Overlay (programming)
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 8 min
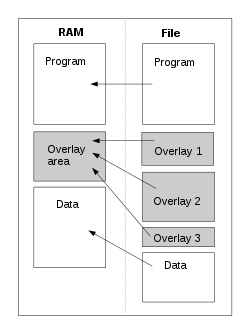
In a general computing sense, overlaying means "the process of transferring a block of program code or other data into main memory, replacing what is already stored".[1] Overlaying is a programming method that allows programs to be larger than the computer's main memory.[2] An embedded system would normally use overlays because of the limitation of physical memory, which is internal memory for a system-on-chip, and the lack of virtual memory facilities.
Usage
Constructing an overlay program involves manually dividing a program into self-contained object code blocks called overlays or links, generally laid out in a tree structure.[lower-alpha 2] Sibling segments, those at the same depth level, share the same memory, called overlay region[lower-alpha 3] or destination region. An overlay manager, either part of the operating system or part of the overlay program, loads the required overlay from external memory into its destination region when it is needed; this may be automatic or via explicit code. Often linkers provide support for overlays.[3]
Example
The following example shows the control statements that instruct the OS/360 Linkage Editor to link an overlay program containing a single region, indented to show structure (segment names are arbitrary):
INCLUDE SYSLIB(MOD1)
INCLUDE SYSLIB(MOD2)
OVERLAY A
INCLUDE SYSLIB(MOD3)
OVERLAY AA
INCLUDE SYSLIB(MOD4)
INCLUDE SYSLIB(MOD5)
OVERLAY AB
INCLUDE SYSLIB(MOD6)
OVERLAY B
INCLUDE SYSLIB(MOD7)
+--------------+
| Root Segment |
| MOD1, MOD2 |
+--------------+
|
+----------+----------+
| |
+-------------+ +-------------+
| Overlay A | | Overlay B |
| MOD3 | | MOD7 |
+-------------+ +-------------+
|
+--------+--------+
| |
+-------------+ +-------------+
| Overlay AA | | Overlay AB |
| MOD4, MOD5 | | MOD6 |
+-------------+ +-------------+
These statements define a tree consisting of the permanently resident segment, called the root, and two overlays A and B which will be loaded following the end of MOD2. Overlay A itself consists of two overlay segments, AA, and AB. At execution time overlays A and B will both utilize the same memory locations; AA and AB will both utilize the same locations following the end of MOD3.
All the segments between the root and a given overlay segment are called a path.
Applications
As of 2015[update], most business applications are intended to run on platforms with virtual memory. A developer on such a platform can design a program as if the memory constraint does not exist unless the program's working set exceeds the available physical memory. Most importantly, the architect can focus on the problem being solved without the added design difficulty of forcing the processing into steps constrained by the overlay size. Thus, the designer can use higher-level programming languages that do not allow the programmer much control over size (e.g. Java, C++, Smalltalk).
Still, overlays remain useful in embedded systems.[4] Some low-cost processors used in embedded systems do not provide a memory management unit (MMU). In addition many embedded systems are real-time systems and overlays provide more determinate response-time than paging. For example, the Space Shuttle Primary Avionics System Software (PASS) uses programmed overlays.[5]
Even on platforms with virtual memory, software components such as codecs may be decoupled to the point where they can be loaded in and out as needed.
Historical use
IBM introduced the concept of a chain job[6] in FORTRAN II. The program had to explicitly call the CHAIN subroutine to load a new link, and the new link replaced all of the old link's storage except for the Fortran COMMON area.
IBM introduced more general overlay handling[7] in IBSYS/IBJOB, including a tree structure and automatic loading of links as part of CALL processing.
In OS/360, IBM extended the overlay facility of IBLDR by allowing an overlay program to have independent overlay regions, each with its own overlay tree. OS/360 also had a simpler overlay system for transient SVC routines, using 1024-byte SVC transient areas.
In the home computer era overlays were popular because the operating system and many of the computer systems it ran on lacked virtual memory and had very little RAM by current standards: the original IBM PC had between 16K and 64K, depending on configuration. Overlays were a popular technique in Commodore BASIC to load graphics screens.[2]
"Several DOS linkers in the 1980s supported [overlays] in a form nearly identical to that used 25 years earlier on mainframe computers."[4][8] Binary files containing memory overlays had de facto standard extensions .OVL[8] or .OVR[9] (but also used numerical file extensions like .000, .001, etc. for subsequent files[10]). This file type was used among others by WordStar[11] (consisting of the main executable WS.COM and the overlay modules WSMSGS.OVR, WSOVLY1.OVR, MAILMERGE.OVR and SPELSTAR.OVR, where the "fat" overlay files were even binary identical in their ports for CP/M-86 and MS-DOS[12]), dBase,[13] and the Enable DOS office automation software package from Enable Software. Borland's Turbo Pascal[14][15] and the GFA BASIC compiler were able to produce .OVL files.
See also
Notes
- ↑ This has nothing to do with the term region in MVT storage management.
- ↑ In OS/360 and successors, there may be multiple regions[lower-alpha 1] each containing a complete overlay tree.
- ↑ The nomenclature varies depending on the system, e.g., in OS/360 region refers to an entire overlay tree.
References
- ↑ "Oxford Dictionaries". 2015-11-26. https://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/american_english/overlay.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Butterfield, James "Jim", ed (June 1986). "Part 4: Overlaying". Loading And Linking Commodore Programs. 74. http://www.atarimagazines.com/compute/issue73/loading_and_linking.php. Retrieved 2022-07-10. "This lets you run programs which are, in effect, much larger than the amount of memory in your computer."
- ↑ "The GNU Linker documentation: Overlay Description". 2008-06-03. http://sourceware.org/binutils/docs/ld/Overlay-Description.html. [1]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Linkers & Loaders. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. 2000. p. 177. ISBN 1-55860-496-0. http://linker.iecc.com/. Retrieved 2022-07-10. [2]
- ↑ National Research Council (November 1993). An Assessment of Space Shuttle Flight Software Development Processes (2 ed.). Washington, DC, USA: National Academy of Sciences, The National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/2222. ISBN 978-0-309-04880-4. http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=2222&page=39. Retrieved 2012-10-29. (208 pages)
- ↑ IBM 7090/7094 Programming Systems – FORTRAN II Programming. Poughkeepsie, New York, USA: IBM Corporation. August 1963. pp. 34–35. Form C28-6054-4 File No. 7090-25. http://bitsavers.org/pdf/ibm/7090/C28-6054-4_7090_FORTRANII.pdf. Retrieved 2022-07-10. (52 pages)
- ↑ IBM 7090/7094 Programming Systems – IBJOB Processor – Overlay feature of IBLDR (1 ed.). Poughkeepsie, New York, USA: IBM Corporation. May 1963. Form C28-6331 File No. 7090-27. http://bitsavers.org/pdf/ibm/7090/C28-6331_IBLDR_overlay_1963.pdf. Retrieved 2021-12-26. (8 pages)
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "PRL file format". 2012-06-05. https://www.seasip.info/Cpm/prl.html. "[…] A PRL file is a relocatable binary file, used by MP/M and CP/M Plus for various modules other than .COM files. The file format is also used for FID files on the Amstrad PCW. There are several file formats which use versions of PRL: SPR (System PRL), RSP (Resident System Process). LINK-80 can also produce OVL (overlay) files, which have a PRL header but are not relocatable. GSX drivers are in PRL format; so are Resident System Extensions (.RSX). […]" [3]
- ↑ "Platz schaffen durch Überlagern - Overlay-Strukturen in Turbo Pascal" (in de). mc 90 (12): 124–130. 1990. https://guru-home.dyndns.org/Overlay.html. Retrieved 2022-08-04. [4]
- ↑ Pearson, Dave, ed. "Create Program Overlays". Turbo Pascal - Norton Guide. p. 149. http://www.x-hacker.org/ng/pascal/ng19519.html. Retrieved 2022-08-04.
- ↑ Getting started with WordStar, MailMerge + SpellStar. Cambridge University Press. 1985. ISBN 0-521-31805-X.
- ↑ "WordStar Again". OS/2 Museum. 2018-01-30. http://www.os2museum.com/wp/wordstar-again/comment-page-1/. "[…] The reason to suspect such difference is that version 3.2x also supported CP/M-86 (the overlays are identical between DOS and CP/M-86, only the main executable is different) […] the .OVR files are 100% identical between DOS and CP/M-86, with a flag (clearly shown in the WordStar 3.20 manual) switching between them at runtime […] the OS interface in WordStar is quite narrow and well abstracted […] the WordStar 3.2x overlays are 100% identical between the DOS and CP/M-86 versions. There is a runtime switch which chooses between calling INT 21h (DOS) and INT E0h (CP/M-86). WS.COM is not the same between DOS and CP/M-86, although it's probably not very different either. […]"
- ↑ "Ashton-Tate ships dBASE IV Version 1.1". Torrance, California, USA: Ashton Tate. 1990-07-31. p. 2-2-2. http://corphist.computerhistory.org/corphist/documents/doc-4434569d4e6a0.pdf. "Version 1.1 has a new dynamic Memory Management System (dMMS) that handles overlays more efficiently: the product requires less memory, which results in more applications space availability. […] The product's lower memory requirements of only 450K of RAM provide improved network support because supplemental hardware memory is no longer required to support networks. […] By speeding up areas of dBASE IV that are overlay-dependent, the new dMMS improves performance when working at the Control Center and in programs that use menus and windows." (5 pages)
- ↑ (in de) Turbo Pascal 7.0 (2 ed.). R. Oldenbourg Verlag (de). 2000. p. 249. ISBN 3-486-25499-5.
- ↑ "Chapter 6. Speicherverwaltung und Dateisysteme - Teil 5: Nicht-zusammenhängende Speicherzuordnung" (in de). Betriebssysteme I. Munich, Germany: Hochschule München. June 2009. http://hm.hgesser.de/bs-ss2009/folien/bs-ss2009-esser-06e-4up.pdf. Retrieved 2014-02-13. (9 pages)
Further reading
- IBM OS Linkage Editor and Loader - Program Numbers 360S-ED-510, 360S-ED-521, 360S-LD-547 (10 ed.). White Plains, New York, USA: IBM Corporation. March 1972. Order No. GC28-6538-9, File No. S360-31. http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/ibm/360/os/R21.0_Mar72/GC28-6538-9_OS_Linkage_Editor_and_Loader_Release_21_Jan72.pdf. (2+244+4 pages)
- Groeber, Marcus; Di Geronimo, Jr., Edward "Ed"; Paul, Matthias R. (2002-03-02) [2002-02-24]. "GEOS/NDO info for RBIL62?". Newsgroup: comp.os.geos.programmer. Archived from the original on 2019-04-20. Retrieved 2019-04-20.
[…] The reason Geos needs 16 interrupts is because the scheme is used to convert inter-segment ("far") function calls into interrupts, without changing the size of the code. The reason this is done so that "something" (the kernel) can hook itself into every inter-segment call made by a Geos application and make sure that the proper code segments are loaded from virtual memory and locked down. In DOS terms, this would be comparable to an overlay loader, but one that can be added without requiring explicit support from the compiler or the application. What happens is something like this: […] 1. The real mode compiler generates an instruction like this: CALL <segment>:<offset> -> 9A <offlow><offhigh><seglow><seghigh> with <seglow><seghigh> normally being defined as an address that must be fixed up at load time depending on the address where the code has been placed. […] 2. The Geos linker turns this into something else: INT 8xh -> CD 8x […] DB <seghigh>,<offlow>,<offhigh> […] Note that this is again five bytes, so it can be fixed up "in place". Now the problem is that an interrupt requires two bytes, while a CALL FAR instruction only needs one. As a result, the 32-bit vector (<seg><ofs>) must be compressed into 24 bits. […] This is achieved by two things: First, the <seg> address is encoded as a "handle" to the segment, whose lowest nibble is always zero. This saves four bits. In addition […] the remaining four bits go into the low nibble of the interrupt vector, thus creating anything from INT 80h to 8Fh. […] The interrupt handler for all those vectors is the same. It will "unpack" the address from the three-and-a-half byte notation, look up the absolute address of the segment, and forward the call, after having done its virtual memory loading thing... Return from the call will also pass through the corresponding unlocking code. […] The low nibble of the interrupt vector (80h–8Fh) holds bit 4 through 7 of the segment handle. Bit 0 to 3 of a segment handle are (by definition of a Geos handle) always 0. […] all Geos API run through the "overlay" scheme […]: when a Geos application is loaded into memory, the loader will automatically replace calls to functions in the system libraries by the corresponding INT-based calls. Anyway, these are not constant, but depend on the handle assigned to the library's code segment. […] Geos was originally intended to be converted to protected mode very early on […], with real mode only being a "legacy option" […] almost every single line of assembly code is ready for it […]
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF