BCN nanotube
Topic: Physics
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
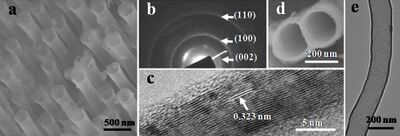
BCN nanotubes are tubular structures with a sub-micrometer diameter and a length much longer than diameter. They are composed of comparable amounts of boron, carbon and nitrogen atoms.
First made in 1994, synthesis methods have included: arc-discharge, laser ablation, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), template route, and pyrolysis techniques. Single-walled B–C–N nanotubes have been made with a hot-filament method.[2]
Solvothermal synthesis
Vertically aligned arrays of ~BC2N nanotubes can be produced by solvothermal synthesis in a stainless steel autoclave from a mixture of sodium azide (NaN3), ammonium fluoroborate (NH4BF4) and methyl cyanide (CH3CN). The mixture, together with the solvent and other additives is heated to 400 °C for ~14 h.[1] The final composition was approx B19C55N26.[1]
Potential applications
The vertically-aligned BCN nanotubes (made as above) exhibit a high and stable specific capacitance (>500 F/g), which exceeds that of alternative carbon nanomaterials, and therefore have potential applications in supercapacitors.[1][3]
Facile synthesis
Another method produced nanotubes of composition : B45%,C31%,N24% [2] The method was grow them on stainless steel by reacting boron, zinc oxide (ZnO), and ethanol in nitrogen and hydrogen at 1150 °C. The resulting nanotubes had an average diameter of about 90 nm.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Zhou, Junshuang; Li, Na; Gao, Faming; Zhao, Yufeng; Hou, Li; Xu, Ziming (2014). "Vertically-aligned BCN Nanotube Arrays with Superior Performance in Electrochemical capacitors". Scientific Reports 4. doi:10.1038/srep06083.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Luo, L; Mo, L; Tong, Z; Chen, Y. "Facile Synthesis of Ternary Boron Carbonitride Nanotubes". Nanoscale Res Lett 4: 834–838. doi:10.1007/s11671-009-9325-7. PMID 20596377.
- ↑ Zhi, C. Y.; Bai, X. D.; Wang, E. G. (2004). "Boron carbonitride nanotubes". Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 4 (1–2): 35–51. doi:10.1166/jnn.2004.018. PMID 15112540.
 KSF
KSF