Fubeca - Social Network for UFABC students
- BC&T's Pedagogical Project (in portuguese)
 KSF
KSF